Understanding Conduction and the Heat Equation
The Efficient Engineer・12 minutes read
Thermal conduction involves the redistribution of thermal energy in objects through vibrations of atoms and free electrons traveling through lattice structures, with heat transfer rate measured as q in Joules per second or Watts. The heat equation, based on Fourier's law, describes how heat flows within materials, influenced by factors like thermal conductivity and material density.
Insights
- Thermal conduction, a method of heat transfer, involves the movement of atoms and molecules within objects due to temperature differences, with heat flowing from high-energy to low-energy areas.
- Fourier's law, a fundamental concept in heat transfer, calculates the rate of heat transfer based on factors like temperature gradient, surface area, and thermal conductivity, essential for understanding how energy moves within materials.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is thermal conduction?
Thermal conduction is the process of thermal energy redistribution within objects due to heating, alongside convection and radiation.
How does heat transfer occur in materials?
Heat transfer in materials happens through vibrations of atoms traveling through lattice structures, transferring energy from high-energy to low-energy areas.
What is the heat transfer rate denoted as?
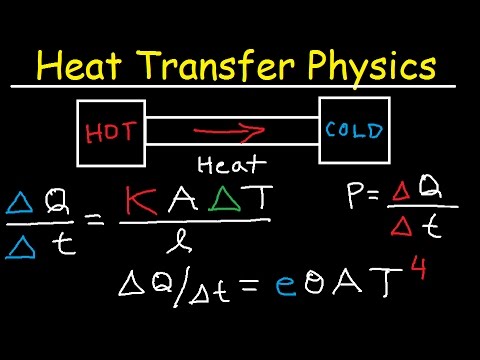
The heat transfer rate, denoted as q, measures the energy flowing through a defined area of an object per second, with units of Joules per second or Watts.
What does Fourier's law calculate?
Fourier's law calculates the heat transfer rate, proportional to the temperature gradient, surface area, and thermal conductivity of a material.
What is thermal diffusivity?
Thermal diffusivity, denoted as Alpha, describes a material's ability to conduct heat relative to its ability to store it, calculated by dividing thermal conductivity by volumetric heat capacity.
Related videos

CPPMechEngTutorials
Heat Transfer (02): Introductory examples, energy balance on a control volume and control surface
The Organic Chemistry Tutor
Thermal Conductivity, Stefan Boltzmann Law, Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convecton, Radiation, Physics
CPPMechEngTutorials
Heat Transfer (01): Introduction to heat transfer, conduction, convection, and radiation

Eric Menonville PHySiK-CHIMIE
Physique-chimie - Terminale - 04 Loi de Newton et évolution de la température

Khan Academy
Thermal energy, temperature, and heat | Khan Academy
Summary
00:00
Understanding Thermal Conduction and Heat Transfer Methods
- Thermal energy redistribution within objects due to heating is termed thermal conduction, one of three heat transfer methods alongside convection and radiation.
- Thermal energy is essentially the random motion of atoms and molecules within an object, with increased temperature leading to more significant motion.
- Heat conduction in materials occurs through vibrations of atoms traveling through lattice structures, transferring energy from high-energy to low-energy areas.
- Metallic materials conduct heat through free electrons moving through the lattice, redistributing energy through collisions with other particles.
- Heat transfer rate, denoted as q, measures the energy flowing through a defined area of an object per second, with units of Joules per second or Watts.
- Fourier's law calculates heat transfer rate, proportional to the temperature gradient, surface area, and thermal conductivity of a material.
- The heat equation describes how heat flows within an object, with the temperature field determining the application of Fourier's law.
- The heat equation is a partial differential equation representing an energy balance within a material, influenced by thermal conductivity, material density, and specific heat capacity.
- Thermal diffusivity, denoted as Alpha, describes a material's ability to conduct heat relative to its ability to store it, calculated by dividing thermal conductivity by volumetric heat capacity.
- The heat equation can be simplified for specific scenarios, such as steady-state cases or those without internal heat generation, with solutions often requiring numerical methods for complex problems.
17:05
"CuriosityStream: High-Quality Documentaries for Less"
- CuriosityStream offers access to high-quality documentaries for less than $15 for an entire year, including the series "What Went Wrong" which delves into catastrophic events like the Grenfell Tower fire, Malaysia Airlines flight MH370 disappearance, and the Concorde air crash, analyzing engineering failures and preventive measures. To access the full CuriosityStream catalog and exclusive Nebula content, visit curiositystream.com/efficientengineer for a yearly subscription.




