Conduction of nerve impulse - Mechanism
BYJU'S・3 minutes read
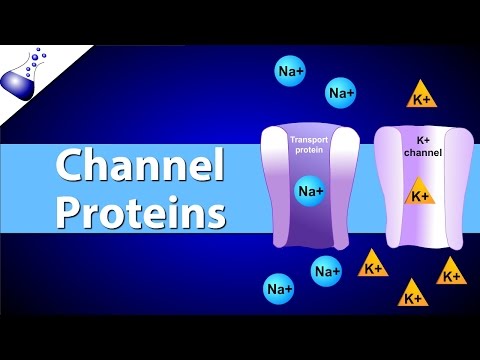
Neurons maintain a resting membrane potential of -70 millivolts due to the higher permeability to potassium ions, creating a negative charge inside the cell. The sodium-potassium pump helps maintain this electrical gradient by transporting ions in and out of the cell, achieving electrochemical equilibrium.
Insights
- Neurons maintain a negative charge inside due to a higher permeability to potassium ions than sodium ions, establishing a resting membrane potential around -70 millivolts.
- The sodium-potassium pump is essential for sustaining this charge by moving more sodium ions out than potassium ions in, contributing to the negative charge that attracts positive ions back in, achieving an electrochemical equilibrium.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is the resting membrane potential?
-70 millivolts
Related videos
Summary
00:00
"Neurons' Potassium Permeability & Resting Potential"
- Neurons have a distinct feature where the cell membrane is highly permeable to potassium ions compared to sodium ions, leading to a higher concentration of potassium inside the cell. This creates a relative negative charge within the cell due to the exit of positive ions, establishing the resting membrane potential of around -70 millivolts.
- The sodium-potassium pump plays a crucial role in maintaining this electrical gradient by actively transporting three sodium ions out of the cell for every two potassium ions moved inside, contributing to the inner negative charge that attracts positive ions back into the cell. The electrochemical equilibrium is achieved with potassium ions moving in and out, balancing the concentration gradient and the negative electrical charge of the membrane.