Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 3 Cells Part B
Doctor Maria's Biology Channel・28 minutes read
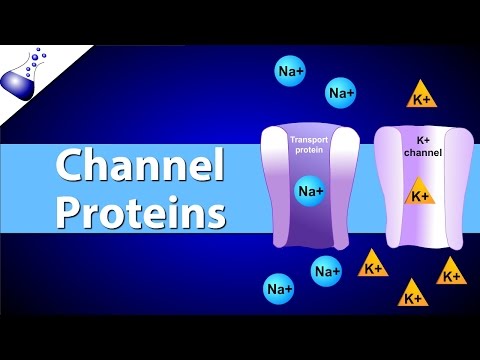
Active transport mechanisms, including primary and secondary transport, move solutes across the plasma membrane with ATP energy input. The Sodium-potassium pump is a vital example of primary active transport, maintaining ion concentrations for nerve impulse generation and cell function.
Insights
- Active transport mechanisms, such as the sodium-potassium pump, use ATP energy to move solutes against concentration gradients, crucial for maintaining cell function and generating nerve impulses.
- Vesicular transport processes like phagocytosis, pinocytosis, and receptor-mediated endocytosis involve the uptake of materials into cells through vesicles, aiding in nutrient absorption, immune defense, and selective molecule internalization, all requiring ATP energy.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is active transport in cells?
Active transport moves solutes against concentration gradients using energy.
Related videos
Summary
00:00
Active Transport Mechanisms: Essential Cellular Energy Processes
- Lecture on unit 4 chapter 3 part b focusing on active transport mechanisms
- Active membrane transport includes active transport and vesicular transport, both requiring ATP energy input
- Active transport moves solutes across the plasma membrane against concentration gradients using carrier proteins or solute pumps
- Different types of carriers include anti-porters, importers, and symporters, moving substances in various directions
- Primary active transport uses ATP directly, while secondary active transport utilizes energy from ionic gradients created by primary transport
- Sodium-potassium pump is a crucial example of primary active transport, maintaining ion concentrations for cell function
- Sodium-potassium pump moves sodium out and potassium into the cell, creating an electrical gradient across the membrane
- Sodium-potassium pump uses ATP to transport ions, maintaining cell membrane potential for nerve impulse generation
- Secondary active transport relies on ion gradients created by primary transport to move other solutes into the cell
- Vesicular transport involves endocytosis and exocytosis, using vesicles to transport materials into or out of the cell, requiring ATP energy
20:01
Cellular Processes and Signaling Mechanisms in Biology
- Phagocytosis involves the formation of a phagosome that merges with a lysosome for digestion, with receptors binding to microorganisms or particles to protect against invaders.
- Pinocytosis, known as cell drinking, brings extracellular fluid and solutes into the cell through folding of the plasma membrane, aiding in nutrient absorption and environmental sampling.
- Receptor-mediated endocytosis is a selective process using specific receptors to internalize molecules like enzymes, LDL, iron, insulin, and viruses, involving clathrin-coated pits or caveolae.
- Exocytosis reverses endocytosis, with vesicles fusing with the cell membrane to release contents like hormones, neurotransmitters, mucus, or cellular waste into the extracellular environment.
- Resting membrane potential, established by the separation of charged particles across the plasma membrane, relies on potassium diffusion, sodium-potassium pump, and negatively charged proteins to maintain a negative charge inside the cell.
- Cell environment interactions involve cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) anchoring cells, assisting in cell movement, attracting white blood cells, and transmitting signals, and plasma membrane receptors binding to chemical signals for cellular activities.
- Contact signaling involves cells recognizing each other through unique surface membrane receptors, crucial in normal development and immunity, while chemical signaling uses ligands to trigger cellular changes like enzyme activation or ion channel opening.
- In immunity, contact signaling occurs between B and T cells for pathogen response, while chemical signaling involves ligands binding to specific receptors on target cells to elicit responses.
- Hormones in endocrine glands are released into the bloodstream to bind to target cells, while paracrine signals act locally in the extracellular medium, causing different responses in cells based on the chemical pathway activated by the ligand-receptor interaction.
- Receptor activation can lead to enzyme activation, ion gate opening, or G-protein activation, indirectly affecting cellular changes through second messenger chemicals like cyclic AMP or calcium, resulting in prolonged responses compared to direct ion channel opening.
39:50
Epinephrine: The Heart of Stress Response
- Epinephrine, also known as adrenaline, binds to a beta adrenergic receptor in the resting state, followed by the activation of a G protein and adenylyl cyclase, an enzyme.
- In the stimulated state, epinephrine binding leads to the dissociation of the G protein, activation of adenylyl cyclase, conversion of ATP into cyclic AMP, resulting in increased heart rate, dilation of skeletal muscle blood vessels, and breakdown of glycogen to glucose, aiding in stress response for faster breathing, thinking, and muscle action. Epinephrine acts as the first messenger, while cyclic AMP serves as the second messenger, functioning intracellularly.