Our Environment in Full chapter (Animation) | CBSE Class 10 Biology ch13 | ecosystem | NCERT Science
Grade booster・11 minutes read
The environment is a complex system with living and non-living components interacting to maintain balance in ecosystems, which are formed by the interaction of plants, animals, and microorganisms in specific areas. Energy flows through food chains, with only 10% transferred between levels, and managing waste involves separating biodegradable and non-biodegradable materials to reduce environmental impact.
Insights
- Ecosystems are intricate systems where living and non-living elements interact, maintaining a delicate balance crucial for their survival and function.
- The flow of energy through food chains, the impact of biomagnification from chemical pollutants, and the importance of managing waste highlight the interconnectedness of environmental components and the necessity for sustainable practices to preserve ecosystems.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What are the components of an ecosystem?
Biotic and abiotic factors interact to form ecosystems.
How does energy flow in an ecosystem?
Energy flows through food chains from producers to consumers.
What is biomagnification?
Chemical pesticides accumulate in organisms through food chains.
How does ozone protect the Earth?
Ozone in the atmosphere shields against harmful sun radiation.
How can waste management reduce environmental impact?
Separating biodegradable and non-biodegradable waste helps minimize environmental harm.
Related videos

Physics Wallah Foundation
OUR ENVIRONMENT in 30 Minutes | Science Chapter 13 | Class 10th CBSE Board

Physics Wallah Foundation
OUR ENVIRONMENT in 30 Minutes || Mind Map Series for Class 10th

BaBa Bangali Ka Gyan
Our Environment Class 10 One Shot | Our Environment Class 10 | Chapter 15 Science Class 10

Khan Academy
Ecology introduction | Ecology | Khan Academy
Magnus Ehinger
Ekosystem
Summary
00:00
Interactions in Ecosystems: Balance and Impact
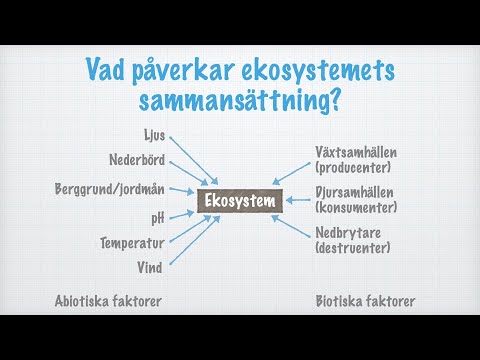
- The environment consists of living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components that interact to maintain balance.
- Ecosystems are formed by the interaction of biotic and abiotic components in specific areas like forests and ponds.
- A pond ecosystem includes animals like turtles, ducks, and fish, plants like water lilies, and microorganisms like bacteria.
- Organisms in an ecosystem are categorized as producers, consumers (herbivores, carnivores, omnivores), and decomposers.
- Energy flows through food chains from producers to consumers, with only 10% of energy transferred between levels.
- Biomagnification occurs when chemical pesticides enter food chains, accumulating in organisms like fish and eventually humans.
- Ozone, formed in the atmosphere, protects Earth from harmful sun radiation, but its depletion is caused by gases like chlorofluorocarbons.
- Managing waste involves separating biodegradable (decomposable by bacteria) and non-biodegradable (synthetic) materials to reduce environmental impact.




