Ch 11 Lecture Presentation Video
Reggie Cobb・44 minutes read
Gregor Mendel's pioneering experiments on pea plants established foundational principles of genetics, including the Law of Segregation and the Law of Independent Assortment, which describe how traits are inherited through alleles. His work demonstrated the significance of dominant and recessive traits, laying the groundwork for genetic understanding and influencing inheritance patterns observed in all organisms.
Insights
- Gregor Mendel's experiments with pea plants revolutionized the understanding of inheritance by challenging the blending theory and introducing the concept of discrete units of inheritance, or alleles, which determine traits in offspring, leading to the formulation of the Law of Segregation and the Law of Independent Assortment.
- Mendel's use of true breeding varieties and controlled breeding methods allowed him to isolate specific traits, such as seed shape and flower color, and to establish clear ratios in the F1 and F2 generations, demonstrating predictable patterns of inheritance that laid the foundation for modern genetics.
- The text also highlights the complexity of inheritance, including concepts like autosomal disorders, multiple alleles, incomplete dominance, and sex-linked traits, emphasizing the nuanced ways in which traits can be passed down and expressed, which can have significant implications for understanding genetic conditions in humans.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is genetic inheritance?
Genetic inheritance refers to the process by which traits and characteristics are passed from parents to their offspring through genes. This process is governed by the principles of genetics, which include the understanding of dominant and recessive alleles, as well as the mechanisms of segregation and independent assortment. Inheritance patterns can be simple, involving single traits, or complex, involving multiple genes that influence a single trait. The study of genetic inheritance is crucial for understanding how traits are expressed in individuals and how they can vary within populations.
How do dominant and recessive traits work?
Dominant and recessive traits are fundamental concepts in genetics that describe how certain characteristics are expressed in an organism. A dominant trait is one that is expressed when at least one dominant allele is present, while a recessive trait requires two recessive alleles for expression. For example, in a genetic cross, if one parent contributes a dominant allele and the other contributes a recessive allele, the offspring will display the dominant trait. This relationship is essential for predicting the phenotypic outcomes of genetic crosses and understanding the inheritance patterns of various traits.
What is a Punnett Square?
A Punnett Square is a graphical tool used in genetics to predict the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring resulting from a genetic cross. It organizes the alleles contributed by each parent, allowing for easy visualization of the potential combinations. By filling in the squares, one can calculate the probabilities of different traits being expressed in the offspring. For instance, in a monohybrid cross, the Punnett Square can show the expected phenotypic ratio, helping to illustrate how traits are inherited according to Mendelian principles.
What are autosomal disorders?
Autosomal disorders are genetic conditions that are linked to genes located on the autosomes, which are the non-sex chromosomes. These disorders can be classified into two main categories: autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive. Autosomal dominant disorders require only one copy of the dominant allele for the disorder to manifest, while autosomal recessive disorders necessitate two copies of the recessive allele. Examples of these disorders include cystic fibrosis for autosomal recessive and Huntington's disease for autosomal dominant. Understanding these disorders is crucial for genetic counseling and predicting inheritance patterns in families.
What is polygenic inheritance?
Polygenic inheritance is a type of genetic inheritance where multiple genes contribute to a single trait, resulting in a continuous range of phenotypes. Unlike traits governed by a single gene, polygenic traits are influenced by the additive effects of several alleles, leading to variations in characteristics such as height, skin color, and eye color. This complexity results in a bell-shaped distribution of phenotypes in a population, illustrating the interplay of multiple genetic factors. Understanding polygenic inheritance is essential for studying traits that do not follow simple Mendelian patterns and for exploring the genetic basis of complex traits.
Related videos

Bozeman Science
Mendelian Genetics
Professor Dave Explains
Mendelian Genetics and Punnett Squares

Larry Gardner
Mendel - From the Garden to the Genome

Khan Academy India - English
Dominance & segregation laws | Heredity & Evolution | Biology | Khan Academy

Vedantu Telugu 8,9 & 10
Heredity | Class 10 | One Shot @VedantuTelugu8910 SUMIYA MA'AM #vedantutelugu8910
Summary
00:00
Mendel's Groundbreaking Discoveries in Genetics
- Gregor Mendel, known as the father of genetics, conducted experiments on pea plants to study inheritance patterns, challenging the prevailing blending concept of inheritance, which suggested offspring would have intermediate traits between their parents.
- Mendel formulated the particulate theory of inheritance, proposing two key laws: the Law of Segregation and the Law of Independent Assortment, which explain how genes are reshuffled from generation to generation, leading to genetic diversity.
- He chose garden peas for his experiments due to their ease of cultivation, short generation time, and the ability to self-pollinate or cross-pollinate manually, allowing for controlled breeding experiments.
- Mendel's experiments involved true breeding varieties of pea plants, focusing on monohybrid crosses that examined one trait at a time, such as tall versus short plants, to understand how traits are inherited.
- He established the concept of alleles, where each trait is represented by two alleles, leading to genotypes such as homozygous dominant (TT), homozygous recessive (tt), and heterozygous (Tt), which determine the phenotype, or observable characteristics.
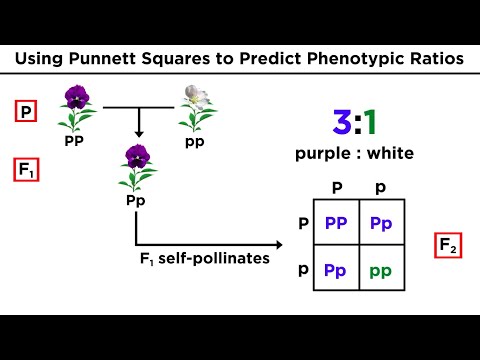
- The F1 generation results from crossing homozygous parents, producing offspring that are all heterozygous and exhibit the dominant trait, while the F2 generation results from crossing F1 individuals, leading to a phenotypic ratio of 3:1 (dominant to recessive traits).
- Mendel used a Punnett Square to predict the outcomes of genetic crosses, illustrating the probability of different genotypes and phenotypes in the offspring, with a typical genotypic ratio of 1:2:1 and a phenotypic ratio of 3:1 for monohybrid crosses.
- He identified several traits in pea plants, including seed shape (round vs. wrinkled), pod shape (inflated vs. constricted), and flower color (purple vs. white), which he used to demonstrate inheritance patterns.
- The Law of Segregation states that each individual carries two alleles for each trait, which separate during gamete formation, ensuring that each gamete receives only one allele from each pair.
- Mendel's findings laid the groundwork for modern genetics, showing that traits are controlled by alleles, with dominant alleles masking the expression of recessive alleles, and his work remains fundamental in understanding inheritance patterns in all organisms.
19:04
Genetic Principles of Inheritance Explained
- Homozygous individuals must be specified as either homozygous dominant or homozygous recessive, while heterozygous individuals can have one dominant and one recessive allele, which may come from either parent.
- Genotype refers to the two alleles an individual possesses; if they are identical, the individual is homozygous, and if different, heterozygous, with heterozygous represented by one capital and one lowercase letter.
- Phenotype is the observable physical trait or expression of the genotype, which can include traits like tasting ability, where tasters have a specific chemical reaction to certain substances.
- Dominant alleles code for normal gene function, while recessive alleles indicate a loss of function; during meiosis, homologous chromosomes separate, leading to Mendel's law of segregation, which states that only one allele for each trait is present in a gamete.
- The Law of Independent Assortment states that the segregation of one trait's alleles occurs independently of another trait's alleles, allowing for various combinations in gametes.
- A dihybrid cross involves crossing two traits, where each parent contributes one allele for each trait; for example, tall (T) and green (G) are dominant traits, while short (t) and yellow (g) are recessive traits.
- In a true dihybrid cross between two heterozygous individuals (TtGg), the expected phenotypic ratio of offspring is 9:3:3:1, with 9 showing both dominant traits (tall and green), 3 tall and yellow, 3 short and green, and 1 short and yellow.
- The Punnett Square, developed by Reginald Punnett, visually represents the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring, allowing for easy calculation of probabilities; for example, a 50% chance of offspring being heterozygous when crossing two heterozygous parents.
- A test cross is used to determine the genotype of an individual with a dominant phenotype by crossing it with a homozygous recessive individual; the resulting offspring's phenotypes reveal the unknown genotype.
- Understanding the principles of segregation and independent assortment is crucial for predicting genetic outcomes, and using tools like Punnett Squares simplifies the process of calculating probabilities for various traits in offspring.
36:36
Genetic Inheritance and Trait Expression Explained
- The text discusses genetic inheritance, specifically focusing on dominant and recessive traits, using examples like Big T (dominant) and Little T (recessive) to illustrate how traits are passed from parents to offspring, including the outcomes of heterozygous and homozygous crosses.
- A two-trait test cross involves crossing an individual with both dominant phenotypes with one that has both recessive phenotypes, resulting in a phenotype ratio of 1:1:1:1 if the individual is heterozygous for both traits, although this exercise is not required for the current study.
- Autosomal disorders are categorized into autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive disorders, with the former requiring only one dominant allele (Big A) to express the disorder, while the latter requires two recessive alleles (Little a).
- Examples of autosomal recessive disorders include methemoglobinemia, which causes bluish skin due to the accumulation of methylhemoglobin, and cystic fibrosis, characterized by thick mucus in the bronchial tubes and pancreatic ducts due to a defective chloride ion channel.
- Autosomal dominant disorders can appear in every generation, with examples including osteogenesis imperfecta, Huntington's disease, and hereditary spherocytosis, where at least one parent must carry the dominant allele for the disorder to be expressed in offspring.
- The text explains that multiple alleles can exist for a single gene, exemplified by the ABO blood type system, where A and B alleles are co-dominant, resulting in blood type AB when both are present, while type O has no antigens.
- Incomplete dominance is described, where the heterozygous phenotype is an intermediate between the two homozygous phenotypes, such as red and white flowers producing pink offspring, with familial hypercholesterolemia as an example of a disorder resulting from this inheritance pattern.
- Pleiotropy is introduced as a condition where a single gene affects multiple traits, with Marfan syndrome as an example, leading to diverse symptoms like long limbs and heart issues due to a mutation in the FBN1 gene on chromosome 15.
- Polygenic inheritance is the opposite of pleiotropy, where multiple genes influence a single trait, such as skin color, height, and eye color, demonstrating a range of phenotypes based on the combination of alleles.
- The text concludes with a discussion on sex-linked traits, emphasizing that these traits are located on the X chromosome and can affect both genders, illustrated by experiments conducted by Thomas Hunt Morgan on fruit flies, which provided insights into X-linked inheritance patterns relevant to humans.
56:14
Inheritance Patterns of X Linked Traits
- The text discusses the inheritance patterns of X-linked traits, specifically focusing on color blindness and hemophilia, highlighting that individuals can be either carriers or express the trait. In the F2 generation, crossing XRy (red-eyed male) with XrXr (female) results in two red-eyed females (XRXr and XrXr) and one red-eyed male (XRY) alongside one non-red male (XrY), illustrating how traits can be passed down through generations.
- It explains that X-linked recessive traits can skip generations, with males having only two possibilities: normal (XY) or colorblind (XcY), while females can be normal (XX), carriers (XcX), or colorblind (XcXc). The inheritance pattern is influenced by the mother, who determines the X chromosome passed to her sons, emphasizing the role of carriers in the transmission of traits.
- For further understanding, the text recommends reviewing supplemental materials, including videos from Bozeman Science and Khan Academy, as well as engaging with the instructor for clarification on complex topics. It stresses the importance of asking questions and utilizing available resources to grasp the significance of X-linked traits in biology.




