Zellen - Überblick
Biologie - simpleclub・4 minutes read
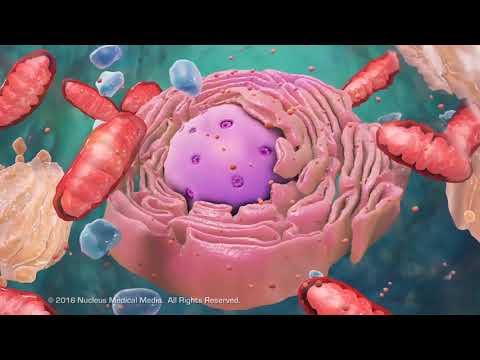
Cells are the fundamental units of all living organisms, categorized into prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus, and eukaryotic cells, which are more complex and contain a nucleus and various organelles. Important cell compartments include the nucleus for genetic information, mitochondria for ATP production, ribosomes for protein synthesis, and chloroplasts for photosynthesis in plants, highlighting the distinct features of plant and animal cells.
Insights
- Cells are the basic building blocks of all living things, from bacteria to plants and animals, highlighting their essential role in the structure and function of life.
- Prokaryotic cells, which do not have a nucleus, are simpler than eukaryotic cells that contain a nucleus and specialized compartments like mitochondria for energy production and ribosomes for protein synthesis, illustrating the complexity and diversity of cellular life.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What are the basic units of life?
Cells are the basic units of life, serving as the fundamental building blocks for all living organisms, including bacteria, plants, and animals. They are essential for the structure and function of life, allowing organisms to grow, reproduce, and respond to their environment. Each cell operates as a miniature factory, carrying out various processes necessary for survival and functioning as part of larger systems within multicellular organisms.
What is a prokaryotic cell?
A prokaryotic cell is a type of cell that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, making it simpler than eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotes, which include bacteria and archaea, have their genetic material located in a region called the nucleoid. These cells are typically smaller and less complex, but they are incredibly diverse and can thrive in a wide range of environments. Their simplicity allows for rapid reproduction and adaptation, contributing to their success as one of the oldest forms of life on Earth.
What is the function of mitochondria?
Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses of the cell, primarily responsible for producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy currency of the cell. They convert nutrients into energy through a process called cellular respiration, which involves breaking down glucose and other molecules in the presence of oxygen. This energy is vital for various cellular functions, including muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and biosynthesis. Mitochondria also play a role in regulating metabolic processes and are involved in cell signaling and apoptosis, or programmed cell death.
What do ribosomes do in cells?
Ribosomes are essential cellular structures responsible for protein synthesis, a critical process for all living organisms. They translate messenger RNA (mRNA) into polypeptide chains, which then fold into functional proteins. Ribosomes can be found floating freely in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum, forming rough ER. The proteins synthesized by ribosomes are crucial for various cellular functions, including enzyme activity, structural support, and signaling. Without ribosomes, cells would be unable to produce the proteins necessary for life.
What is the role of chloroplasts?
Chloroplasts are specialized organelles found in plant cells and some algae, playing a vital role in photosynthesis. They contain chlorophyll, the green pigment that captures sunlight, and convert light energy into chemical energy by transforming carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. This process not only provides energy for the plant but also contributes to the oxygen supply in the atmosphere, making chloroplasts essential for life on Earth. Additionally, chloroplasts are involved in other metabolic processes, including the synthesis of fatty acids and amino acids.
Related videos

CSU LIFE
Cells

Cognito
GCSE Biology - Cell Types and Cell Structure #2

Grade booster
THE FUNDAMENTAL UNIT OF LIFE in 1 Shot | FULL Chapter Animation | Class 9th Biology | NCERT Science

Magnet Brains
Cell Structure and Functions Full Chapter Class 8 Science | NCERT Science Class 8 Chapter 8
Nucleus Biology
Overview of Cell Structure
Summary
00:00
Understanding Cell Types and Functions
- Cells are the fundamental units of all living organisms, including bacteria, plants, and animals, serving as the building blocks for complex life forms.
- Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and are simpler than eukaryotic cells, which are more complex and contain a nucleus, as well as various organelles.
- Key cell compartments include the nucleus (genetic information), mitochondria (ATP production), ribosomes (protein synthesis), and chloroplasts (photosynthesis in plants), with distinct features for plant and animal cells.




