Class 11 Biology cell biology part 2
Department Of Information Technology・48 minutes read
Plastics are essential organelles in plant cells, storing pigments and giving color; with three types including chloroplasts, chromoplasts, and leucoplasts. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a membrane factory and cell support system, aiding in material transportation, detoxification, and cell membrane formation.
Insights
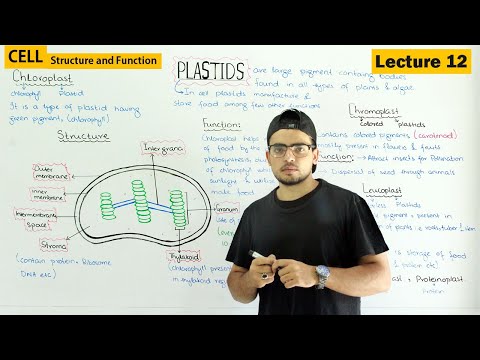
- Plastids are essential organelles in plant cells, coming in three types: chloroplasts, chromoplasts, and leucoplasts, each storing different pigments that contribute to the coloration of plant parts.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) is a crucial cell organelle responsible for membrane production, cell support, material transportation, detoxification, and the formation of lysosomes and cell membranes, playing a vital role in cell health and function.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What distinguishes plant and animal cells?
Plastics are essential cell organelles found in plant cells but absent in animal cells, distinguishing the two types of cells.
What are the types of plastids based on pigment color?
There are three types of plastids based on the color of the pigment stored inside: chloroplast, chromoplast, and leucoplast.
What is the main function of chloroplasts?
The main function of chloroplasts is photosynthesis, a process divided into light and dark reactions, occurring in thylakoid membranes and stroma.
What is the function of liquid plast in plants?
The main function of liquid plast is food storage, with different types storing various nutrients.
What is the function of Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) in cells?
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) functions as a membrane factory, provides mechanical support, aids in material transportation, and plays a crucial role in cell health.
Related videos
PoWer Of KnOwledge Academy
Plastids | Chloroplast, Chromoplast & Leucoplast | Video 12

Exam Winner Plus One
Plus One Biology Christmas Exam | Cell the Unit Of Life | Full Chapter | Chapter 8 | Exam Winner
Learn Easy Science
Learn all about plant cells in 2 MINUTES 🌱 | Easy science video

Biology Reader
Protoplasm | Definition, Diagrams, Components, Properties and Functions

Beverly Biology
Organelles of the Cell
Summary
00:00
Plastics: Essential Organelles Distinguishing Plant and Animal Cells
- Plastics are essential cell organelles found in plant cells but absent in animal cells, distinguishing plant and animal cells.
- Plastics, like other organelles, are membrane-covered structures that store pigments, giving color to plant cells.
- There are three types of plastics based on the color of the pigment stored inside: chloroplast, chromoplast, and leucoplast.
- Chloroplasts contain green pigment called chlorophyll, found in all green parts of plants, primarily in leaves.
- The number of chloroplasts in a cell can vary greatly, from one to over a thousand, influencing the color intensity of leaves.
- Chloroplasts have an indefinite shape, often oval, and are present in various plant parts, contributing to the green color of nature.
- The main function of chloroplasts is photosynthesis, the process divided into light and dark reactions, occurring in thylakoid membranes and stroma.
- Chromoplasts contain non-green pigments and are found in colored parts of plants like flowers and fruits.
- Chromoplasts have a double membrane structure with a unique layer called the granum, containing different pigments like brown and red.
- Leucoplasts, another type of plastid, contribute to pollination by attracting insects and birds with their colorful pigments.
22:21
Liquid plast and endoplasmic reticulum in cells.
- Liquid plast is a type of colorless plastic containing white pigment, commonly found in plant parts lacking green or other pigments, such as roots.
- Liquid plast is categorized based on the stored material, with three types: carbohydrate-storing mileoblast, protein-storing leuroblast, and lipid-storing elaioblast.
- The main function of liquid plast is food storage, with each type storing different nutrients.
- Liquid plast can convert into chloroplasts when exposed to light, leading to color changes in plant parts like potatoes, papayas, and tomatoes.
- Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a cell organelle found only in eukaryotic cells, absent in prokaryotic cells, and is a highly folded, membranous structure forming a network-like system.
- ER consists of three parts: cisternae, vesicles, and tubules, with ribosomes on the surface, freely floating in the cytoplasm.
- ER functions as a membrane factory, producing various cell membranes, and acts as a cytoskeleton, providing mechanical support to cells.
- ER aids in material transportation within cells and to the outside, earning the nickname "cell circulatory system."
- ER plays a crucial role in forming primary lysosomes, cell plates, and recycling cell membranes, contributing to cell health and function.
44:24
Cell Membrane and ER: Essential Cell Functions
- Cell membrane is a living sponsor inside the cell, aiding in repair and regeneration.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) provides extra membrane for repairing cell damage.
- ER assists in the formation of primary lysosomes and cell organelles.
- ER transports materials for cell wall formation.
- ER aids in detoxification by neutralizing toxins within the cell.
- ER plays a crucial role in the formation of different cell membranes and material circulation.
- Cell Theory states that all living beings are made of cells, the structural and functional unit of life.
- Cells contain basic components common in all living beings, with similar chemical composition.
- Cells can be totipotent, capable of producing other cell types.
- Golgi bodies help in collection, storage, modification, packing, and transportation of cellular materials, also known as packaging.
01:05:14
"Ribosomes: Protein Factories in All Cells"
- Cell theory exceptions and drawbacks are discussed, with a focus on early life exceptions and drawbacks.
- Ribosomes are introduced as the smallest cell organelles without a membrane, requiring an electron microscope for observation.
- Ribosomes are universal cell organelles found in all cell types, including prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
- Ribosomes are described as organelles within organelles, found freely in the cytoplasm and within other cell organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts.
- Ribosomes are composed of RNA and protein, making them nucleoproteins, and exist in two types: 70s and 80s based on size and speed.
- The function of ribosomes is detailed as the site of protein synthesis, known as the protein factory within the cell.
- Ribosomes also prepare proteins for extracellular use, including hormones and enzymes, and are involved in transporting proteins outside the cell.




