Endosymbiotic Theory
Amoeba Sisters・2 minutes read
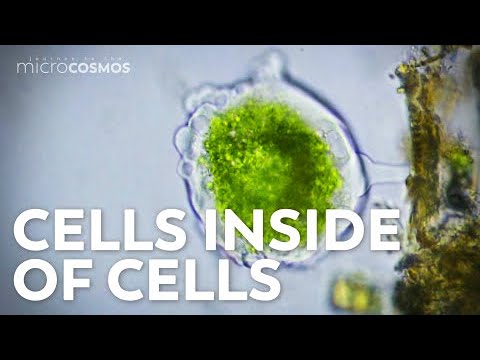
Scientific theories like the endosymbiotic theory explain scientific events with evidence, being testable and repeatedly tested. The theory details the evolution of eukaryote cells from prokaryotic cells in symbiosis, with mitochondria and chloroplasts having their DNA and dividing similarly to bacteria, supporting the theory.
Insights
- The endosymbiotic theory proposes that eukaryote cells evolved from prokaryotic cells through symbiosis, with mitochondria and chloroplasts being remnants of this process, supported by their DNA similarities and division mechanisms.
- Endosymbiosis, a key concept in biology, is not only a historical occurrence but is also observable in modern organisms like termites, showcasing the ongoing nature of symbiotic relationships in nature.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What are scientific theories?
Explanations supported by evidence, testable, and repeatable.
How do mitochondria and chloroplasts divide?
Similarly to bacteria, supporting endosymbiotic theory.
What is the endosymbiotic theory?
Explains evolution of eukaryote cells from prokaryotic cells.
Does endosymbiosis occur today?
Yes, seen in organisms like termites with gut prokaryotes aiding in wood digestion.
How are scientific theories tested?
Through repeated testing and evidence-based support.
Related videos
Summary
00:00
Endosymbiotic Theory: Evolution and Evidence
- Scientific theories, such as the endosymbiotic theory, are explanations of scientific events supported by evidence and must be testable and repeatedly tested.
- The endosymbiotic theory explains the evolution of eukaryote cells from prokaryotic cells that lived in symbiosis, with some prokaryotes evolving into mitochondria and chloroplasts.
- Mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA, similar to bacterial DNA, and divide similarly to bacteria, supporting the endosymbiotic theory.
- Endosymbiosis is not just a past event but also occurs today, as seen in organisms like termites with prokaryotes in their gut aiding in wood digestion.