GCSE Biology - Nervous System and Reflex Arc #58
Cognito・4 minutes read
The nervous system relies on various types of neurons to transmit electrical impulses rapidly through synapses, allowing it to process sensory information via the central nervous system and respond through motor neurons. An example of this efficiency is the reflex arc, which enables immediate reactions, such as withdrawing a hand from a sharp object, to protect the body.
Insights
- The nervous system is made up of various types of neurons that communicate through synapses, allowing for the quick transmission of electrical impulses and enabling the body to relay information rapidly, which is crucial for responding to changes in the environment.
- The central nervous system (CNS) plays a vital role in processing sensory information and coordinating responses; for instance, a reflex arc involves a quick reaction to stimuli, such as withdrawing a hand from a sharp object, illustrating how the nervous system efficiently protects the body from harm.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
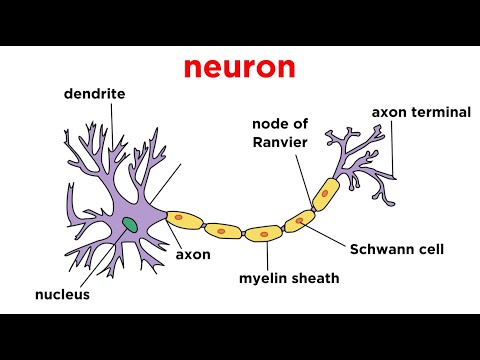
What is a neuron?
A neuron is a specialized cell in the nervous system responsible for transmitting information throughout the body. Neurons are characterized by their long, thin structure, which allows them to connect with numerous other neurons, forming a complex network. They communicate through synapses, where electrical impulses trigger the release of neurotransmitters, enabling the transfer of signals from one neuron to another. This intricate communication system is essential for processing and relaying information, making neurons fundamental to the functioning of the nervous system.
How does the central nervous system work?
The central nervous system (CNS) is the control center of the body, consisting of the brain and spinal cord. It processes sensory information received from sensory neurons that detect various stimuli, such as changes in temperature or chemical levels. Once the CNS interprets this information, it formulates an appropriate response and sends signals back to the body through motor neurons. These motor neurons communicate with effectors, such as muscles or glands, to execute the necessary actions, thereby coordinating bodily responses to internal and external changes.
What is a reflex arc?
A reflex arc is a neural pathway that mediates a reflex action, allowing for a rapid response to stimuli without the need for conscious thought. When a stimulus, like touching something sharp, is detected by sensory receptors in the skin, a sensory neuron transmits an impulse to the spinal cord. Here, the impulse is quickly relayed to a motor neuron, which activates an effector, such as a muscle, to withdraw the hand from the source of danger. This mechanism exemplifies the efficiency of the nervous system in protecting the body by facilitating immediate reactions to potentially harmful situations.
What are sensory neurons?
Sensory neurons are specialized nerve cells that play a crucial role in the nervous system by detecting and transmitting sensory information from the environment to the central nervous system (CNS). These neurons are equipped with receptors that respond to various stimuli, such as light, sound, temperature, and chemical changes. Once a stimulus is detected, sensory neurons convert this information into electrical impulses and send them to the CNS for processing. This allows the body to perceive and react to changes in the environment, making sensory neurons essential for survival and interaction with the world.
What do motor neurons do?
Motor neurons are a type of nerve cell responsible for transmitting signals from the central nervous system (CNS) to effectors, such as muscles and glands, to initiate movement or action. After the CNS processes sensory information and determines an appropriate response, motor neurons carry the impulses that instruct the effectors to perform specific functions. For example, when the brain decides to move a muscle, motor neurons relay the command, resulting in muscle contraction and movement. This communication is vital for executing voluntary actions and reflexes, highlighting the essential role of motor neurons in the nervous system.
Related videos

IGCSE Study Buddy
14. Coordination and response(Part 1)(Cambridge IGCSE Biology 0610 for exams in 2023, 2024 and 2025)

Grade booster
#controlandcoordination full chapter | cbse Class 10th Biology | NCERT class 10 science chapter 7
Professor Dave Explains
Types of Tissue Part 4: Nervous Tissue

Class 10 Learn With Mansi
Control And Coordination | Chapter 6 | Complete Chapter | "लक्ष्य" 2025

Neuroscientifically Challenged
10-Minute Neuroscience: Neurons
Summary
00:00
Understanding the Nervous System's Response Mechanism
- The nervous system consists of various types of neurons, which are long, thin cells with numerous branch connections that facilitate the transmission of electrical impulses. These neurons communicate through synapses, where an electrical impulse triggers the release of chemicals that diffuse across the gap to initiate a new electrical impulse in the next neuron, allowing for the rapid relay of information throughout the nervous system.
- The central nervous system (CNS), comprising the brain and spinal cord, processes sensory information received from sensory neurons that detect changes in the body, such as temperature or carbon dioxide levels. Once the CNS determines an appropriate response, it sends impulses back to the body via motor neurons to effectors, typically muscles or glands, which execute the necessary actions.
- A reflex arc exemplifies the nervous system's rapid response mechanism, where a stimulus, such as touching a sharp object, is detected by receptor cells in the skin. This triggers a sensory neuron to send an impulse to the spinal cord, where it is relayed to a motor neuron that activates an effector, like a muscle, to quickly withdraw the hand from danger, demonstrating the efficiency of the nervous system in protecting the body.




