Mendelian Genetics
Bozeman Science・15 minutes read
Gregor Mendel's experiments with pea plants led to the discovery of key genetic principles, including the Law of Segregation and the Law of Independent Assortment, which established how traits are inherited as distinct units. His findings not only laid the foundation for modern genetics but also highlighted ethical considerations surrounding the inheritance of genetic disorders like Huntington's Disease, as illustrated by pedigree charts.
Insights
- Gregor Mendel's experiments with pea plants established foundational principles of genetics, including the Law of Segregation and the Law of Independent Assortment, which demonstrate that traits are inherited as distinct units rather than blending, leading to predictable ratios in offspring traits, as evidenced by the 3:1 ratio of purple to white flowers in his F2 generation.
- The study of genetic disorders like Huntington's Disease illustrates the real-world implications of Mendel's findings, as the inheritance pattern can be visualized using pedigree charts, highlighting the ethical concerns surrounding genetic testing and family planning, particularly when a dominant gene can be unknowingly passed to future generations.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is genetic inheritance?
Genetic inheritance refers to the process by which traits and characteristics are passed from parents to their offspring through genes. This fundamental biological mechanism is governed by specific laws, such as Mendel's Law of Segregation and Law of Independent Assortment, which describe how alleles segregate during gamete formation and how different traits are inherited independently of one another. Understanding genetic inheritance is crucial for predicting the likelihood of certain traits appearing in future generations, as well as for studying genetic disorders and their implications for health and family planning.
How do Punnett squares work?
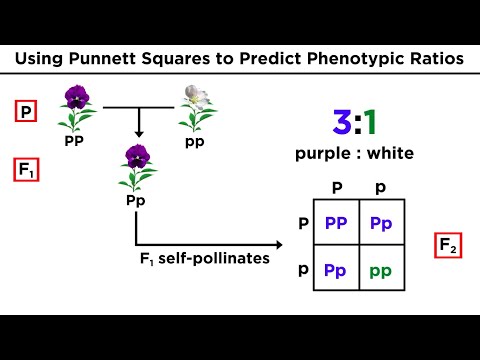
Punnett squares are a graphical tool used in genetics to predict the probability of offspring inheriting particular traits from their parents. By organizing the alleles of each parent along the top and side of a grid, the Punnett square allows for the visualization of all possible combinations of alleles that can occur during fertilization. For example, if one parent has a dominant allele for a trait (represented as "P") and the other has a recessive allele (represented as "p"), the Punnett square can show the expected ratios of offspring traits, such as a 3:1 ratio of dominant to recessive traits in certain crosses. This method is essential for understanding genetic probabilities and making informed predictions about inheritance patterns.
What is Huntington's Disease?
Huntington's Disease is a hereditary neurodegenerative disorder caused by a dominant allele, leading to the progressive degeneration of nerve cells in the brain. Symptoms typically manifest in middle adulthood and include uncontrollable movements, cognitive decline, and emotional disturbances, ultimately resulting in severe disability and death. Because it is an autosomal dominant condition, individuals with one copy of the mutated gene (genotype big H little h) have a 50% chance of passing the disorder to their children, raising significant ethical considerations regarding genetic testing and family planning for those at risk of inheriting the disease.
What is the Law of Segregation?
The Law of Segregation is a fundamental principle of genetics proposed by Gregor Mendel, stating that during the formation of gametes, the two alleles for a trait separate so that each gamete carries only one allele for each gene. This means that offspring inherit one allele from each parent, resulting in a 50% chance of inheriting either allele. This law is crucial for understanding how traits are passed down through generations and helps explain the predictable ratios observed in genetic crosses, such as the classic 3:1 ratio of dominant to recessive traits seen in Mendel's pea plant experiments.
What is a pedigree chart?
A pedigree chart is a visual representation of family relationships and the inheritance of specific traits or genetic disorders across generations. It uses symbols, such as squares for males and circles for females, to depict family members and their genetic status. For instance, in the case of Huntington's Disease, a pedigree chart can illustrate how the disorder is passed from parents to children, helping to identify carriers and assess the risk of transmission. Pedigree charts are valuable tools in genetics for understanding inheritance patterns, making informed decisions about genetic testing, and addressing ethical concerns related to family planning and health management.
Related videos

Reggie Cobb
Ch 11 Lecture Presentation Video
Professor Dave Explains
Mendelian Genetics and Punnett Squares

Larry Gardner
Mendel - From the Garden to the Genome

Khan Academy India - English
Dominance & segregation laws | Heredity & Evolution | Biology | Khan Academy

Vedantu Telugu 8,9 & 10
Heredity | Class 10 | One Shot @VedantuTelugu8910 SUMIYA MA'AM #vedantutelugu8910
Summary
00:00
Mendel's Pea Plant Experiments and Genetic Laws
- Gregor Mendel, known for his foundational work in genetics, conducted experiments with pea plants, using a paintbrush to transfer pollen between them to control parentage and observe offspring traits.
- Mendel's experiments with pea plants allowed him to identify key genetic principles, leading to the formulation of two fundamental laws: the Law of Segregation and the Law of Independent Assortment.
- The first cross in Mendelian genetics is referred to as the P cross (parental cross), and the resulting offspring are called F1 (filial one) generation; Mendel's initial cross of purple and white flowers produced all purple offspring.
- Upon crossing the F1 generation of purple flowers with themselves, Mendel observed a 3:1 ratio of purple to white flowers in the F2 generation, demonstrating that traits are inherited as distinct units rather than blending.
- Mendel's findings indicated that purple flowers are dominant (represented as "P") and white flowers are recessive (represented as "p"), leading to the conclusion that traits are passed down through genes.
- A Punnett square is a tool used to predict the probability of offspring traits by organizing parental alleles; for example, crossing big P (purple) and little p (white) results in a 3:1 ratio of purple to white flowers.
- Mendel's Law of Segregation states that during gamete formation, the alleles for a trait separate so that each gamete carries only one allele for each gene, resulting in a 50% chance of inheriting either allele.
- The Law of Independent Assortment asserts that the inheritance of one trait does not affect the inheritance of another trait, allowing for independent sorting of genes during gamete formation.
- Practice problems can be solved using Punnett squares to determine probabilities; for instance, crossing round peas (big R) with wrinkled peas (little r) yields a 1 in 4 chance of producing wrinkled seeds.
- Mendel's work laid the groundwork for understanding genetic inheritance, emphasizing the importance of using tools like Punnett squares to analyze genetic crosses and predict offspring traits accurately.
12:30
Genetic Traits and Huntington's Disease Inheritance
- The probability of obtaining a specific genetic trait can be calculated using the Law of Multiplication; for instance, the odds of flipping two heads in a row is 1 in 4, derived from multiplying the individual probabilities of 1 in 2 for each flip (1/2 * 1/2 = 1/4).
- Huntington's Disease, a dominant genetic disorder identified in the 1800s, leads to degeneration of nerve fibers in the brain, resulting in uncontrollable shakes and eventual death, with symptoms typically manifesting in middle age, making it possible for individuals to unknowingly pass the gene to their children.
- A pedigree chart illustrates the inheritance of Huntington's Disease, where squares represent males and circles represent females; for example, if a parent with the genotype big H little h (Huntington's carrier) has children with a parent of genotype little h little h (non-carrier), there is a 1 in 2 chance that any child will inherit the disease, raising ethical concerns about genetic testing and its implications for family planning and insurance.




