Fixed Exchange Rates - How Are They Managed?
EconplusDal・2 minutes read
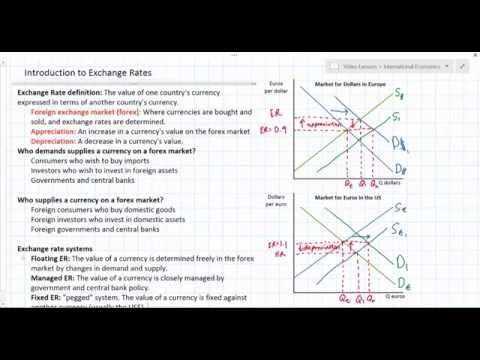
Floating exchange rates are determined by demand and supply, while fixed exchange rates require government intervention to maintain by manipulating currency reserves based on overvaluation or undervaluation, with adjustments like devaluation or revaluation to influence trade performance or inflation rates. Interest rate manipulation can also impact exchange rates, but it's less direct and can have unintended consequences.
Insights
- In floating exchange rates, currency value changes based on market demand and supply, leading to appreciation with higher demand and depreciation with more supply, free from government interference.
- Fixed exchange rates require government intervention to stabilize currency values, involving actions like buying or selling reserves to adjust supply, or devaluation/revaluation to impact trade and inflation, showing the intricacies of managing currency values.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
How are floating exchange rates determined?
By demand and supply without government intervention.
What is the role of government in fixed exchange rates?
Government intervention is required to maintain fixed rates.
How can a government adjust a fixed exchange rate?
By selling or buying currency reserves.
What are the methods of adjusting fixed exchange rates?
Devaluation and revaluation by governments.
How does interest rate manipulation impact exchange rates?
It can indirectly influence exchange rates.
Related videos
Summary
00:00
Exchange Rate Determination and Government Intervention
- Floating exchange rates are determined by demand and supply without government intervention, leading to currency appreciation with increased demand and depreciation with increased supply.
- Fixed exchange rates require government or Central Bank intervention to maintain, involving holding large domestic and foreign currency reserves to manipulate demand and supply.
- To maintain a fixed exchange rate, if the currency is overvalued, the government can sell domestic currency reserves to increase supply and lower the exchange rate; if undervalued, they can buy up the currency to increase demand and raise the exchange rate.
- Fixed exchange rates can be adjusted by governments through devaluation or revaluation, with devaluation lowering the currency value and revaluation increasing it, with the aim of influencing trade performance or inflation rates. Interest rate manipulation can also impact exchange rates, but it's less direct and can have unintended consequences.