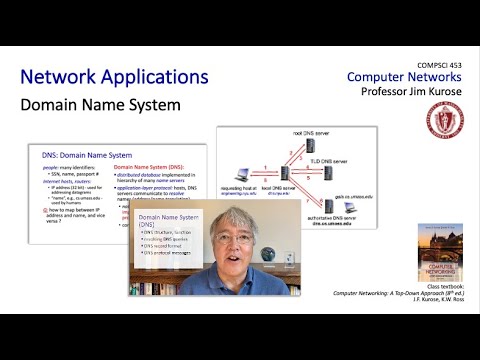
How a DNS Server (Domain Name System) works.
PowerCert Animated Videos・4 minutes read
DNS was developed to convert domain names to IP addresses for easier communication between computers, with resolver server, root servers, TLD servers, and authoritative name servers working together to locate and provide the IP address for the requested domain.
Insights
- DNS (Domain Name System) serves as a crucial intermediary between human-readable domain names and computer-friendly IP addresses, ensuring seamless communication between users and their desired online destinations.
- The hierarchical structure of resolver servers, root servers, TLD servers, and authoritative name servers collaborates systematically to locate and furnish the IP address associated with a specific domain, facilitating the smooth functioning of internet connectivity and website accessibility.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
How do computers convert domain names to IP addresses?
Computers convert domain names to IP addresses using the Domain Name System (DNS). DNS searches for the matching IP address in its database, starting from your ISP's resolver server, then moving to root servers, TLD servers, and finally authoritative name servers to find the IP address for the domain. This hierarchical process allows for easier communication between computers using numbers and humans using names.
What is the purpose of DNS in computer communication?
The purpose of DNS in computer communication is to bridge the gap between how computers communicate using numbers like IP addresses and how humans use names. DNS was developed to convert domain names to IP addresses for easier communication. When you type a web address in your browser, DNS searches for the matching IP address in its database, enabling seamless communication between computers and websites.
How does DNS hierarchy work in locating IP addresses?
DNS hierarchy works in locating IP addresses by utilizing resolver servers, root servers, TLD servers, and authoritative name servers in a hierarchical manner. These servers work together to search for and provide the IP address for the requested domain. The process starts from the resolver server at your ISP and progresses through the hierarchy until the IP address for the domain is found, allowing your computer to communicate with the desired website.
What are the key components involved in DNS resolution?
The key components involved in DNS resolution include resolver servers, root servers, TLD servers, and authoritative name servers. These components work together in a hierarchical manner to locate and provide the IP address for the requested domain. The resolver server at your ISP initiates the search, which then progresses through the hierarchy until the IP address for the domain is found, facilitating seamless communication between computers and websites.
Why was DNS developed for computer communication?
DNS was developed for computer communication to address the disparity between how computers communicate using numbers like IP addresses and how humans use names. By converting domain names to IP addresses, DNS enables easier communication between computers and websites. When you enter a web address in your browser, DNS searches for the corresponding IP address, allowing for efficient and accurate communication in the digital realm.
Related videos
Summary
00:00
DNS: Bridging Names to IP Addresses
- Computers communicate using numbers like IP addresses, while humans use names. To bridge this gap, DNS (Domain Name System) was developed to convert domain names to IP addresses for easier communication.
- When you type a web address in your browser, DNS searches for the matching IP address in its database, starting from your ISP's resolver server, then moving to root servers, TLD servers, and finally authoritative name servers to find the IP address for the domain.
- The resolver server, root servers, TLD servers, and authoritative name servers work together in a hierarchical manner to locate and provide the IP address for the requested domain, allowing your computer to communicate with the desired website.