Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
The Finance Storyteller・4 minutes read
NPV and IRR are fundamental concepts in finance, where NPV involves converting future cash flows into present values using a discount rate, while IRR focuses on finding the discount rate that makes the NPV zero through a trial-and-error process.
Insights
- Net Present Value (NPV) is calculated by converting future cash flows into present values using a discount rate, while Internal Rate of Return (IRR) identifies the discount rate that results in an NPV of zero.
- Understanding NPV is crucial as it serves as the foundation for comprehending IRR calculations, which involve a systematic approach to determining the rate that equates to zero NPV.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
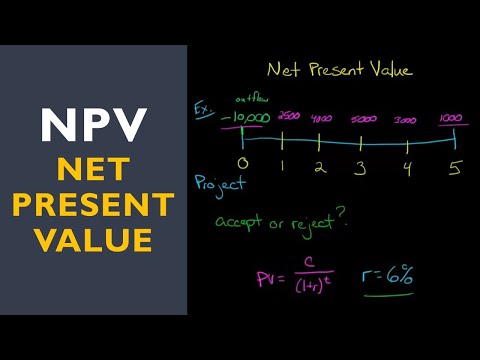
What is Net Present Value (NPV)?
NPV is a finance concept converting future cash flows into present values using a discount rate to determine the sum of present values.
How are Net Present Value (NPV) and Internal Rate of Return (IRR) related?
NPV is the starting point for understanding IRR in finance, with IRR calculations focusing on finding the discount rate that makes the NPV zero.
What does Internal Rate of Return (IRR) represent?
IRR is the rate at which the NPV of cash flows becomes zero, determined through a step-by-step trial and error process in finance.
How is Net Present Value (NPV) calculated?
NPV calculations involve converting future cash flows into present values using a discount rate, with the sum of present values determining the NPV in finance.
What is the process for determining Internal Rate of Return (IRR)?
The determination of IRR involves finding the discount rate that makes the NPV zero through a step-by-step trial and error process in finance.
Related videos
Summary
00:00
Understanding NPV and IRR in Finance
- Net Present Value (NPV) and Internal Rate of Return (IRR) are closely related concepts in finance, with NPV being the starting point for understanding IRR.
- NPV calculations involve converting future cash flows into present values using a discount rate, with the sum of present values determining the NPV.
- IRR calculations, on the other hand, focus on finding the discount rate that makes the NPV zero, with a step-by-step trial and error process leading to the determination of the Internal Rate of Return.