REFLEX ACTION | Control & Coordination | Class 10 Biology TS, AP Stateboard/CBSE
Vedantu Telugu 8,9 & 10・33 minutes read
The focus of the biology class is on reflex actions, with the spinal cord playing a crucial role in coordinating immediate responses separate from the brain. Reflex actions include both natural, innate responses like blinking at sudden light and conditioned, learned responses such as swimming after being put in water.
Insights
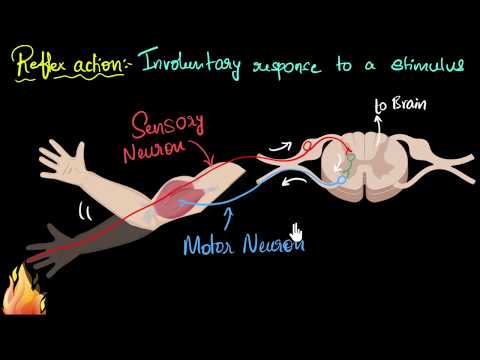
- Reflex actions are immediate, involuntary responses to stimuli that involve sensory neurons, relay neurons, motor neurons, and effector organs, following a sequence from stimulus reception to effector response, bypassing direct involvement of the brain.
- Reflex actions encompass natural reflex actions (innate responses like blinking at sudden light) and conditioned reflex actions (acquired through learning, such as swimming after being put in water), with the spinal cord playing a vital role in coordinating these automatic, rapid, and unconscious self-protective responses.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is the role of the spinal cord in reflex actions?
The spinal cord efficiently coordinates reflex actions by quickly transmitting information between sensory and motor neurons, bypassing the brain.
How are reflex actions defined?
Reflex actions are immediate, involuntary responses to stimuli that aid in self-protection and include actions like blinking at sudden light flashes.
What are the components of a reflex arc?
A reflex arc involves a sequence of steps including stimulus reception, sensory neuron transmission, relay neuron involvement, motor neuron activation, and effector response.
What distinguishes natural reflex actions from conditioned reflex actions?
Natural reflex actions are innate, automatic responses to stimuli like removing a hand from a hot object, while conditioned reflex actions are acquired through learning or experience.
How does the brain contribute to reflex actions?
The brain is not directly involved in reflex actions; instead, the spinal cord quickly coordinates responses by bypassing the brain and efficiently controlling bodily functions.
Related videos
Khan Academy India - English
Reflex action (& reflex arc) | Control & Coordination | Biology | Khan Academy

UDAAN
Control And Coordination FULL CHAPTER | Class 10th Science | Chapter 6 | Udaan

Grade booster
#controlandcoordination full chapter | cbse Class 10th Biology | NCERT class 10 science chapter 7

Class 10 Learn With Mansi
Control And Coordination | Chapter 6 | Complete Chapter | "लक्ष्य" 2025

IGCSE Study Buddy
14. Coordination and response(Part 1)(Cambridge IGCSE Biology 0610 for exams in 2023, 2024 and 2025)
Summary
00:00
"Spinal Cord: Key to Reflex Actions"
- Reflex action is the focus of the current session in biology class.
- The spinal cord is a crucial part of the central nervous system, connected to the brain.
- The brain is divided into four parts: forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain.
- The spinal cord helps the brain efficiently control the human body.
- Spinal cord is like a branch office to the brain, aiding in bodily functions.
- Reflex actions are immediate, involuntary responses to stimuli.
- Reflex actions include blinking at sudden light flashes or removing a hand from a hot object.
- The process of reflex action involves sensory neurons, relay neurons, motor neurons, and effector organs.
- Brain is not directly involved in reflex actions; the spinal cord quickly coordinates responses.
- The sequence of reflex action involves stimulus reception, sensory neuron transmission, relay neuron involvement, motor neuron activation, and effector response.
27:49
"Reflex Arc: Rapid, Automatic Responses"
- Reflex action involves several steps:
- First, the stimulus is received by the receptor.
- The sensory neuron then passes this information to the association neuron.
- The association neuron transfers it to the motor neuron in the spinal cord.
- Subsequently, the motor neuron conveys the information to the effector.
- Finally, the effector acts upon the instruction, resulting in a response.
- The pathway of reflex action is termed a reflex arc.
- Reflex arc is the shortest route for an impulse from receptor to effector.
- The reflex arc involves the transfer of impulses through neurons.
- Spinal cord plays a crucial role in reflex actions, bypassing the brain.
- Reflex actions are automatic, rapid, and unconscious responses to stimuli, aiding in self-protection.
56:15
Neuron types and reflex actions explained
- The correct answer to a question regarding neuron types was determined to be option A, which represents a sensory neuron.
- Reflex actions were discussed, highlighting two types: natural reflex actions and conditioned reflex actions.
- Natural reflex actions, such as removing a hand from a hot object, are innate and do not require prior learning or experience.
- Conditioned reflex actions, like swimming after being put in water, are acquired through experience or learning and differ from natural reflex actions.




