Lecture: 01 | Database Management & Warehousing | GATE Data Science & AI #gate2024 #datascience
Piyush Wairale IITM - Data Science & AI・12 minutes read
Data is organized into structured and unstructured formats, with databases serving as collections of related data managed by Database Management Systems (DBMS) that use Structured Query Language (SQL) for interactions. Understanding these concepts is vital for effectively analyzing and designing databases, which will be further explored in the next video focusing on database design and the Entity-Relationship model.
Insights
- Data is composed of various forms of information, such as text, numbers, images, and videos, but it only gains significance when placed in context. This distinction emphasizes the importance of organizing data into databases, which structure this information in a way that makes it easier to manage and analyze, with databases typically arranged in tables with defined columns and rows.
- Database Management Systems (DBMS) serve as the software backbone for storing and managing these organized data collections, enabling users to perform essential operations like inserting and querying data. Understanding the types of data—structured, which adheres to a fixed schema, and unstructured, which does not—along with the tools like SQL for relational databases and NoSQL for unstructured data, is crucial for effective data management and analysis.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is data in simple terms?
Data refers to raw bits of information that can include various forms such as text, numbers, images, and videos. However, on its own, data lacks meaning and context. To transform data into something useful, it must be analyzed and interpreted within a specific context. This process allows individuals and organizations to derive insights, make decisions, and understand patterns from the raw information they collect. Essentially, data serves as the foundational building block for knowledge and information systems.
How does a database work?
A database functions as an organized collection of related data, designed to facilitate easy access and management. Typically structured in a tabular format, databases consist of defined columns and rows, where each column represents a specific attribute of the data, and each row corresponds to a unique entry. This organization allows users to efficiently store, retrieve, and manipulate data. By using a database, individuals and organizations can maintain large volumes of information in a structured manner, making it easier to perform operations such as searching, updating, and reporting.
What is a Database Management System?
A Database Management System (DBMS) is specialized software that enables users to store, retrieve, and manage databases effectively. It provides a systematic way to handle data, allowing users to perform various operations such as inserting new data, updating existing records, and querying the database for specific information. A DBMS acts as an intermediary between users and the database, ensuring data integrity, security, and efficient access. By utilizing a DBMS, organizations can streamline their data management processes and enhance their ability to analyze and utilize data for decision-making.
What is SQL used for?
Structured Query Language (SQL) is a programming language specifically designed for managing and interacting with relational databases. It allows users to perform a variety of operations, including querying data to retrieve specific information, inserting new records, updating existing entries, and deleting data as needed. SQL provides a standardized way to communicate with databases, making it easier for users to manipulate and analyze structured data. By using SQL, individuals can efficiently manage large datasets and extract valuable insights, which are crucial for informed decision-making in various fields.
What are structured and unstructured data?
Structured data refers to information that is organized in a predefined format, typically following a fixed schema, such as tables in relational databases. This type of data is easily searchable and can be efficiently managed using traditional database systems. In contrast, unstructured data lacks a specific format or structure, making it more challenging to analyze and manage. Examples of unstructured data include text files, images, and videos. Understanding the difference between structured and unstructured data is essential for selecting the appropriate database technology and management strategies to handle various types of information effectively.
Related videos

Neso Academy
Introduction to Data Models

DatabaseTown
Relational Database Vs Object Oriented Database | Difference between Relational Database and OODB

MilEstOne CrEaTor
What is RDBMS ( Relational Database Management System )

Piyush Wairale IITM - Data Science & AI
Lecture: 02 | Database Management & Warehousing | GATE Data Science & AI #gate2024 #datascience
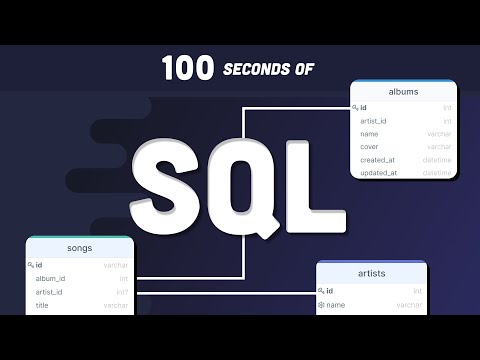
Fireship
SQL Explained in 100 Seconds
Summary
00:00
Understanding Data and Database Fundamentals
- Data consists of raw bits of information, including text, numbers, images, and videos, which require context to become meaningful and useful for analysis.
- A database is an organized collection of related data, allowing for easy access and management, typically structured in a tabular format with defined columns and rows.
- Data can be categorized into structured data, which follows a fixed schema (e.g., relational databases), and unstructured data, which lacks a fixed structure (e.g., JSON files, images).
- Database Management System (DBMS) is software used to store, retrieve, and manage databases, allowing users to perform operations like inserting, updating, and querying data.
- Structured Query Language (SQL) is used to interact with relational databases, while NoSQL databases, such as MongoDB and Cassandra, are used for unstructured data.
- In a relational database, attributes (columns) must have unique constraints, ensuring that each entry (row) is distinct, such as unique roll numbers for students.
- Data types in SQL include integers (INT) for numerical values and character types (VARCHAR, CHAR) for text, which dictate the kind of data that can be stored in each column.
- The next video will cover the database design process and the Entity-Relationship (ER) model, essential for understanding database fundamentals and design.




