Glycolysis (and Exploding Sugar Demo!)
BioMan Biology・4 minutes read
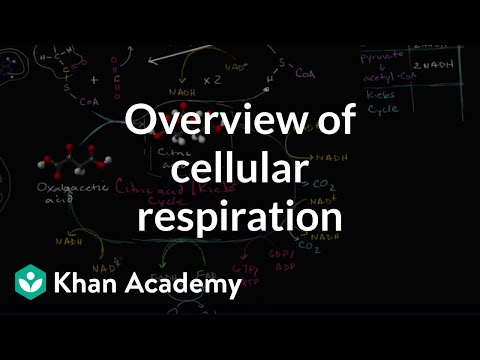
Cellular respiration is a crucial process where cells convert glucose and oxygen into ATP, generating carbon dioxide and water as byproducts, with glycolysis being the initial step that occurs in the cytoplasm and yields a net gain of ATP and other molecules. Viewers are invited to explore further through an interactive resource at biomanbio.com, which also offers additional educational materials.
Insights
- Cellular respiration is essential for life, as it allows cells to convert glucose and oxygen into ATP, the energy source necessary for all living organisms, while also producing carbon dioxide and water as byproducts. This process highlights the importance of both energy production and waste management in biological systems.
- Glycolysis, the initial stage of aerobic respiration, comprises a detailed 10-step process that occurs in the cytoplasm, beginning with the investment of ATP to activate glucose and ultimately yielding a net gain of 2 ATP, 2 pyruvates, and 2 NADH, demonstrating the complexity and efficiency of energy extraction from nutrients.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a crucial biological process that allows cells to convert glucose and oxygen into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of living organisms. This process is essential for sustaining life, as ATP provides the energy required for various cellular functions. During cellular respiration, glucose is broken down, and in the presence of oxygen, it produces carbon dioxide and water as byproducts. The overall reaction can be summarized by the equation: glucose + oxygen → ATP + carbon dioxide + water. This process not only fuels cellular activities but also plays a significant role in maintaining the balance of gases in the atmosphere.
How does glycolysis work?
Glycolysis is the initial stage of aerobic respiration and takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. It consists of a series of ten enzymatic reactions that can be divided into four distinct phases. The first phase is the energy investment phase, where two ATP molecules are consumed to activate glucose. Next is the lysis phase, where the six-carbon glucose molecule is split into two three-carbon pyruvate molecules. The third phase, known as the oxidation phase, involves the removal of electrons and hydrogen from glucose, resulting in the formation of NADH. Finally, in the ATP formation phase, a net gain of two ATP molecules, two pyruvate molecules, and two NADH molecules is achieved. This process is vital for energy production and sets the stage for further energy extraction in subsequent stages of cellular respiration.
What are the byproducts of cellular respiration?
The byproducts of cellular respiration are carbon dioxide and water, which are produced alongside ATP during the breakdown of glucose. In the process of aerobic respiration, glucose reacts with oxygen to yield ATP, while carbon dioxide is released as a waste product. This release of carbon dioxide occurs during both glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, which follows glycolysis. Water is also formed during the electron transport chain, the final stage of cellular respiration, where electrons are transferred through a series of proteins. The production of these byproducts is essential for maintaining the balance of gases in the environment, as carbon dioxide is utilized by plants during photosynthesis, while water is crucial for various biological processes.
Why is ATP important for cells?
ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is often referred to as the energy currency of the cell because it provides the necessary energy for a wide range of cellular processes. It is essential for functions such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse transmission, and biochemical reactions that require energy input. ATP is produced during cellular respiration, particularly through glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. The energy stored in ATP can be easily released when the molecule is hydrolyzed, allowing cells to perform work efficiently. Without ATP, cells would be unable to carry out vital functions, leading to a breakdown of biological processes and ultimately affecting the organism's survival.
Where can I learn more about glycolysis?
To learn more about glycolysis, you can explore interactive educational resources available online, such as those found on biomanbio.com. This platform offers engaging activities that allow users to visualize and understand the glycolysis process in a hands-on manner. Additionally, the website provides various free educational materials, including games and quizzes, which can enhance your learning experience. These resources are designed to make complex biological concepts more accessible and enjoyable. Engaging with such interactive content can deepen your understanding of glycolysis and its role in cellular respiration, making it a valuable tool for students and anyone interested in biology.
Related videos
Summary
00:00
Understanding Cellular Respiration and Glycolysis
- Cellular respiration is a vital process where cells break down glucose from food and oxygen from the air to produce ATP, the energy molecule essential for all living organisms. This process also generates carbon dioxide and water as waste products, following the equation for aerobic respiration: glucose + oxygen → ATP + carbon dioxide + water.
- Glycolysis, the first step of aerobic respiration, occurs in the cytoplasm and involves a 10-step process divided into four phases: 1) Energy investment phase, where 2 ATP molecules are used to energize glucose; 2) Lysis phase, where glucose is split into two 3-carbon pyruvate molecules; 3) Oxidation phase, where electrons and hydrogens are stripped from glucose, forming NADH; and 4) ATP formation phase, resulting in a net gain of 2 ATP, 2 pyruvates, and 2 NADH.
- For further exploration of glycolysis, users can engage with the respiration interactive activity available at biomanbio.com, with a link provided in the video description. The video encourages viewers to like, subscribe, and access additional free educational resources, including games and quizzes, on the Bioman Biology platform.