Menstrual Cycle - IGCSE 0610 / O LEVEL Biology 5090
Genuine Biology CAIE・17 minutes read
The menstrual cycle in females involves monthly blood discharge known as Menses, starting at puberty and lasting 3-7 days. Hormones like FSH, estrogen, LH, and progesterone regulate the cycle, influencing ovulation and uterine lining maintenance.
Insights
- Menstrual cycle is a crucial biological process in females, signaling puberty and preparing the body for potential pregnancy through a complex series of stages involving hormone regulation and ovulation.
- Various factors like stress, diet, and environment can impact the regularity of the menstrual cycle, which typically lasts around 28 days but can vary widely, taking about three years to stabilize after puberty.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is the purpose of the menstrual cycle?
The menstrual cycle prepares the body for pregnancy.
How long does the average menstrual cycle last?
The average menstrual cycle lasts 28 days.
What role do ovaries play in the menstrual cycle?
Ovaries release eggs and produce hormones.
How do hormones regulate the menstrual cycle?
Hormones like FSH, estrogen, LH, and progesterone control the menstrual cycle.
What happens if fertilization does not occur during the menstrual cycle?
The Corpus Luteum breaks down, leading to menstruation.
Related videos

Peekaboo Kidz
Why Do Girls Get Periods? | Menstruation | The Dr Binocs Show | Peekaboo Kidz

Maitri
EVERYTHING about IRREGULAR PERIODS | MAITRI | Dr Anjali Kumar | Menstruation Series Ep 3

GetsetflySCIENCE by Gaurav Thakur
How PERIODS Are KILLING Women?
Speed Pharmacology
Pharmacology – MENSTRUAL CYCLE AND HORMONAL CONTRACEPTIVES (MADE EASY)

Teal Swan
Periods + Menstruation (A Spiritual Perspective on Periods and Menstruation) - Teal Swan -
Summary
00:00
Understanding the Female Menstrual Cycle
- Menstrual cycle signifies puberty in females with monthly blood discharge known as Menses lasting 3-7 days, varying in length.
- Average adult female menstrual cycle is 28 days, ranging from 21 to 33 days, starting at puberty around ages 11-13.
- Factors like stress, diet, and environment affect menstrual regularity, taking about three years to stabilize.
- Menstrual cycle importance lies in pregnancy preparation, with other mammals like apes also experiencing similar cycles.
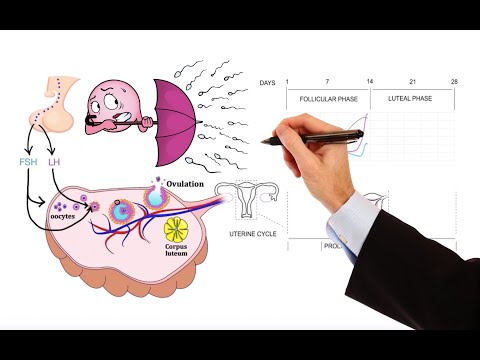
- Ovaries play a crucial role in the menstrual cycle, with primary follicles maturing into Graffian follicles releasing eggs.
- Ovulation occurs monthly, with ovaries alternating egg release, leading to Corpus Luteum formation if pregnancy doesn't happen.
- Menstrual cycle stages include menstrual flow, follicle development, ovulation, and Corpus Luteum maintenance.
- Hormones like FSH, estrogen, LH, and progesterone regulate the menstrual cycle, influencing ovulation and uterine lining maintenance.
- Progesterone maintains the uterine lining for embryo implantation, inhibiting ovulation and FSH/LH production if fertilization occurs.
- If fertilization doesn't happen, Corpus Luteum breaks down, leading to menstruation, starting the cycle anew.
27:05
Hormones and fertility in menstrual cycle
- Corpus luteum secretes progesterone and estrogen until the placenta forms, after which the placenta takes over hormone production during pregnancy.
- Progesterone released by the Corpus luteum maintains the uterus lining, with the placenta later assuming this role and inhibiting FSH and LH to support pregnancy.
- Menstrual cycle stages include menstruation, an infertile period until around day 9 or 10, ovulation on day 14, and a fertile period lasting from days 11 to 16 due to sperm survival in the female reproductive system.




