Work, Energy, and Power: Crash Course Physics #9
CrashCourse・10 minutes read
Work in physics is the application of force over a distance, measured in Joules and calculated as force times distance times the cosine of the angle. Energy and work are closely related, with work representing a change in energy when an external force is applied, while power is defined as work over time measured in Watts.
Insights
- Work in physics involves applying a force over a distance, with the amount of work done calculated by multiplying the force by the distance. This relationship is fundamental in understanding how energy is transferred and transformed in physical systems.
- Energy and work are intricately linked concepts, where work represents a change in energy due to external forces. Different forms of energy, such as kinetic and potential energy, play crucial roles in determining how work is done and how systems behave in response to forces applied.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is work in physics?
Work is applying force over a distance.
How is work measured?
Work is commonly measured in Joules.
What is the relationship between energy and work?
Work is a change in energy with an external force.
What is kinetic energy?
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion.
What is potential energy?
Potential energy is stored energy that can do work.
Related videos

Physics Wallah Foundation
WORK AND ENERGY in 1 Shot || FULL Chapter Coverage (Concepts+PYQs) || Class 9th Physics

Vedantu JEE English
Work Power Energy JEE L1 [What Is Work and Power? Finding Work By Force] | JEE Physics | JEE 2023

Step by Step - Fisica e Mate
FISICA Teoria #10 - LAVORO e POTENZA, ENERGIA CINETICA, TEORMA dell'ENERGIA CINETICA
EarthPen
POWER | Easy Physics Animation

Science and Fun Education
Work Energy and Power One Shot Physics | Class 11 Physics NCERT Full Explanation with Ashu Sir
Summary
00:00
Understanding Work, Energy, and Power in Physics
- Work in physics is defined as applying a force over a distance to a system, with the amount of work equal to the force multiplied by the distance.
- Work is commonly measured in Joules and can be calculated using the equation force times distance times the cosine of the angle between the force and the direction of movement.
- If the force applied is not constant, the work done can be found by integrating the force over the distance moved.
- Energy and work are closely related, with work being a change in energy when an external force is applied to a system.
- Kinetic energy is the energy of motion and is calculated as half the mass of an object times its velocity squared.
- Potential energy, like gravitational and spring potential energy, is energy that could be used to do work.
- Conservative systems do not lose energy through work, while non-conservative systems can lose energy, such as through friction generating heat.
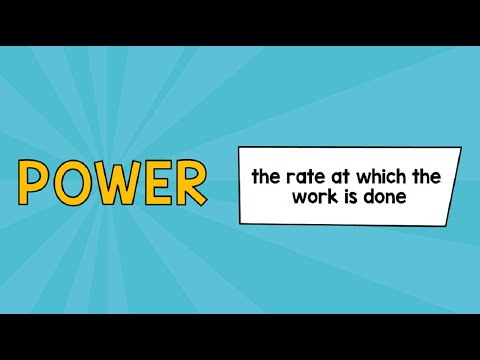
- Average power is defined as work over time and is measured in Watts, with one Watt being equal to one Joule per second.
- Power can also be described as the net force applied to an object with a particular average velocity, with two equations for average power reflecting the same relationship using different qualities.




