Electromagnetic Waves | 9-1 GCSE Science Physics | OCR, AQA, Edexcel
SnapRevise・2 minutes read
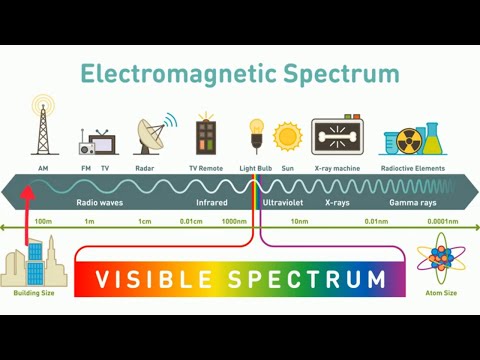
Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum without a medium, with electric and magnetic fields oscillating to create transverse waves. They travel at the same speed regardless of frequency and can range from gamma rays to radio waves with specific names like microwaves and radio waves, each transferring energy to heat up objects through different methods.
Insights
- Electromagnetic waves travel at a constant speed in a vacuum, regardless of their frequency, allowing for a continuous spectrum from gamma rays to radio waves.
- Microwaves and infrared waves are examples of specific frequencies of electromagnetic waves that have practical applications in heating food and objects, showcasing the diverse uses of these waves beyond simple transmission.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
How do electromagnetic waves travel?
Through a vacuum without a medium.
What is the speed of electromagnetic waves in a vacuum?
Constant regardless of frequency.
What are some examples of electromagnetic waves?
Gamma rays, radio waves, microwaves, etc.
How do microwaves heat food in a microwave oven?
By transferring energy to water molecules.
How do infrared waves transfer energy to objects?
By emitting heat to heat up other objects.
Related videos
MooMooMath and Science
What is the ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM

Professor Dave Explains
What is Light? Maxwell and the Electromagnetic Spectrum

PHYSICS with Umesh Rajoria
1. EM Waves complete basics | Maxwell's Equations | Electromagnetic Waves Waves | 12th #cbse #neet

The Efficient Engineer
Understanding Thermal Radiation

Philip Chang
Light Matter and Telescopes
Summary
00:00
"Essence of Electromagnetic Waves"
- Electromagnetic waves, like light, can travel through a vacuum without needing a medium.
- Electric and magnetic fields oscillate to create electromagnetic waves, making them transverse waves.
- Electromagnetic waves travel at the same speed in a vacuum, regardless of frequency.
- Electromagnetic waves can have various frequencies, from gamma rays to radio waves, forming a continuous spectrum.
- Different frequencies of electromagnetic waves have specific names, such as microwaves and radio waves.
- Microwaves in a microwave oven transfer energy to water molecules in food, heating them up.
- Infrared waves emitted by heated objects, like in an electric heater, can transfer energy to heat up other objects, such as people.




