Overview of Cell Structure
Nucleus Biology・4 minutes read
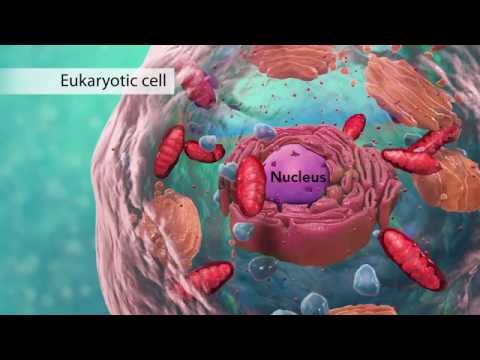
Cells are the smallest living units with common features like a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and DNA. Eukaryotic cells have organelles like the nucleus, while prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles.
Insights
- Eukaryotic cells, present in plants and animals, contain a nucleus and organelles, while prokaryotic cells, like bacteria, lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, showcasing a fundamental distinction in cellular structure.
- Organelles within cells have specific roles, including the nucleus controlling DNA, ribosomes synthesizing proteins, and mitochondria generating energy, emphasizing the importance of these specialized components in cellular function and survival.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What are the common features of cells?
Cells share features like a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and DNA.
What distinguishes eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and organelles, while prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles.
What are the specialized functions of organelles in cells?
Organelles like the nucleus, ribosomes, and mitochondria perform unique functions within cells.
What are the distinguishing features of plant cells?
Plant cells have chloroplasts for photosynthesis and a cell wall for structural support.
How do cells facilitate movement and particle trapping?
Cells utilize structures like cilia and flagella for movement and particle trapping.
Related videos
Summary
00:00
Cell Structure and Function in Organisms
- Cells are the smallest living units of an organism, sharing common features like a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and DNA. Eukaryotic cells, found in plants and animals, have organelles like the nucleus, while prokaryotic cells, like bacteria, lack a nucleus and membrane-enclosed organelles.
- Organelles are specialized parts of a cell with unique functions, such as the nucleus acting as the control center containing DNA, ribosomes synthesizing proteins, and the endoplasmic reticulum transporting materials. The Golgi apparatus customizes proteins, vacuoles store materials, lysosomes break down cellular debris, and mitochondria produce energy.
- Plant cells have chloroplasts for photosynthesis and a cell wall for support, while animal cells lack a cell wall. Unique structures like cilia in respiratory cells and flagella in some bacteria aid in movement or trapping particles. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and organelles, while all cells share a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and genetic material.