#controlandcoordination full chapter | cbse Class 10th Biology | NCERT class 10 science chapter 7
Grade booster・12 minutes read
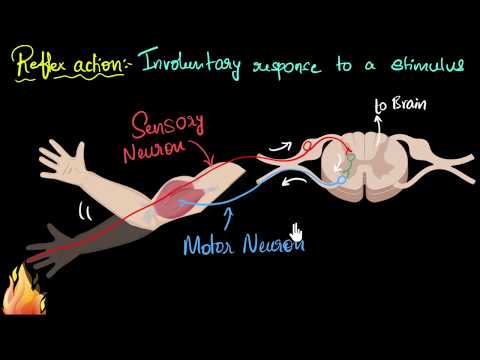
Living things respond to stimuli for protection with the help of nervous and hormonal systems, including neurons that transmit information through synapses. Reflex actions are quick responses to stimuli that involve receptors, sensory neurons, relay neurons, motor neurons, and effectors, coordinated by the brain within the protective cranium.
Insights
- Neurons play a crucial role in transmitting information through nerve conduction, converting stimuli into electrical impulses, and facilitating quick reflex actions through the reflex arc.
- The brain, safeguarded by meninges and cerebrospinal fluid, orchestrates both voluntary and involuntary body functions, showcasing the intricate coordination required for responding to stimuli effectively.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
How do nerve cells respond to stimuli?
Nerve cells have distinct parts like cell body, nucleus, dendrites, axon, and nerve endings that aid in responding to stimuli.
What are reflex actions?
Reflex actions are quick responses to stimuli that take a short pathway for immediate movements, involving receptors, sensory neurons, relay neurons, motor neurons, and effectors.
What is the function of olfactory receptors?
Olfactory receptors in the nose detect smell and convert it into electrical impulses for transmission to the brain.
How do neurons transmit information?
Neurons transmit information through nerve conduction, passing impulses through synapses to relay messages between different parts of the body.
What is the role of the brain in the body?
The brain, protected by meninges and cerebrospinal fluid within the cranium, coordinates body functions, both voluntary and involuntary, by processing and responding to sensory information.
Related videos

IGCSE Study Buddy
14. Coordination and response(Part 1)(Cambridge IGCSE Biology 0610 for exams in 2023, 2024 and 2025)

Cognito
GCSE Biology - Nervous System and Reflex Arc #58
Khan Academy India - English
Reflex action (& reflex arc) | Control & Coordination | Biology | Khan Academy

Physics Wallah Foundation
CONTROL AND COORDINATION in 60 Minutes | Science Chapter 7 | Class 10th CBSE Board

Class 10 Learn With Mansi
Control And Coordination | Chapter 6 | Complete Chapter | "लक्ष्य" 2025
Summary
00:00
"Neurons and Reflexes: Body's Protective Responses"
- Living things respond to stimuli for protection, aided by the nervous and hormonal systems.
- Nerve cells, or neurons, have distinct parts like cell body, nucleus, dendrites, axon, and nerve endings.
- Sense organ neurons have receptors that detect stimuli and convert them into electrical impulses.
- Olfactory receptors in the nose detect smell, while gustatory receptors in the tongue detect taste.
- Neurons transmit information through nerve conduction, passing impulses through synapses.
- Sensory neurons carry information from sense organs to the brain or spinal cord, while motor neurons transmit to muscles or glands.
- Reflex actions are quick responses to stimuli, taking a short pathway for immediate movements.
- The reflex arc includes receptors, sensory neurons, relay neurons, motor neurons, and effectors.
- The brain, protected by meninges and cerebrospinal fluid within the cranium, coordinates body functions, voluntary and involuntary.




