OUR ENVIRONMENT in 30 Minutes | Science Chapter 13 | Class 10th CBSE Board
Physics Wallah Foundation・36 minutes read
Ecosystems consist of living organisms and their non-living environment, with decomposers playing a vital role in nutrient recycling and energy transfer through food chains, where energy diminishes at each trophic level due to the "10% Law." Environmental issues such as ozone layer depletion and waste management are crucial topics for students to understand, as they have significant implications for sustainability and health.
Insights
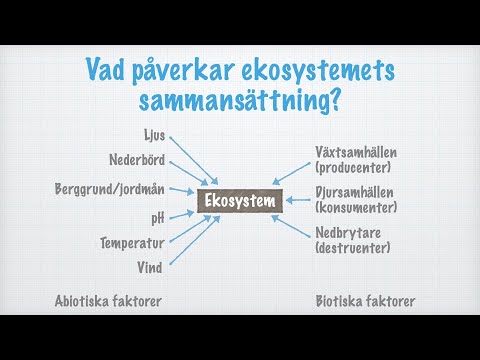
- An ecosystem is a unique area where living organisms interact with each other and their non-living environment, emphasizing the importance of both biotic (like plants and animals) and abiotic (such as soil and water) factors in sustaining life and maintaining ecological balance.
- Decomposers, including fungi and bacteria, are vital in recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem by breaking down dead organic matter, which prevents waste accumulation and supports the energy flow through food chains, where energy transfer is limited to about 10% efficiency at each trophic level.
- Environmental issues such as ozone layer depletion and waste management are critical topics, with the text highlighting the harmful effects of substances like CFCs on ozone and advocating for responsible waste disposal methods, including recycling and composting, to promote sustainability and protect health.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is an ecosystem?
An ecosystem is a geographical area where various living organisms coexist and interact with each other and their abiotic (non-living) environment, such as soil, air, and water. This complex web of interactions includes both biotic factors, like plants and animals, and abiotic factors, such as climate and nutrients. Ecosystems can vary widely in size and type, ranging from small ponds to vast forests, and they play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of nature. Understanding ecosystems is essential for recognizing how different species depend on one another and their environment for survival.
How do decomposers function in ecosystems?
Decomposers play a vital role in ecosystems by breaking down dead organic matter, such as fallen leaves, dead animals, and other waste products. This process prevents the accumulation of waste and recycles nutrients back into the soil, making them available for plants and other organisms. Decomposers, which include bacteria and fungi, are essential for maintaining the health of ecosystems, as they facilitate energy flow through the food chain. By converting dead matter into simpler substances, they help sustain the balance of nutrients necessary for the growth of producers, which are the foundation of the food web.
What is the ozone layer?
The ozone layer is a region of Earth's stratosphere that contains a high concentration of ozone (O3) molecules. It plays a crucial role in protecting living organisms from harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation emitted by the sun. Without the ozone layer, these UV rays can cause serious health issues, including skin cancer and cataracts, as well as negatively impact ecosystems. The depletion of the ozone layer, primarily caused by human-made chemicals like chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), has raised significant environmental concerns, highlighting the importance of protecting this vital layer to ensure the health of both humans and the planet.
What are the types of ecosystems?
Ecosystems can be categorized into two main types: natural ecosystems and artificial ecosystems. Natural ecosystems, such as forests, deserts, and aquatic environments, function independently without human intervention, supporting a diverse range of organisms. In contrast, artificial ecosystems, like crop fields, gardens, and aquariums, are created and maintained by humans, requiring careful management of resources such as soil, water, and light. Each type of ecosystem has its unique characteristics and functions, contributing to the overall biodiversity and ecological balance of the planet.
Why is waste management important?
Waste management is crucial for maintaining environmental health and sustainability. It involves the proper disposal and recycling of waste materials to prevent pollution and conserve resources. Waste can be categorized into biodegradable and non-biodegradable types, and effective management strategies include composting biodegradable waste, using landfills for non-biodegradable materials, and promoting recycling practices. By managing waste responsibly, we can reduce the impact on landfills, minimize pollution, and ensure that valuable resources are reused, ultimately contributing to a healthier environment for future generations.
Related videos

Grade booster
Our Environment in Full chapter (Animation) | CBSE Class 10 Biology ch13 | ecosystem | NCERT Science

Physics Wallah Foundation
OUR ENVIRONMENT in 30 Minutes || Mind Map Series for Class 10th

Etoos Education
ECOSYSTEM in 1 shot - All Concepts, Tricks & PYQ's Covered | NEET | ETOOS India
Magnus Ehinger
Ekosystem

Exphub 9th &10th
Our Environment Complete Chapter🔥|Class 10 Science| NCERT covered| Prashant Kirad
Summary
00:00
Understanding Ecosystems and Environmental Importance
- An ecosystem is defined as a geographical area where various living organisms coexist and interact with each other and their abiotic (non-living) environment, such as soil, air, and water.
- Decomposers play a crucial role in ecosystems by breaking down dead organic matter, which prevents the accumulation of waste and allows energy to flow through the food chain, where energy transfer occurs at approximately 10% efficiency at each trophic level.
- The ozone layer, located in the stratosphere, is essential for protecting living organisms from harmful ultraviolet rays emitted by the sun, highlighting the importance of environmental protection.
- The chapter on "R Environment" is significant for students, as it carries a weightage of 28 to 30 marks in the board exam, with 5 marks specifically allocated to environmental topics, making it a valuable area for exam preparation.
- The chapter is divided into two main parts: the first focuses on ecosystems, while the second addresses environmental issues, particularly ozone layer depletion and waste management.
- Key components of ecosystems include biotic factors (living organisms) and abiotic factors (non-living elements), which together create a unique environment that supports various forms of life.
- Ecosystems can be categorized into different types based on their physical conditions and the organisms they support, such as ponds, rivers, deserts, and artificial ecosystems like aquariums.
- Organisms within ecosystems are classified into three main categories: producers (autotrophs that create their own food, such as green plants and cyanobacteria), consumers (organisms that eat other organisms, including herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores), and decomposers (saprotrophic organisms that feed on dead matter).
- Producers, such as green plants and certain bacteria, are vital for energy production in ecosystems, while consumers, including herbivores like grasshoppers and carnivores like snakes, rely on producers for sustenance.
- Decomposers, which include various bacteria and fungi, are essential for recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem by breaking down dead and decaying matter, thus maintaining the balance of the ecosystem.
12:43
Ecosystem Dynamics and Energy Flow Explained
- Decomposers, such as fungi and bacteria, play a crucial role in ecosystems by breaking down dead organic matter, which releases nutrients back into the soil, maintaining soil mineral levels essential for plant growth.
- Ecosystems are categorized into two main types: Natural Ecosystems, which require no human intervention, and Artificial Ecosystems, which are created and maintained by humans.
- Natural Ecosystems can be further divided into Terrestrial Ecosystems (e.g., forests, deserts, mountains) and Aquatic Ecosystems (e.g., rivers, ponds, lakes), all of which function independently without human effort.
- Artificial Ecosystems, such as crop fields, gardens, parks, and aquariums, require human management, including the provision of soil, sunlight, water, and maintenance of living conditions for plants and animals.
- The functioning of ecosystems is based on the interdependence of living organisms and abiotic factors, illustrated through food chains that show how energy and nutrients flow from producers to various levels of consumers.
- In a food chain, producers (like plants) convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis, which is then consumed by primary consumers (herbivores), followed by secondary consumers (carnivores), and so on, creating a trophic level hierarchy.
- The food chain example includes a sequence where a plant is eaten by a grasshopper (primary consumer), which is then eaten by a mouse (secondary consumer), followed by a snake (tertiary consumer), and finally a hawk (quaternary consumer).
- Food webs illustrate the interconnectedness of multiple food chains within an ecosystem, showing that organisms can have various feeding relationships, such as a grasshopper being eaten by both a mouse and a frog.
- Energy transfer in food chains follows the "10% Law," which states that only 10% of the energy from one trophic level is passed on to the next; for example, if plants have 10,000 kilojoules of energy, primary consumers receive only 1,000 kilojoules.
- Understanding these concepts is essential for recognizing the balance and sustainability of ecosystems, as well as the importance of each organism's role in energy transfer and nutrient cycling.
25:09
Energy Flow and Toxin Accumulation in Ecosystems
- The text discusses energy transfer in a food chain, stating that energy is transferred at a rate of 10%, meaning that for every 1000 joules of energy, only 100 joules are available for the next trophic level, emphasizing the importance of understanding energy flow in ecosystems.
- It highlights that as energy moves through the food chain, it decreases at each trophic level, with 90% of energy being lost primarily as heat, which limits the number of organisms that can be supported at higher levels.
- A homework question is posed regarding a grass plant that has absorbed 300 joules of energy from the sun, prompting students to calculate how much energy is available to the next trophic level.
- The concept of bio-magnification is introduced, explaining that toxins accumulate in living organisms as they move up the food chain, with the concentration of toxins increasing at each trophic level due to non-biodegradable substances.
- An example is provided where plants absorb toxins at a concentration of 2 parts per million (ppm), which then accumulate in fish that consume these plants, leading to higher toxin levels in larger fish that eat smaller fish.
- The text explains that humans, being at the top of the food chain, often have the highest levels of toxins in their bodies due to the accumulation of these substances through consumption of contaminated fish.
- It discusses environmental issues, particularly the depletion of the ozone layer caused by chemicals like chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), which break down ozone molecules and allow harmful ultraviolet rays to reach the Earth, leading to health risks such as skin cancer and cataracts.
- Waste management is addressed, categorizing waste into biodegradable and non-biodegradable types, and suggesting methods for managing waste, such as composting biodegradable materials and using landfills for non-biodegradable waste.
- The text describes incineration as a method of waste disposal where waste is burned at high temperatures to reduce it to ash, which can be repurposed, and emphasizes the importance of sewage treatment to prevent pollution in water bodies.
- Finally, it encourages recycling and reducing waste generation, advocating for responsible resource use to ensure sustainability for future generations, and suggests practical steps like reusing items and recycling materials such as paper and metal.
37:50
Recycling Paper and Class Engagement Insights
- The paper used in newspapers is recycled, resulting in a little blackish or greyish appearance.
- A numerical question is posed, requiring an answer to be submitted in the comment box.
- In addition to three hours, there is a mention of five hours, which also needs to be addressed.
- The session concludes with a promise to return in the next class with a new topic.




