HUMAN BRAIN | Everything You Need To Know | The Dr Binocs Show | Peekaboo Kidz
Peekaboo Kidz・23 minutes read
The brain is a vital organ controlling bodily functions, learning, and emotions. Various conditions like dyslexia, Alzheimer's, and strokes can impact brain health, requiring attention and proper care.
Insights
- The brain consists of different regions such as the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem, each responsible for specific functions like thinking, muscle control, and automatic bodily processes.
- Neurological conditions like dyslexia and Alzheimer's disease showcase the complexity of brain disorders, affecting cognitive abilities, memory, and daily tasks, with unique causes and impacts on individuals' lives.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is the function of the cerebrum?
Controls thinking, muscle control, and learning.
How does the brain generate electricity?
Generates 12 to 25 watts of electricity.
What is the role of the amygdala in the brain?
Responsible for emotions, survival instincts, and memory storage.
What causes migraines?
Triggered by certain foods, more severe than tension headaches.
What is dyslexia?
Neurological condition affecting reading, writing, and speaking abilities.
Related videos

Peekaboo Kidz
How Your Brain Works? - The Dr. Binocs Show | Best Learning Videos For Kids | Peekaboo Kidz

RajNEET Medical Education
Parts of brain in Hindi | Fore Brain | Mid Brain | Hind Brain | Cerebellum | Functions | Location
Bozeman Science
The Brain

Brittany Musick
The Brain: History Channel

TEDx Talks
TEDxOrangeCoast - Daniel Amen - Change Your Brain, Change Your Life
Summary
00:00
"Brain: Functions, Structure, and Common Issues"
- The brain is an essential organ that controls all bodily functions and allows for learning, thinking, feeling, and more.
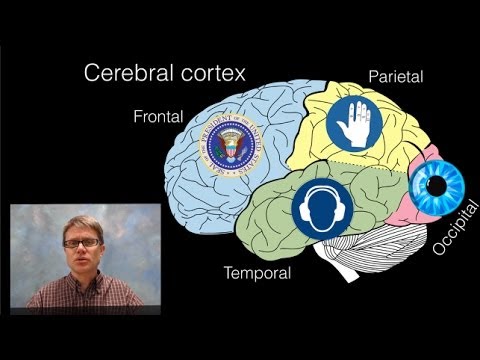
- The cerebrum, the largest part of the brain, controls thinking, muscle control, and learning.
- The cerebellum helps maintain balance and regulates motor movements.
- The brain stem controls automatic functions like breathing and heart rate.
- The amygdala is responsible for emotions, survival instincts, and memory storage.
- The brain generates 12 to 25 watts of electricity and produces chemicals after exercise that enhance learning.
- Headaches are not felt in the brain but are caused by pressure on nerves, blood vessels, and muscles around the head and neck.
- Tension headaches result from muscle contractions, while migraines are more severe and can be triggered by certain foods.
- Brain freeze occurs when cold substances rapidly affect blood flow in the brain's arteries, causing a sudden pain sensation.
- Fainting, or syncope, is a temporary loss of consciousness due to a drop in blood pressure, often triggered by a vasovagal response.
24:03
Neurological Conditions: Dyslexia, Alzheimer's, Stroke
- Albert Einstein, Walt Disney, and Steven Spielberg are famous and successful individuals who are dyslexic.
- Dyslexia is a neurological condition affecting reading, spelling, writing, and speaking abilities.
- Dyslexia does not indicate lack of intelligence but rather challenges in processing tasks at a normal speed.
- Dyslexic individuals may struggle with remembering names, directions, word retrieval, and writing.
- Dyslexia involves difficulty recognizing phonemes and relies more on the right side of the brain.
- Despite reading challenges, dyslexic individuals excel in creative fields like painting, storytelling, and invention.
- Dyslexia comes from Greek words meaning difficulty with language, and dyslexic brains are often more creative.
- Alzheimer's disease is a severe brain disorder affecting memory, thinking skills, and daily tasks.
- Alzheimer's is caused by misfolded proteins, neurofibrillary tangles, and the breakdown of brain structure.
- A component called Tor in neurofibrillary tangles leads to the disintegration of brain cells.
- There is no cure for Alzheimer's, but exercise, healthy eating, and mental stimulation may help delay its onset.
- Alzheimer's patients may exhibit memory loss, confusion, hallucinations, and repetitive behaviors.
- Alzheimer's affects over 6 million Americans, with projections of nearly 13 million by 2050.
- A stroke occurs when blood flow to the brain is interrupted, leading to brain cell death.
- Strokes can be hemorrhagic (blood vessel breakage) or ischemic (clot blocking blood supply).
- Clots causing strokes can form due to changes in heartbeats, leading to blockages in brain arteries.
- Symptoms of stroke include slowed speech, blurred vision, and weakness on one side of the body.
- Immediate medical attention is crucial to prevent brain damage, with treatments like tissue plasminogen activator or surgery.
- Staying healthy through diet, exercise, and stress reduction can reduce the risk of stroke.
- Someone in the world has a stroke every two seconds, with 87% of strokes being ischemic.




