14. Coordination and response(Part 1)(Cambridge IGCSE Biology 0610 for exams in 2023, 2024 and 2025)
IGCSE Study Buddy・6 minutes read
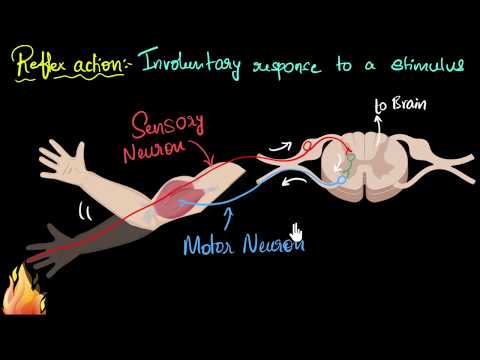
Organisms rely on the nervous system to maintain homeostasis by receiving and processing information through sensory, relay, and motor neurons, with stimuli detected by sensory neurons, receptors, and effectors coordinating responses in the body through reflex arcs to protect from harm. Involuntary responses, like reflex arcs, are fast and automatic reactions that do not involve the brain, demonstrating the importance of synapses in ensuring one-directional impulse transmission for quick coordination of stimuli with effector responses.
Insights
- The nervous system is vital for maintaining homeostasis in organisms by coordinating organs and systems, with sensory, relay, and motor neurons playing key roles in processing information and generating appropriate responses.
- Understanding the distinction between voluntary and involuntary responses is crucial, as involuntary responses, like reflex arcs, are fast, automatic reactions that do not involve the brain, showcasing the efficiency of synapses in ensuring rapid coordination between stimuli and effector responses.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is the role of the nervous system in organisms?
The nervous system plays a crucial role in receiving and processing information to generate appropriate responses for maintaining homeostasis in organisms.
What are the components of the mammalian nervous system?
The mammalian nervous system consists of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system (all nerves outside the brain and spinal cord), with three types of neurons: sensory, relay, and motor neurons.
How does the nervous system process stimuli?
The nervous system processes stimuli through sensory neurons detecting environmental changes, receptors identifying stimuli, and effectors responding to signals from the nervous system to generate appropriate responses.
What is the difference between voluntary and involuntary responses?
Voluntary responses are consciously controlled actions, while involuntary responses are fast and automatic reactions that do not involve the brain, such as reflex arcs that quickly coordinate stimuli with effector responses to protect the body from harm.
How do reflex arcs function in the nervous system?
Reflex arcs in the nervous system quickly coordinate stimuli with effector responses through synapses, ensuring one-directional impulse transmission for fast and automatic reactions that protect the body from harm.
Related videos

Grade booster
#controlandcoordination full chapter | cbse Class 10th Biology | NCERT class 10 science chapter 7

Cognito
GCSE Biology - Nervous System and Reflex Arc #58

Class 10 Learn With Mansi
Control And Coordination | Chapter 6 | Complete Chapter | "लक्ष्य" 2025
Khan Academy India - English
Reflex action (& reflex arc) | Control & Coordination | Biology | Khan Academy

Physics Wallah Foundation
CONTROL AND COORDINATION in 60 Minutes | Science Chapter 7 | Class 10th CBSE Board
Summary
00:00
Nervous System: Coordination for Homeostasis and Responses
- Organisms require proper coordination between organs and systems to maintain homeostasis, with the nervous system playing a key role in receiving and processing information to generate appropriate responses.
- The mammalian nervous system consists of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system (all nerves outside the brain and spinal cord), with three types of neurons: sensory, relay, and motor neurons.
- Understanding stimuli, receptors, and effectors is crucial in comprehending the nervous system's pathway of impulses, with a stimulus being any environmental change detected by sensory neurons, receptors detecting stimuli, and effectors responding to signals from the nervous system.
- Differentiating between voluntary and involuntary responses is essential, with involuntary responses being fast and automatic reactions that do not involve the brain, such as reflex arcs that protect the body from harm by quickly coordinating stimuli with effector responses through synapses ensuring one-directional impulse transmission.




