The Brain: History Channel
Brittany Musick・57 minutes read
The human brain, a complex organ responsible for vital functions and emotions, undergoes intricate processes that affect behaviors and performance, ranging from Navy SEAL training focusing on fear management to the study of psychopathy and memory retention. Research continues to explore enhancing cognitive abilities and potential connections to extrasensory perception, indicating a future where advancements may significantly improve our understanding of brain function and capabilities.
Insights
- The human brain, despite its small size, is a powerhouse, consuming 20% of the body's energy and evolving over time to accommodate complex functions, with the brain stem managing essential involuntary processes and the limbic system handling emotional responses, particularly through the amygdala's role in fear.
- Navy SEAL training emphasizes the importance of mental resilience, as recruits face intense scenarios designed to expose them to chaos and fear, demonstrating that techniques like goal setting and mental rehearsal can significantly improve their ability to manage panic, thereby increasing their chances of success from 25% to 33%.
- Research into psychopathy reveals that individuals with this condition often have a significantly smaller amygdala, impairing their ability to empathize and learn from mistakes, while studies on memory highlight the distinct roles of different brain regions, such as the hippocampus, in storing and recalling information, emphasizing that memory is crucial to identity but not the sole determinant of self.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is the human brain's function?
The human brain is a complex organ that serves as the control center for the body, responsible for processing sensory information, regulating bodily functions, and enabling cognitive abilities such as thinking, memory, and emotion. Weighing about 3 pounds, it consumes a significant portion of the body's energy, reflecting its vital role in maintaining life and facilitating interaction with the environment. The brain's structure has evolved over time, akin to an old house with added rooms, allowing for advanced functions and adaptations. It governs everything from basic survival instincts to complex decision-making, showcasing its importance in both physical and mental health.
How does fear affect the brain?
Fear triggers a complex response in the brain, primarily involving the amygdala, which is responsible for processing emotional reactions, particularly those related to danger. When faced with a threat, the amygdala activates panic responses, releasing stress hormones like adrenaline and cortisol that heighten alertness but can also impair rational thought. This reaction is often faster than the cortex's response, which is responsible for logical reasoning. Training and techniques can help individuals manage these fear responses, allowing for better control in high-stress situations, such as those faced by Navy SEAL recruits during their rigorous training exercises.
What is the role of memory in identity?
Memory plays a crucial role in shaping an individual's identity, as it encompasses the recollection of personal experiences, significant life events, and learned information. The brain's hippocampus is essential for forming and retrieving memories, and its functioning is vital for both short-term and long-term memory processes. However, cases like that of Clive Wearing, who suffers from severe amnesia due to hippocampal damage, illustrate that while memory is integral to identity, it is not the sole determinant. Despite his memory loss, Clive's personality remains intact, highlighting the complexity of identity and the brain's ability to adapt and reorganize itself after damage.
What techniques help manage fear?
Various techniques can assist individuals in managing fear, particularly in high-pressure situations. Strategies such as goal setting, mental rehearsal, self-talk, and arousal control have been shown to enhance performance and increase resilience against fear responses. For instance, Navy SEAL recruits utilize these methods during their training to improve their ability to cope with stress and panic. By practicing these techniques, recruits can increase their pass rates and develop a greater capacity for mental adaptability, allowing them to respond effectively in chaotic environments and maintain focus despite overwhelming fear.
How does dopamine influence behavior?
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays a significant role in motivation and the pursuit of pleasure. It is released in anticipation of rewarding experiences, driving individuals to engage in behaviors that provide excitement and satisfaction. For example, extreme sports enthusiasts, such as base jumpers, experience a surge of dopamine during their jumps, which enhances their anticipation and excitement, even in the face of fear. This complex interplay between dopamine and fear signals from the amygdala creates a unique decision-making process, where the desire for thrill can sometimes outweigh the instinct to retreat from danger, illustrating the powerful influence of dopamine on behavior and risk-taking.
Related videos
Summary
00:00
Understanding the Brain's Role in Fear Management
- The human brain, weighing 3 pounds, consumes 20% of the body's energy, evolving over time like an old house with added rooms and connections.
- The brain stem, the oldest part, governs vital functions like heart rate and respiration, operating without conscious thought, shared with reptiles and mammals.
- The limbic system, developed later, processes emotions; the amygdala, small as a fingernail, is crucial for emotional reactions, particularly fear.
- Navy SEAL training focuses on controlling fear responses; only 36 out of 140 candidates typically complete the program, emphasizing mental adaptability over physical prowess.
- The amygdala triggers panic responses, while the cortex, particularly the frontal lobes, processes rational thought, taking longer to react to threats than the amygdala.
- Training exercises like the hooded box drill expose recruits to chaos, teaching them to manage fear and respond effectively in high-stress situations.
- The underwater pool competency test lasts up to 20 minutes, where recruits face simulated drowning scenarios, testing their ability to manage panic and follow emergency procedures.
- The brain releases stress hormones like adrenaline and cortisol during fear, enhancing alertness but complicating rational thought, making it harder to control panic.
- Techniques like goal setting, mental rehearsal, self-talk, and arousal control help recruits manage fear, increasing their pass rate from 25% to 33%.
- Dopamine, released in anticipation of pleasure, motivates behavior; extreme sports enthusiasts, like base jumpers, experience high risks, driven by the pursuit of adrenaline and excitement.
19:01
Dopamine Thrills and Psychopathy Insights
- Base jumpers experience a dopamine release during jumps, enhancing anticipation and excitement, despite fear signals from the amygdala causing nervousness and racing thoughts before the jump.
- Newcomer Cresta feels heightened excitement and nervousness during gear checks, indicating her jump is imminent, while her amygdala triggers panic due to the 400-foot drop.
- Physiological responses include adrenaline and cortisol release, increasing heart rate and stress, while dopamine creates a euphoric anticipation, leading to a complex decision-making process.
- The striatum, a brain region with high dopamine receptor density, mediates the battle between pleasure-seeking and fear, influencing Cresta's decision to jump or retreat.
- Successful jumps lead to immediate preparation for the next, as base jumpers seek new, challenging locations, indicating a potential addiction to thrill-seeking behavior.
- Research on psychopathy at New Mexico prisons reveals that 1 in 20 inmates may have personality disorders, prompting studies on brain differences and treatment development.
- Dr. Keel's research involves brain scans of psychopathic inmates to understand their reactions to mistakes, revealing they show less concern for errors compared to non-psychopaths.
- Psychopaths exhibit impulsive behavior and manipulative tendencies, with above-average intelligence, complicating their ability to learn from mistakes and understand moral violations.
- Studies show psychopaths have a shrunken amygdala, about 177% smaller than average, impairing their ability to empathize and understand the emotional consequences of their actions.
- Memory research indicates the brain's complex network allows for vast storage, with individuals like artist Steven Wiltshire demonstrating extraordinary visual memory, while others, like Clive Wearing, suffer severe amnesia.
37:47
Memory's Role in Identity and Performance
- The hippocampus is crucial for memory storage and retrieval; without it, new memories cannot form, indicating its role in both short-term and long-term memory processes.
- Short-term memory allows for temporary recall, such as remembering a phone number briefly, while long-term memory encompasses significant life events and personal history.
- Clive Wearing suffers from severe hippocampal damage, resulting in both anterograde and retrograde amnesia, preventing him from forming new memories and recalling past ones.
- Despite memory loss, Clive retains procedural memory, allowing him to speak and play the piano, indicating that different types of memory are stored in separate brain regions.
- Clive's emotional state improved over time, attributed to brain plasticity, which allows the brain to adapt and reorganize itself after damage, enhancing memory retention.
- After 23 years of diary writing, Clive no longer felt the need to document his daily experiences, suggesting a shift in his memory processing and emotional response.
- Memory is integral to identity, but Clive's personality remains intact despite his memory loss, demonstrating that memory is not the sole determinant of self.
- In sports, brain function is increasingly recognized as vital for performance, with about 50% of athletic success linked to mental processes rather than just physical ability.
- Athletes utilize arousal modulation to manage emotional responses during competition, balancing excitement and calmness to optimize performance, particularly in high-pressure situations.
- Achieving a "zone" state in sports involves synchronized brain and body functions, allowing athletes to perform effortlessly, characterized by low anxiety and heightened focus on the task at hand.
56:02
Exploring Human Senses and Psychic Abilities
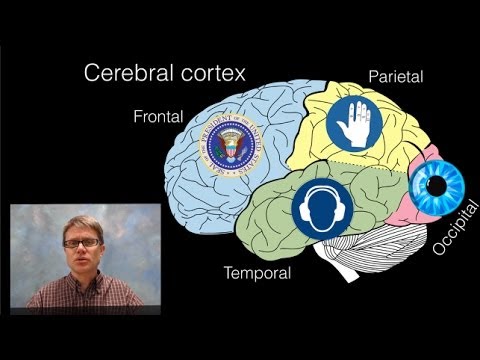
- Our five senses—touch, sight, smell, taste, and hearing—connect our brains to the outside world, interpreting sensory information from our skin, eyes, nose, tongue, and ears.
- Dr. Dean Raiden studies psychic phenomena at The Institute of Noetic Sciences, suggesting that humans may possess some form of extrasensory perception (ESP) despite skepticism from most scientists.
- Common examples of ESP include gut feelings while driving and sensing being stared at, with many people reporting these experiences in everyday life.
- Dr. Raiden's experiments with over 300 volunteers in shielded rooms show that subjects often respond accurately to emotional images before seeing them, indicating a potential psychic ability.
- John Edward, a TV medium, demonstrates high accuracy in readings, with his success suggesting he may possess exceptional psychic abilities akin to a top athlete in their sport.
- Scientific testing of mediums like John Edwards involves EEG and EKG monitoring to analyze brain and heart activity while they connect with deceased individuals' information.
- In controlled experiments, John Edwards achieved an accuracy rate of 80-90%, with his heart rate syncing with the sitter's, indicating a connection beyond mere observation.
- The concept of ESP may relate to quantum entanglement, a theory suggesting interconnectedness at a fundamental level, though its application to the brain remains unproven.
- DARPA is funding research to enhance human cognitive abilities, including a program at Columbia University that improves visual processing speed using EEG technology.
- Breakthroughs in brain-computer interfaces, such as monkeys controlling robots with thoughts, suggest future applications in medicine, enhancing mobility for amputees and quadriplegics.
01:13:34
Synthetic Brain Enhancements for Memory and Sleep
- Research is underway to create a synthetic hippocampus for humans, potentially allowing instant memory downloads, such as language dictionaries or city maps, enhancing learning and navigation.
- New drugs, called okines, may enable sleep-deprived individuals, like shift workers and students, to function effectively without sleep, while portable brain scanners could provide real-time brain activity insights during activities like sports.