Electro Chemistry - One Shot Lecture | CHAMPIONS - JEE/NEET CRASH COURSE 2022
PW English Medium・2 minutes read
Electrochemistry is essential for understanding chemical processes involving electron movement, with significant applications in everyday items like batteries and electric vehicles. Key concepts include the differences between spontaneous galvanic and non-spontaneous electrolytic cells, the role of Gibbs free energy, and the calculations necessary for predicting electrochemical behaviors and reactions.
Insights
- Electrochemistry examines the movement of electrons in chemical processes, which has practical applications in everyday items like batteries, electronic devices, and electric vehicles, underscoring its relevance in modern technology and transportation.
- Batteries exemplify electrochemistry, functioning as energy sources for various devices, with some being rechargeable and others designed for single use, highlighting the importance of understanding their electrochemical principles.
- The concept of electroplating, where a thin layer of metal is deposited on objects, illustrates another application of electrochemistry in manufacturing and decorative processes, showcasing its versatility.
- The distinction between galvanic cells and electrolytic cells is fundamental; galvanic cells operate spontaneously to convert chemical energy into electrical energy, while electrolytic cells require external energy to drive non-spontaneous reactions, which is crucial for understanding energy transformations in electrochemical systems.
- In galvanic cells, spontaneous reactions occur, resulting in a negative Gibbs free energy (ΔG), while electrolytic cells involve positive ΔG, indicating the need for energy input, which is essential knowledge for predicting cell behavior.
- The electrodes in electrolytic cells are connected to a power source, with the anode being positive and the cathode negative, contrasting with galvanic cells where the anode is negative and the cathode is positive, emphasizing the importance of electrode charge understanding.
- The Nernst equation is a vital tool for calculating the electromotive force (emf) of a cell under non-standard conditions, allowing for adjustments based on varying concentrations and conditions, which is critical for practical applications in electrochemistry.
- Understanding the relationship between standard Gibbs free energy change (ΔG°) and standard emf (E°) is crucial, as it provides insights into the spontaneity of reactions and helps predict the feasibility of electrochemical processes.
- The behavior of electrolytes, particularly the differences between strong and weak electrolytes, is significant in electrochemistry; strong electrolytes exhibit predictable conductivity patterns, while weak electrolytes show increased conductivity with dilution, which is essential for practical applications and calculations in the field.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is electrochemistry?
Electrochemistry is the study of chemical processes that involve the movement of electrons. It encompasses various applications, including batteries, electronic devices, and electric vehicles, highlighting its significance in everyday life. By understanding electrochemical principles, one can appreciate how energy is stored and converted in these systems, as well as the underlying reactions that facilitate these processes.
How do batteries work?
Batteries operate through electrochemical reactions that convert chemical energy into electrical energy. They consist of two electrodes, an anode and a cathode, immersed in an electrolyte. During discharge, a spontaneous reaction occurs, allowing electrons to flow from the anode to the cathode, powering devices. Some batteries are rechargeable, enabling the reverse process where electrical energy is converted back into chemical energy, demonstrating the principles of electrochemistry in action.
What is electroplating?
Electroplating is a process that uses electrochemistry to deposit a thin layer of metal onto an object. This is achieved by passing an electric current through a solution containing metal ions, causing them to reduce and adhere to the surface of the object. Electroplating is widely used for decorative purposes, corrosion resistance, and improving wear properties of materials, showcasing the practical applications of electrochemical principles in manufacturing and decoration.
What are galvanic and electrolytic cells?
Galvanic and electrolytic cells are two types of electrochemical cells that differ in their operation. Galvanic cells generate electrical energy from spontaneous chemical reactions, while electrolytic cells require an external energy source to drive non-spontaneous reactions. In galvanic cells, the anode is negative, and the cathode is positive, whereas in electrolytic cells, the signs are reversed. Understanding these differences is crucial for grasping the fundamental concepts of electrochemistry and its applications.
What is the Nernst equation?
The Nernst equation is a mathematical formula used to calculate the electromotive force (emf) of an electrochemical cell under non-standard conditions. It accounts for the concentrations of reactants and products, allowing for the determination of cell potential when conditions deviate from standard states. The equation is expressed as Ecell = E°cell - (0.059/n) log(Q), where E°cell is the standard emf, n is the number of electrons transferred, and Q is the reaction quotient. This equation is essential for predicting the behavior of electrochemical cells in various scenarios.
Related videos
Tyler DeWitt
Introduction to Electrochemistry

LearnoHub - Class 11, 12
Electrochemistry Class 12 One Shot | CBSE NEET JEE | Chapter 3

Xylem Class 12 CBSE
CLASS 12 CBSE - Chemistry - Electrochemistry | Xylem CBSE 11 & 12

Vora Classes NEET & Boards
Buniyaad NCERT Line by Electrochemistry | Boards | NEET #neet #cbse #cbseboard #neet2024

Vedantu Master Tamil
Electrochemistry | One Shot Marathon | Class 12 | Gethu Batch | CBSE 2024 |🔥 Shimon Sir
Summary
00:00
Understanding Electrochemistry and Its Applications
- Electrochemistry is a crucial chapter in chemistry, focusing on the study of chemical processes that involve the movement of electrons, and it has numerous applications in daily life, such as in batteries, electronic devices, and vehicles.
- Batteries are a primary example of electrochemistry in action, as they power various devices like remote controls, smartphones, and laptops, with some batteries being rechargeable while others are single-use.
- Electrochemistry also plays a role in transportation, as electric vehicles rely on electrochemical processes for energy storage and conversion, highlighting its importance in modern commuting.
- The concept of electroplating, where a thin layer of gold is applied to objects, is another application of electrochemistry, demonstrating how it is used in manufacturing and decoration.
- Understanding electrolytic conductance is essential, as it determines whether a compound can conduct electricity and to what extent, with a focus on numerical problems and formulas relevant for exams.
- The electrochemical cell is a key concept in electrochemistry, divided into two main types: galvanic cells, which involve spontaneous reactions, and electrolytic cells, which require external energy to drive non-spontaneous reactions.
- In galvanic cells, spontaneous reactions occur naturally, and the Gibbs free energy (ΔG) is negative, indicating that chemical energy is converted into electrical energy during the discharge process.
- Conversely, electrolytic cells involve non-spontaneous reactions that require an external energy source, such as electricity, to convert electrical energy into chemical energy, resulting in a positive Gibbs free energy (ΔG).
- A practical analogy for understanding these concepts is the charging and discharging of smartphones: charging represents the non-spontaneous process of an electrolytic cell, while using a charged phone exemplifies the spontaneous process of a galvanic cell.
- The session emphasizes the importance of grasping the differences between galvanic and electrolytic cells, including their energy transformations and Gibbs free energy implications, to prepare for further studies in electrochemistry.
17:30
Electrolytic Cells and Their Energy Dynamics
- An electrolytic cell is a non-spontaneous process, meaning it requires an external energy source, typically a battery, to drive the reactions occurring within it.
- In an electrolytic cell, the Gibbs free energy change (ΔG) is positive, indicating that the process is not spontaneous and requires energy input for the conversion of electrical energy into chemical energy.
- The electrodes in an electrolytic cell are connected to a battery, with the positive terminal connected to the anode and the negative terminal connected to the cathode, establishing their respective charges.
- The electrolyte used in the electrolytic cell is sodium chloride (NaCl), which dissociates into sodium ions (Na⁺) and chloride ions (Cl⁻) in solution, facilitating the movement of ions towards the electrodes.
- Sodium ions (Na⁺) are attracted to the negative electrode (cathode) where they gain electrons (reduction), while chloride ions (Cl⁻) are attracted to the positive electrode (anode) where they lose electrons (oxidation).
- The reduction reaction at the cathode can be represented as Na⁺ + e⁻ → Na(s), where sodium ions gain electrons to form solid sodium.
- The oxidation reaction at the anode can be represented as 2Cl⁻ → Cl₂(g) + 2e⁻, where chloride ions lose electrons to form chlorine gas.
- The anode is defined as the electrode where oxidation occurs (loss of electrons), while the cathode is where reduction occurs (gain of electrons), establishing their roles in the electrochemical process.
- In a galvanic cell, which operates spontaneously, the chemical energy is converted into electrical energy without the need for an external battery, and the Gibbs free energy change (ΔG) is negative.
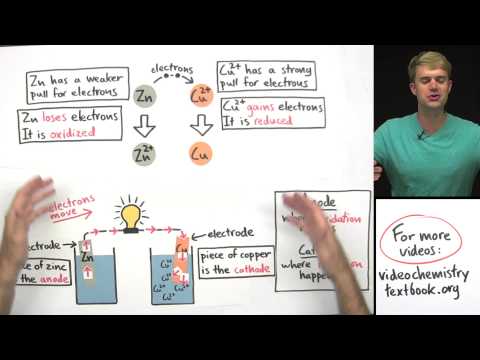
- The galvanic cell consists of two different containers with solutions (e.g., ZnSO₄ and CuSO₄), where zinc (Zn) acts as the anode (oxidation) and copper (Cu) acts as the cathode (reduction), leading to the spontaneous reactions of Zn → Zn²⁺ + 2e⁻ and Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Cu(s).
34:43
Zinc and Copper Reactions in Galvanic Cells
- Zinc ions (Zn²⁺) are produced by the oxidation of zinc metal, which releases two electrons during the process. These electrons do not remain in the solution but are transferred to the electrode, resulting in a negatively charged anode.
- The copper ions (Cu²⁺) in the solution accept electrons from the electrode, converting into solid copper (Cu). This process indicates that the cathode is positively charged due to the gain of electrons.
- As the reaction progresses, the concentration of Zn²⁺ in the solution increases while the concentration of sulfate ions (SO₄²⁻) remains relatively unchanged, leading to a higher concentration of Zn²⁺ compared to SO₄²⁻.
- Conversely, the concentration of Cu²⁺ decreases as it is deposited as solid copper on the cathode, while the concentration of SO₄²⁻ remains stable, resulting in a higher concentration of SO₄²⁻ compared to Cu²⁺.
- To maintain electrical neutrality in the galvanic cell, a salt bridge is used, typically made of potassium chloride (KCl) in an agar solution, which helps balance the charge between the two half-cells.
- The flow of electrons in a galvanic cell occurs from the anode (negative electrode) to the cathode (positive electrode), while the flow of conventional current is in the opposite direction, from cathode to anode.
- The anode is always negatively charged in a galvanic cell, while the cathode is positively charged, and this relationship is consistent across different types of electrochemical cells.
- In an electrolytic cell, the signs of the electrodes are reversed compared to a galvanic cell; thus, if the anode is negative in a galvanic cell, it will be positive in an electrolytic cell.
- The representation of a galvanic cell includes a salt bridge, with the anode on the left side and the cathode on the right side. The ions are written first, followed by their solid states, ensuring that ions are always placed before solids in the representation.
- For half-cell representation, only the relevant half-reaction is shown, such as the reduction of Cu²⁺ to Cu at the cathode, with the salt bridge included to indicate the connection to the other half-cell.
52:18
Understanding Redox Reactions and Cell Representation
- The cathode part of a cell representation involves a metallic electrode immersed in a solution containing its own cation, while a gas ion electrode includes a gas, such as H2, converting into H+ and electrons, indicating oxidation.
- In a cell representation, the anode is where oxidation occurs, and it is essential to include a salt bridge; the order of components should start with the ions, followed by the gas (if present), and conclude with the solid electrode, typically a platinum electrode if no other solid is specified.
- A redox half-cell is defined when both the oxidized and reduced parts are ions, requiring inert electrodes like platinum or palladium for representation, as they do not react with other electrodes.
- To represent a cell from given reactions, identify the anode and cathode by determining where oxidation and reduction occur, then write the cell notation with the salt bridge, ions, gases, and electrodes in the correct order.
- For the reaction of H2 converting to 2H+, two electrons are lost, indicating oxidation at the anode, while Cl2 gaining two electrons to form 2Cl- indicates reduction at the cathode, leading to the correct cell representation.
- When representing a cell, only the ions should be included without stoichiometric coefficients, and if no solid electrode is specified, a platinum solid electrode can be used.
- In a galvanic cell, the net cell reaction is derived from adding the half-reactions, ensuring that electrons cancel out, and the final representation should not include electrons in the net reaction.
- Oxidation potential refers to an element's tendency to lose electrons, while reduction potential indicates the tendency to gain electrons; these potentials are inversely related for any given element.
- An oxidizing agent oxidizes others while getting reduced itself, thus having a high reduction potential, whereas a reducing agent reduces others and gets oxidized, indicating a high oxidation potential.
- Understanding the roles of oxidizing and reducing agents is crucial, as oxidizing agents facilitate oxidation in other substances while reducing agents facilitate reduction, with their respective potentials reflecting their abilities to gain or lose electrons.
01:10:37
Fundamentals of Electrochemistry and Cell Reactions
- Understanding the concepts of oxidation potential, reduction potential, oxidizing agents, and reducing agents is crucial for grasping electrochemistry, which is foundational for various applications in daily life, such as using electricity for water, light, and electronic devices.
- The electromotive force (emf) of a cell is influenced by four main factors: the nature of the chemical reaction, the concentration of reactants and products, the pressure of gaseous reactants and products, and the temperature of the system.
- Standard Ambient Temperature and Pressure (SATP) conditions are defined as having a concentration of 1 molar, a temperature of 298 Kelvin, and a pressure of approximately 1 atmosphere (or 1 bar). Under these conditions, standard emf values for cells are calculated.
- The Nernst equation is used to calculate the emf of a cell when conditions deviate from standard states. The standard emf (E°) of a cell is determined by the equation E°cell = E°cathode - E°anode, where E°cathode and E°anode are the standard reduction potentials of the cathode and anode, respectively.
- A positive standard emf indicates a spontaneous reaction, characteristic of galvanic cells, while a negative standard emf indicates a non-spontaneous reaction, typical of electrolytic cells.
- The Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE) is used as a reference point for measuring reduction potentials, assigned a value of zero. Other elements' reduction potentials are calculated relative to this standard.
- The electrochemical series ranks elements based on their reduction potentials, with elements below hydrogen having positive reduction potentials and those above having negative potentials, indicating their tendency to undergo oxidation or reduction.
- Elements higher in the electrochemical series can displace those lower from their aqueous solutions due to their greater oxidation potential, which is a critical concept for predicting reaction outcomes in electrochemistry.
- When arranging metals by their reducing power, the order reflects their ability to reduce other substances, with stronger reducing agents being positioned higher in the series, indicating a greater tendency to lose electrons.
- Understanding these principles and calculations is essential for solving electrochemical problems and predicting the behavior of various reactions in both academic and practical applications.
01:30:06
Understanding Reducing Agents and Cell Emf
- Reducing potentials indicate the tendency of a species to gain electrons, with higher positive values representing stronger reducing agents; for example, Ag+ has the highest reduction potential, followed by Hg, Cr, Mg, and K in decreasing order.
- The concept of reducing power refers to a substance's ability to reduce another species, which is similar to the role of a reducing agent; it is essential to understand this distinction for answering related questions.
- In a galvanic cell, students are tasked with identifying the cathode and anode reactions, determining which electrode is negatively charged, and recognizing that ions serve as current carriers in the cell.
- Given standard reduction potential values of three metallic ions (0.52, -3.03, and -1.18), students must calculate the order of reducing power by determining oxidation potentials, where the highest oxidation potential corresponds to the strongest reducing power.
- The standard electromotive force (emf) of a cell can be calculated using the formula: E°cell = E°cathode - E°anode, where students must identify the cathode and anode based on reduction reactions.
- For a cell reaction involving Ag+ and Cu2+, students must find the reduction potential of Ag+ and use the given values to calculate the standard emf, resulting in a value of 0.80 volts for Ag+ to Cu.
- The Nernst equation is introduced to calculate the actual emf of a cell under non-standard conditions, expressed as Ecell = E°cell - (0.059/n) log(Q), where Q is the reaction quotient based on concentrations of reactants and products.
- At equilibrium, the cell emf (Ecell) equals zero, while the standard emf (E°cell) remains non-zero; this relationship is crucial for understanding cell behavior at equilibrium.
- To apply the Nernst equation, students must first determine the net cell reaction, identify half-reactions, and calculate the reaction quotient (Q) based on the concentrations of ions involved.
- An example calculation demonstrates how to find the standard emf of a cell involving zinc and copper, leading to a final calculation of the actual emf using the Nernst equation, resulting in a specific value based on given concentrations.
01:47:18
Electrochemistry Fundamentals and Calculations Explained
- To calculate the electromotive force (emf) of a cell, subtract 0.03 from 1.1, resulting in an emf of 1.07 volts, which requires practice to master the calculation process efficiently.
- The relationship between standard Gibbs free energy change (ΔG°) and standard emf (E°) of the cell is expressed as ΔG° = -nFE°, where n is the number of electrons exchanged, F is Faraday's constant (96,500 coulombs), and E° is the standard emf of the cell.
- Faraday's law of electrolysis states that the charge of one mole of electrons is 96,500 coulombs, derived from multiplying the charge of a single electron (1.6 x 10^-19 coulombs) by Avogadro's number (6.02 x 10^23).
- The number of faradays is directly proportional to the moles of electrons; for example, 2 moles of electrons correspond to 2 faradays, and 9 faradays indicate 9 moles of electrons.
- To calculate the total charge (Q) in an electrolysis scenario, use the formula Q = I × t, where I is the current (in amperes) and t is the time (in seconds). For a current of 96.5 A over 100 seconds, the total charge is 9,650 coulombs.
- The number of faradays can be calculated by dividing the total charge by the charge in one faraday (96,500 coulombs). For 9,650 coulombs, the number of faradays is 0.1.
- To find the amount of sodium deposited at the cathode, use the mole concept: with 0.1 moles of electrons, 0.1 moles of sodium are deposited, resulting in a mass of 0.1 moles × 23 g/mol = 2.3 grams of sodium.
- The volume of chlorine gas (Cl2) evolved at the anode can be calculated using the relationship that moles of Cl2 are half the moles of electrons. For 0.1 moles of electrons, the moles of Cl2 are 0.1/2 = 0.05, leading to a volume of 0.05 moles × 22.4 L/mol = 1.12 liters of Cl2 gas.
- In an electrolytic cell, positive ions migrate to the cathode for reduction, while negative ions move to the anode for oxidation. The preferential discharge of ions is determined by their reduction potentials, with the ion having a higher reduction potential being reduced first.
- For a solution containing NaCl, H+, and OH-, H+ will be reduced at the cathode to produce H2 gas, while Cl- will be oxidized at the anode to produce Cl2 gas, resulting in a basic NaOH solution.
02:03:45
Electrochemical Reactions and Conductivity Explained
- The discussion begins with the electrochemical reaction involving AgNO3 solution, where Ag+ ions gain electrons to form solid Ag, while OH- ions undergo oxidation to liberate O2 gas, resulting in an acidic solution containing HNO3.
- The concept of electrolytic conductance is introduced, emphasizing the relationship between resistance (R), length (l), area (a), and resistivity (ρ), with the formula R = ρ(l/a) being fundamental for calculations.
- The reciprocal of resistance (1/R) is defined as conductance (G), and the reciprocal of resistivity (1/ρ) is termed conductivity (K), with the cell constant (G*) defined as l/a, leading to the important expression K = G × G*.
- Units for resistance (Ω), conductance (Ω⁻¹ or mho), resistivity (Ω·cm), and conductivity (Ω⁻¹·cm⁻¹ or siemens/cm) are detailed, highlighting the importance of understanding these units for numerical problems.
- A numerical example is provided where the conductivity (K) of a 0.1 N KCl solution is given as 1.2 × 10⁻² S/cm, and resistance (R) is 60 Ω, prompting the calculation of the cell constant (G*).
- The calculation of G* is performed using the formula G* = K/G, where G is derived from G = 1/R, leading to G* = (1.2 × 10⁻² S/cm) / (1/60) = 7.2 cm⁻¹.
- Another numerical problem involves finding the resistance (R) of a 0.02 M KCl solution with a conductivity of 2 × 10⁻³ S/cm and a cell constant (G*) of 0.1 cm⁻¹, using the relationship K = G × G* to derive R.
- Molar conductivity (λm) is defined as the conductivity of one mole of electrolyte, calculated using the formula λm = K × 1000/C, where C is the concentration in molarity, while equivalent conductivity (λequivalent) is calculated as λequivalent = K × 1000/n, with n being normality.
- The relationship between molar and equivalent conductivity is established as λm = λequivalent × n factor, allowing for conversions between the two based on the electrolyte's charge.
- The behavior of strong and weak electrolytes is discussed, with strong electrolytes exhibiting a linear relationship in conductivity graphs, while weak electrolytes do not reach infinite dilution, necessitating alternative methods for calculating their conductance at maximum dilution.
02:21:42
Understanding Conductivity in Weak Electrolytes
- Weak electrolytes exhibit a significant increase in equivalent or molar conductivity with dilution, as the degree of ionization rises according to Ostwald's dilution law.
- Conductance is maximized when ions are kept apart, which is achieved through increased dilution of the solution, leading to improved molar conductivity values.
- The value of molar conductivity cannot be determined at zero concentration or infinite dilution; this is addressed by Kohlrausch's law, which relates to the independent migration of ions.
- Kohlrausch's law states that at infinite dilution, each ion has a specific conductance value, which remains constant regardless of the electrolyte's strength, similar to a fixed identification number.
- To calculate the infinite dilution values for weak electrolytes, one can use the known values of strong electrolytes, such as NaOH, NaCl, and HCl, and apply mathematical relationships to derive the required values.
- For example, the infinite dilution of NaOH can be expressed as the sum of the infinite dilution values of Na⁺ and OH⁻ ions, while NaCl can be expressed as the sum of Na⁺ and Cl⁻ ions.
- The infinite dilution value for H₂O can be calculated by adding the infinite dilution values of H⁺ and OH⁻ ions, using the equations derived from strong electrolytes.
- At infinite dilution, the equivalent conductance of any electrolyte reaches its maximum value and is constant, indicating that all ions are fully ionized and can migrate independently without inter-ionic attraction.
- The electrolysis of dilute sulfuric acid with a platinum electrode results in the reduction of H⁺ ions at the cathode, producing hydrogen gas (H₂).
- In the electrolysis of potassium sulfate (K₂SO₄) and sodium sulfate (Na₂SO₄) solutions, H₂ gas is produced at the cathode and O₂ gas at the anode, confirming the behavior of ions during electrolysis.
02:37:30
Calculating Conductivity of Acid and KCl Solutions
- To calculate the equivalent conductivity (λ_eq) of 0.1 normal formic acid, use the formula λ_eq = k × (1000 / normality). Given that the cell constant (g*) is 2, and the resistance (R) is 200, first calculate the conductance (g) as g = 1 / R = 1 / 200, then g = (1 / 200) × 2 = 1 / 100. Substitute this into the formula to find λ_eq = (1 / 100) × (1000 / 0.1), which simplifies to λ_eq = 1000 / 10 = 100.
- For a 0.02 molar KCl solution with a specific conductance (k) of 2.768 × 10^-3 and a resistance (R) of 82.4 ohms at 25°C, calculate g* using the relationship k = g × g*. First, find g as g = 1 / R = 1 / 82.4. Then, substitute the values into the equation to find g* = k / g, where g = 1 / 82.4, and k = 2.768 × 10^-3, leading to g* = (2.768 × 10^-3) / (1 / 82.4).




