Reasons for the seasons - Rebecca Kaplan
TED-Ed・5 minutes read
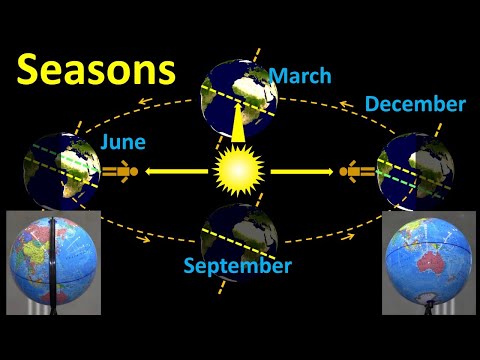
Seasons are influenced by Earth's orbit, axial tilt, and the amount of sunlight received, impacting temperature variations throughout the year. The angle of the sun's rays and the number of daylight hours also play a crucial role in determining the amount of solar energy received, affecting temperature changes in different regions.
Insights
- Seasons are not experienced uniformly across the globe, with only two regions having distinct four seasons that are reversed from each other. This highlights the complexity of Earth's axial tilt and elliptical orbit in creating seasonal variations.
- The angle of sunlight and the number of daylight hours are crucial factors in determining temperature variations in different regions. Despite receiving 24 hours of daylight in summer, the North Pole remains cold due to the spread-out sunlight and the angle of the sun's rays affecting the energy received per square kilometer.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
How many regions on Earth experience four distinct seasons?
Two regions
What factors create seasons on Earth?
Earth's elliptical shape and axial tilt
What role do daylight hours play in regional temperatures?
Crucial role in warming or cooling regions
Why does the North Pole remain cold despite 24 hours of daylight in summer?
Spread-out sunlight due to sun's angle
How does Earth's orbit affect seasonal changes?
Varying temperatures throughout the year
Related videos

California Academy of Sciences
Why Do We Have Different Seasons? | California Academy of Sciences

Next Generation Science
Movement and Position of the Earth – Seasons

Peekaboo Kidz
EARTH'S ROTATION & REVOLUTION | Why Do We Have Seasons? | The Dr Binocs Show | Peekaboo Kidz
LiacosEM
Seasons: What causes summer and winter?

Earth Rocks!
Seasons
Summary
00:00
Astronomical mechanisms behind Earth's seasonal changes
- Seasons were perceived differently in childhood, with specific months associated with certain weather patterns, but in reality, only two regions on Earth experience four distinct seasons, which are reversed in each.
- Earth's orbit is nearly circular, but its elliptical shape and axial tilt of 23.5 degrees are key factors in creating seasons by affecting the amount of sunlight received, leading to varying temperatures throughout the year.
- The number of daylight hours plays a crucial role in warming or cooling regions, with locations closer to the poles experiencing longer daylight hours in summer, but the angle of the sun's rays also impacts the amount of solar energy received, influencing temperature variations.
- Despite the North Pole receiving 24 hours of daylight in summer, the spread-out sunlight due to the sun's angle results in less energy per square kilometer, explaining why it remains cold despite extended daylight hours, showcasing the intricate astronomical mechanisms behind seasonal changes.




