12th Biology | Chapter 10 | Human Health & Diseases | Lecture 1 | Maharashtra Board |
JR Tutorials・81 minutes read
Abhishek updates viewers on Biology tutorials, focusing on Human Health and Disease, immunity, acquired immunity's importance in fighting infections, and the significance of balance for optimal health, emphasizing the body's defense mechanisms against diseases. The lecture covers specific examples of defense mechanisms, the immune system's response to infections, the role of vaccines, antibodies in fighting infections, and the impact of immune memory on preventing diseases, with a focus on blood groups, antigens, antibodies, and the R factor's significance in determining blood compatibility and addressing potential health risks for babies.
Insights
- The immune system is divided into innate and acquired immunity, with acquired immunity playing a crucial role in fighting infections through specific mechanisms like mucus trapping pathogens and liver detoxifying enzymes.
- The R factor in blood groups is essential for determining blood compatibility, especially in cases like erythroblastosis, where incompatible blood types between a mother and baby can lead to health risks due to the baby's antibodies attacking its own blood cells.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is the importance of immunity in the body?
Immunity protects against pathogens, maintaining overall health.
How do vaccines stimulate the immune system?
Vaccines contain inactive viruses to trigger immune response.
What are the functions of antibodies in the body?
Antibodies neutralize toxins, catch antigens, and agglutinate.
How does the body develop active immunity?
Active immunity forms antibodies naturally after virus exposure.
Why is the R factor significant in blood compatibility?
The R factor determines positive or negative blood types.
Related videos

Sankalp NEET Vedantu
HUMAN HEALTH AND DISEASE CLASS 12 ONE SHOT | NCERT LINE BY LINE AND PYQS | NEET 2024 | BY MD SIR
Stanford
The Necessity of the Immune System

Competition Wallah
HUMAN HEALTH AND DISEASES in 1 Shot: All Concepts, Tricks & PYQs | NEET Crash Course | Ummeed

Vedantu JEE English
Human Health And Disease Class 12 One-Shot | CBSE Class 12 Term 2 | Sindur Ma'am | Vedantu Enlite

Unacademy NEET
Human Health and Disease in One Shot | 1 Day 1 Chapter | NEET 2024 | Seep Pahuja
Summary
00:00
"12th Grade Biology: Immunity and Health"
- Abhishek welcomes viewers and updates on the progress of the 12th standard Biology tutorials, having completed nine chapters already.
- The upcoming lesson focuses on Human Health and Disease, defining health and discussing diseases, symptoms, causes, and treatments.
- Viewers are encouraged to download the tutorials' application for future courses, doubt sessions, and quizzes.
- Abhishek emphasizes the importance of physical, mental, and social fitness for overall health, as defined by the World Health Organization.
- The discussion shifts to immunity, defined as the host's ability to protect itself from pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and protozoa.
- Immunity is categorized into two types: innate immunity, present since birth, and acquired immunity, developed over a lifetime.
- Four types of immunity are detailed: physical barriers like skin, mucosal barriers like mucus-producing cells, physiological barriers like liver enzymes, and cellular barriers like immune cells.
- The lecture delves into the importance of acquired immunity in fighting infections and maintaining overall health.
- Specific examples are provided, such as the role of mucus in trapping pathogens and the liver's detoxifying enzymes.
- The discussion highlights the body's intricate defense mechanisms against diseases and the significance of maintaining a balanced immune system for optimal health.
12:39
Infections, Cells, and Antigens: A Summary
- Lijo Science is discussed, focusing on the detection of infections through eyes.
- The presence of infections in the stomach is highlighted, affecting food.
- Cellular barriers are explained, including the classification of granulocytes.
- Neutrophils are detailed as the primary cells for combating bacteria.
- Monocytes and macrophages are discussed for their phagocytic function.
- The process of neutrophils and monocytes attacking bacteria is explained.
- The reproduction of viruses is detailed, emphasizing the increase in severity.
- Antigens on cells are described, leading to attacks by viruses.
- The role of Neutrophils in recognizing antigens is highlighted.
- The concept of MHC Van and its role in antigen presentation is explained.
25:43
"Body's Defense: Understanding Infection and Immunity"
- Understanding the foreign treatment of the body, the reason behind the attack on sales is clarified.
- The speed of eating has slowed down, while the speed of reproduction has increased significantly.
- Infection costs in disease as panels move from one place to another in the body.
- Plasmodium, a protozoa, enters the body and multiplies within cells.
- Plasmodium takes glucose from cells, multiplies, and infects other cells, gradually destroying them.
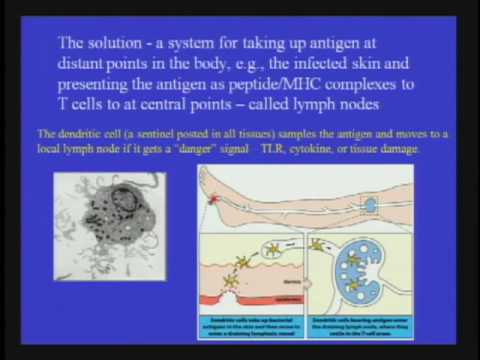
- The immune system's response involves dendrites engaging with lymphocytes to fight the infection.
- Lymphocytes present in the body fight different types of viruses, creating specific immunity.
- T cells start making copies to fight the virus, leading to the formation of different cell types.
- Helper T cells interact with B lymphocytes, leading to the creation of plasma cells crucial for future immunity.
- Plasma cells have a significant role in the immune response, with a long-lasting impact on the body's defense against infections.
39:24
"Immune Memory: Fighting Infections with Vaccines"
- Memory B cells and memory T cells are always ready to fight, but only if necessary.
- Memory T cells and memory B cells work together to fight off infections.
- Memory T cells store information about past infections to respond quickly in the future.
- Vaccines contain inactive or dead forms of viruses to stimulate the immune system without causing infection.
- Antibodies released by plasma cells help fight off infections by capturing and neutralizing viruses.
- Neutrophils and macrophages work together to destroy captured viruses.
- Helper T cells play a crucial role in activating and motivating other immune cells.
- Viruses can directly attack lymphocytes, weakening the immune response.
- The immune system's ability to respond quickly to infections is crucial in preventing diseases like polio.
- India's success in eradicating polio showcases the effectiveness of vaccines and immune memory.
50:43
"Antibodies combat toxins, viruses, and bacteria"
- Bacteria multiply and release toxins, causing sickness.
- Antibodies function to neutralize toxins released by viruses and bacteria.
- Neutrophils and macrophages are called to combat viruses.
- Antibodies have three functions: neutralizing toxins, catching antigens, and agglutination.
- Acquired immunity is divided into active and passive immunity.
- Active immunity involves the body naturally developing antibodies after exposure to a virus.
- Passive immunity is acquired through vaccines or artificial means.
- Antibodies have a specific structure with variable and constant regions.
- The variable region of antibodies binds to antigens, while the constant region remains the same.
- Agglutination is a function of antibodies that involves binding to antigens.
01:03:17
Understanding Blood Groups and Disease Prevention
- Parasite is mentioned as a term to describe a certain entity.
- The text discusses the functions of bacteria and their importance.
- Macrophages and Neutrophils are highlighted as key components.
- Neutralization of toxins by bacteria is explained.
- Blood group determination is detailed, focusing on antigens and antibodies.
- The presence of antigens A and B in blood groups is explained.
- The significance of antigens and antibodies in blood groups is emphasized.
- The concept of blood group O, lacking antigens, is discussed.
- The R factor, related to antigens, is introduced.
- The importance of the R factor in disease prevention is highlighted, specifically in Rh factor-related issues like erythroblastosis.
01:16:47
Blood Type Compatibility and Health Risks
- The presence of certain factors in the baby's blood, particularly related to the mother's blood type, can impact the baby's health. If the baby's blood type is incompatible with the mother's, it can lead to conditions like erythroblastosis and result in the baby's antibodies attacking its own blood cells.
- Understanding the R factor is crucial in determining blood compatibility. If the R factor is present, it indicates a positive blood type, while its absence signifies a negative blood type. This factor plays a significant role in addressing potential health risks for the baby based on blood compatibility.




