Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) - Pathophysiology, Symptoms, Treatment
PhysioPathoPharmaco・2 minutes read
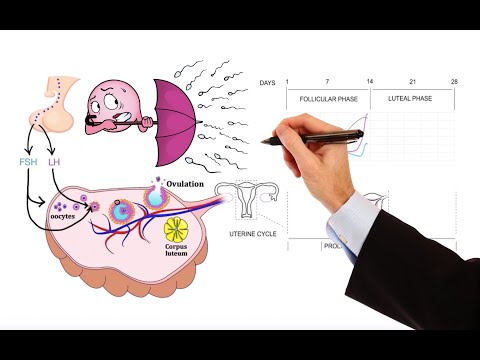
Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) regulates hormone production in the ovary by stimulating LH and FSH release, while PCOS results from ovulation failure due to increased GnRH pulse frequency causing hormonal imbalances and cyst formation, leading to symptoms like hirsutism and menstrual irregularities. Treatment for PCOS involves oral contraceptives, weight loss, metformin, and spironolactone to manage symptoms and hormonal imbalances.
Insights
- Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) from the hypothalamus triggers luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) release, impacting estrogen and progesterone regulation in the ovary.
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) results from disrupted ovulation due to elevated GnRH pulse frequency, leading to hormonal imbalances marked by high LH and low FSH levels, causing cysts on the ovary and symptoms like hirsutism, acne, irregular periods, and infertility.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What hormone stimulates LH and FSH release?
GnRH
What causes Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)?
Increased GnRH pulse frequency
What are the symptoms of hyperandrogenism in PCOS?
Hirsutism, acne, menstrual irregularities
How is Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) treated?
Oral contraceptives, weight loss, metformin, spironolactone
What is the role of LH and FSH in the ovary?
Regulate estrogen and progesterone production
Related videos

JJ Medicine
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) | Overview of Associated Conditions, Diagnosis & Treatments
Nucleus Medical Media
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome | PCOS | Nucleus Health

The Yoga Institute
How to Cure PCOS Naturally at Home? Causes, Symptoms, and Natural Treatement | Women Health

Living Springs Retreat
How to Balance Male and Female Hormones - Barbara O'Neill - 2018
Speed Pharmacology
Pharmacology – MENSTRUAL CYCLE AND HORMONAL CONTRACEPTIVES (MADE EASY)
Summary
00:00
"Pulsatile GnRH and PCOS Hormonal Imbalances"
- Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) is released from the hypothalamus in a pulsatile manner, stimulating the release of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) from the anterior pituitary, which then act on the ovary to regulate estrogen and progesterone production.
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) occurs when follicles fail to ovulate due to increased GnRH pulse frequency, leading to hormonal imbalances with elevated LH levels and decreased FSH levels, resulting in cyst formation on the ovary.
- Hyperandrogenism in PCOS causes symptoms like hirsutism and acne, along with menstrual irregularities and infertility due to lack of ovulation, exacerbated by insulin resistance and increased androgen production.
- Treatment for PCOS includes oral contraceptives to regulate hormone levels, weight loss, metformin to address insulin resistance, and spironolactone to block androgen receptors, aiming to manage symptoms and hormonal imbalances associated with the condition.




