IRR (Internal Rate of Return)
Edspira・6 minutes read
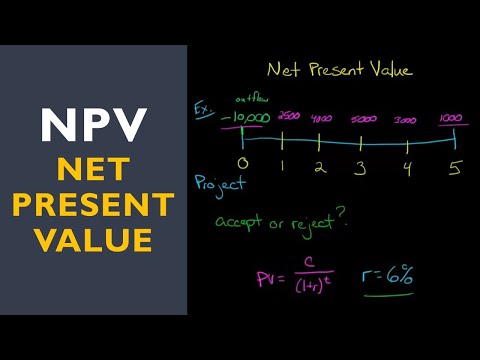
IRR is a method for project evaluation, similar to NPV, determining the discount rate that makes the NPV zero to decide on project acceptance based on a break-even point. In a project example, calculating an IRR of 30% compared to the original 8% discount rate indicates project acceptance if the calculated Big R exceeds the original discount rate.
Insights
- IRR is a method that calculates the discount rate at which a project's Net Present Value becomes zero, indicating the break-even point and providing a decision rule for project acceptance based on whether this rate exceeds the original discount rate.
- In contrast to NPV, IRR focuses on identifying the specific discount rate that aligns with a project's financial viability, offering a unique perspective on evaluating investment opportunities beyond traditional methods like NPV.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is Internal Rate of Return (IRR)?
IRR is a method to evaluate projects.
How does IRR differ from NPV?
IRR involves setting NPV to zero.
What is the decision rule for IRR?
Accept project if Big R exceeds original discount rate.
How is IRR calculated in projects?
IRR determines discount rate making NPV zero.
What does a positive NPV indicate?
Positive NPV indicates project acceptance.
Related videos
Summary
00:00
Evaluating Projects with Internal Rate of Return
- Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is a method to evaluate projects for decision-making, similar to Net Present Value (NPV).
- In a project example, investing $100 at year zero and receiving $130 at year one, the NPV calculation with an 8% discount rate yields a positive $20.37, indicating project acceptance.
- Contrasting with NPV, IRR involves setting the NPV to zero and solving for a different discount rate (Big R), which in this case is 30%, compared to the original 8% (little r).
- IRR determines the discount rate that makes the NPV zero, serving as a break-even point, with a decision rule of accepting the project if the calculated Big R exceeds the original discount rate.