How Exchange Rates Are Determined
Money & Macro・8 minutes read
Exchange rates are determined by a variety of factors such as inflation and interest rates, with the dominant variable varying by country and time. Traders engage in arbitrage to profit from price differences between countries, while speculators in the foreign exchange market attempt to predict the actions of arbitrageurs to influence exchange rate expectations.
Insights
- The unknown dominant variable influencing exchange rates varies for each country and time, making it challenging to predict and control.
- Traders engaging in arbitrage exploit price differences between countries, impacting currency supply and demand, while speculators in the foreign exchange market attempt to forecast arbitrageurs' actions, shaping exchange rate expectations.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
How are exchange rates determined?
Exchange rates are determined by a combination of factors such as inflation, interest rates, supply and demand on foreign exchange markets, and the actions of traders engaging in arbitrage. These rates represent the price of one currency in terms of another, indicating how much of a foreign currency can be purchased with the home currency. While the exact dominant variable affecting exchange rates can vary by country and time, the interplay of economic indicators and market forces ultimately dictates these values.
What is the significance of Purchasing Power Parity theory?
The Purchasing Power Parity theory posits that prices in different countries should be similar when expressed in a common currency, which can impact exchange rates. This theory suggests that exchange rates should adjust to equalize the purchasing power of different currencies, influencing the relative value of each currency in the foreign exchange market. By examining price differentials across countries, economists can gain insights into potential exchange rate movements and the underlying economic conditions driving these changes.
How do interest rates and financial returns affect exchange rates?
Interest rates and financial returns play a crucial role in explaining short-term movements in exchange rates, according to economists. Changes in interest rates can influence investor behavior, affecting the demand for currencies and impacting exchange rates. Higher interest rates in a country can attract foreign investment, leading to an appreciation of the currency, while lower rates may result in depreciation. Financial returns also factor into exchange rate movements, as investors seek profitable opportunities in different markets based on expected returns.
What is the role of arbitrage in the foreign exchange market?
Traders engage in arbitrage in the foreign exchange market to profit from price differences between countries, impacting supply and demand for currencies. Arbitrageurs exploit these price differentials by buying and selling currencies simultaneously to take advantage of discrepancies in exchange rates. Their actions can influence market dynamics, leading to adjustments in exchange rates as supply and demand conditions shift. By participating in arbitrage, traders contribute to market efficiency and help align exchange rates across different regions.
How do speculators influence exchange rate expectations?
Speculators in the foreign exchange market attempt to predict the actions of arbitrageurs and other market participants, influencing exchange rate expectations. By speculating on future currency movements, these individuals can impact market sentiment and drive changes in exchange rates. Speculative activity can introduce volatility into the foreign exchange market, as traders make bets on the direction of currency values based on various factors such as economic data, geopolitical events, and market trends. The actions of speculators can shape market perceptions and contribute to fluctuations in exchange rates over time.
Related videos
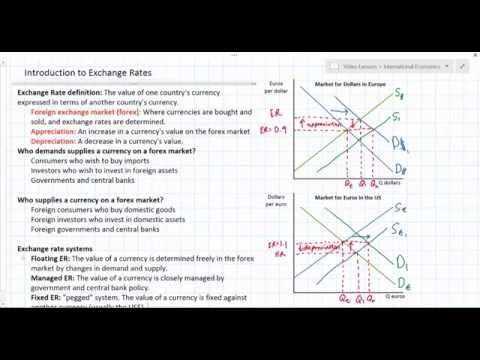
Jason Welker
Introduction to Exchange Rates and Forex Markets

EconplusDal
Fixed Exchange Rates - How Are They Managed?

Wendover Productions
The Growing Revolt Against the US Dollar

CA Wallah by PW
Business Economics: International Trade | CA Foundation Chanakya 2.0 Batch 🔥

Finance & Accounting Basics w/ Sir Jonas Ordaniel
FINANCIAL MARKETS (INTRODUCTION TO FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT PART3) - BUSINESS FINANCE
Summary
00:00
Factors Influencing Exchange Rates: An Overview
- Exchange rates are determined by inflation and interest rates, but the dominant variable for each country and time is unknown.
- The exchange rate is the price of one currency expressed in another, with a standard to indicate how much foreign currency can be bought with the home currency.
- Exchange rates are determined by supply and demand on foreign exchange markets, with prices influenced by these factors.
- Traders engage in arbitrage to profit from price differences between countries, impacting supply and demand for currencies.
- The Purchasing Power Parity theory suggests that prices in different countries should be similar, affecting exchange rates.
- Interest rates and financial returns play a role in explaining exchange rate movements in the short term, according to economists.
- Speculators in the foreign exchange market try to predict the actions of arbitrageurs, influencing exchange rate expectations.




