CompTIA A+ Certification Video Course
PowerCert Animated Videos・136 minutes read
Keyboards and mice are essential input devices for computers, while digital cameras and barcode readers assist in data transfer and scanning. Printers and storage devices like Blu-ray discs and memory cards enhance data management and sharing, with various cable types and network setups facilitating communication. Security protocols, network configurations, and diagnostic tools contribute to efficient network management and troubleshooting, ensuring optimal performance and connectivity.
Insights
- Keyboards are essential input devices for computers, featuring alphabets, numbers, and symbols for command input.
- Digital cameras store images on internal drives or SD cards, transferring data to computers via USB or SD cards.
- Scanners create digital copies of physical documents, connecting to computers with USB cables for data transfer.
- Touchscreens detect finger touches for input, commonly used in all-in-one computers, tablets, and certain phones.
- Printers allow computer printing via USB or parallel cables, with network printers connecting through Ethernet or wireless.
- CPUs are crucial components measured in megahertz, with Intel and AMD offering various types like dual-core and quad-core for multitasking capabilities.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is a keyboard?
A keyboard is an input device for computers with keys for commands.
Related videos

Code.org
How Computers Work: What Makes a Computer, a Computer?

Youth Af
Class 11 Computer Science | Chapter 1 | Computer System | NCERT | CBSE | ONE SHOT 2023-24
Simply Coding
Storage Devices

Edexcel IT Guru
Edexcel IGCSE - ICT - Chapter 1 - Lesson 1 Digital Devices with practice questions

ExplainingComputers
Very Useful Small Computing Things
Summary
00:00
Computer Input Devices and Connectivity Options
- A keyboard is a basic input device for computers, used to input commands with keys made of alphabets, numbers, and symbols.
- Keyboards are equipped with two connector types: the older 6 pin D connector and the modern USB connector, often with adapters for compatibility.
- A mouse is another input device for computers, used for pointing and clicking, typically with one or two buttons.
- Digital cameras store images on internal hard drives or SD cards, which can be transferred to computers via USB cables or SD cards.
- Barcode readers scan barcodes using light, connecting to computers through serial, USB, or wireless connections.
- Scanners create digital copies of physical documents or photos, typically with a flatbed and connected to computers via USB cables.
- Touchscreens function as input devices by detecting finger touches, commonly used in all-in-one computers, tablets, and certain phones.
- Webcams capture video and images for video conferencing, connecting to computers via USB cables and often used with messaging applications like Skype.
- Media card readers allow computers to read memory cards from devices like cameras, connecting via USB cables and accommodating various card sizes.
- Docking stations transform laptops into desktop computers by connecting to larger monitors, keyboards, and other peripherals, specific to laptop manufacturers.
19:26
Display and Print Technology Overview
- Resolution of 1028x768 is known as Extended Graphics Array (EGA).
- Super Extended Graphics Array (SXGA) has a resolution of 1280x1024.
- Super Extended Graphics Array Plus (SXGA+) has a resolution of 1400x1050.
- Ultra Extended Graphics Array (UXGA) has a resolution of 1600x1200.
- Widescreen Ultra Extended Graphics Array (WUXGA) has a resolution of 1920x1200.
- Contrast ratio in displays refers to the difference between black and white.
- Printers allow printing from computers using USB or parallel cables for local connections.
- Network printers can connect through Ethernet ports or wireless antennas.
- Printers can be shared over a network to allow other computers to print.
- Different types of printers include non-impact (laser, inkjet, thermal) and impact (dot matrix).
38:36
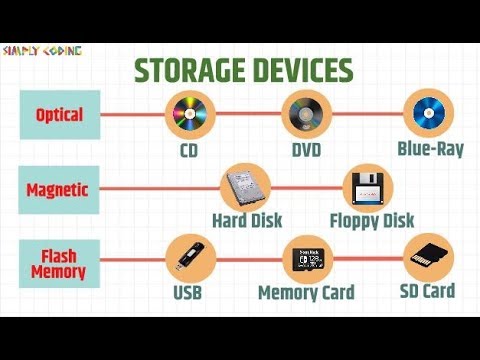
Data Storage Devices and Troubleshooting Tips
- Blu-ray has recordable drives called BD-R for burning data once and BD-RE for erasing and rewriting data.
- Standard single-sided Blu-ray discs hold 25 GB of data, while double-layer discs hold 50 GB.
- Solid state discs, like thumb drives, use memory chips for data storage, ranging from 500 MB to 256 GB.
- Secure digital (SD) cards, including mini and micro SD, are used in digital cameras and smartphones for storage.
- Compact flash cards are common in DSLR cameras for quick storage and transfer to computers.
- XD picture cards were proprietary in Olympus and Fujifilm cameras.
- EMMC is embedded multimedia controller memory found in smartphones and tablets.
- Hot spares can be swapped without powering off equipment, while cold spares require power-off.
- Troubleshooting cell phones involves issues like unresponsive touch screens, app loading problems, and GPS malfunctions.
- Laptops may face issues like no-display, dim displays needing inverter replacement, and battery charging problems.
56:55
Motherboard Form Factors and Interface Technologies
- Micro ATX motherboards are smaller than ATX boards, measuring 9.6 inches by 9.6 inches, designed for smaller computer cases, cheaper, and consume less power.
- BTX form factor improves on ATX with better board design for improved cooling, horizontal memory and bus slots for better airflow, and flexible structure for various case sizes.
- ITX form factor, starting with mini-ITX in 2001, caters to smaller, space-saving computers, consumes less power, and is cooled by heat sinks rather than fans.
- NLX form factor by Intel suits low-end, low-profile computers, using riser cards instead of perpendicular expansion cards, typically found in slimline cases.
- Motherboards feature various input/output interfaces, like PS2 connectors for mouse and keyboard, USB ports for multiple peripherals, and different versions with varying transfer speeds.
- Serial ports, mainly for terminals and modems, are being replaced by USB ports for faster data transfer.
- Parallel ports, like serial ports, are being phased out in favor of USB ports, sending data signals simultaneously over multiple channels.
- Video adapters on motherboards, if present, are integrated and generate images to monitors, with VGA being common but not powerful for extensive graphic applications.
- Firewire, or IEEE 1394, is used for devices like digital cameras, with transfer speeds of 400 Mbits per second, but less popular than USB.
- NIC, or network interface card, connects computers to networks via ethernet cables, providing dedicated connections with transfer speeds ranging from 10 to 1,000 Mbits per second.
01:16:14
Computer Hardware Essentials: NIC, RAM, Cooling
- A Network Interface Card (NIC) converts serial data into parallel data for computer understanding.
- NIC provides a computer with a dedicated network connection and has a unique MAC address.
- Wireless network cards connect wirelessly to networks using built-in antennas.
- Laptops can use PC cards for added capabilities like Wi-Fi, network, or modem cards.
- Random Access Memory (RAM) is temporary memory installed on the motherboard.
- RAM comes in different types like DIMM and SIMM, with DIMM being more common.
- DIMM has a 64-bit data path, while SIMM has a 32-bit data path.
- Cooling is crucial for computers to prevent overheating and component damage.
- Case fans are essential for cooling, with intake and exhaust fans creating a constant airflow.
- CPUs require heatsinks for passive cooling, and thermal compound ensures optimal contact for heat dissipation.
01:35:37
Understanding Computer Hardware Components and Performance
- RDRAM speed of 800 MHz x bus width of 2 bytes results in a total bandwidth of 1600 MB per second.
- RIMM technology requires all memory slots on the motherboard to be used for proper functionality.
- C-RIMM can be installed as a dummy RIMM if other RIMMs are unavailable to ensure continuity.
- Dual channel mode necessitates identical DIMMs in pairs on the motherboard for increased memory access speed.
- Motherboard and DIMMs must be compatible and inserted in specific slots for dual channel mode to work.
- Triple channel mode allows communication with three DIMMs simultaneously, increasing data transfer speed.
- Single-sided and double-sided RAM refer to the memory controller's access to memory chips, affecting speed.
- ECC RAM detects and corrects memory processing errors, identified by the number of memory chips on the module.
- Buffered RAM adds stability by buffering data before sending it to the CPU, reducing electrical load.
- SODIMM, smaller RAM used in laptops, comes in different types like DDR, DDR2, and DDR3, requiring correct installation for compatibility.
- CPU socket on the motherboard holds the CPU, with modern ZIF sockets allowing easy installation.
- Intel and AMD offer various CPU socket types like LGA and PGA, each with specific pin counts and processor compatibility.
- CPU speed is measured in megahertz, with multicore processors like dual core and quad core enhancing multitasking capabilities.
- Intel and AMD are major CPU manufacturers, with Intel processors like Pentium and AMD processors like Athlon.
- CPUs can be 32 or 64-bit, with 64-bit CPUs capable of addressing significantly more memory than 32-bit CPUs.
- In a 64-bit system, more data can be stored in RAM, reducing reliance on slower hard drives and improving computer speed.
01:54:52
"Enhancing Computer Performance Through Hardware Components"
- A 64-bit system is faster than a 32-bit system due to memory cache made of SRAM, which holds data and instructions for the processor.
- Cache memory stores common data for quick access by the CPU, enhancing computer performance.
- Cache memory comes in different levels, with level one cache being the fastest and located on the processor itself.
- The chipset on a motherboard controls data flow between the CPU, peripherals, and memory through the north and south bridge chips.
- The north bridge chip connects the CPU, memory, and AGP or PCI Express slots, while the south bridge chip handles lower functions like PCI, USB, IDE, and SATA.
- Buses on the motherboard facilitate data and signal transfer between components, with higher bus speeds improving computer performance.
- Input output bus slots on motherboards, like PCI and PCI Express, allow for expansion of computer capabilities.
- AGP slots were developed to accelerate 3D computer graphics, with a dedicated pathway to the processor for faster data transfer.
- PCI Express is the latest bus slot technology, transferring data in serial and offering faster speeds than PCI.
- The BIOS, stored on a motherboard chip, initializes computer peripherals during boot, with settings stored in a CMOS chip powered by a small battery.
02:13:49
"BIOS Functions and Computer Maintenance Tips"
- Increasing the computer's speed can raise its temperature, while reducing the clock speed can lower the temperature.
- Overheating issues in a computer can be addressed by adjusting the clock speed.
- The BIOS can monitor the CPU temperature and automatically shut down the computer if it reaches a critical level.
- BIOS settings can be modified to adjust temperature thresholds and fan speeds.
- Virtualization can be enabled or disabled in the BIOS, affecting the computer's ability to run multiple operating systems.
- Password protection in the BIOS prevents unauthorized access and changes to settings.
- The power-on self-test (POST) checks the computer's hardware before booting the operating system.
- Beep codes generated during POST help identify hardware issues, such as keyboard errors or memory module problems.
- Some BIOS systems have intrusion detection features to alert users if the computer case is opened.
- RAID (redundant array of independent disks) setups like RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, and RAID 10 offer different levels of fault tolerance and data redundancy.
02:33:47
Networking Cables and Firewalls: A Summary
- Different standards are used to wire cables, such as A and B standards.
- Crossover cables connect similar devices directly without a hub or switch.
- Rollover cables connect computers or terminals to a router's console port.
- Loopback cables are for testing, tricking a computer into thinking it's connected to a network.
- Firewalls prevent unauthorized access by filtering incoming internet information.
- Host-based firewalls are software firewalls installed on a computer to protect it.
- Twisted pair cable categories vary in maximum speed, with Category 7 offering 10,000 Mbits per second.
- Unshielded twisted pair cables are common for local area networks, while shielded cables offer protection against interference.
- Coaxial cables are used by cable providers for broadband internet and high-quality video.
- Fiber optic cables use light pulses for fast data transmission, with single-mode for long distances and multimode for short distances.
02:54:12
Understanding IP Addresses, Subnets, and Protocols
- An IP address consists of two parts: one for the network and one for the host.
- A subnet mask is used to determine which part of an IP address belongs to the network and which part belongs to the host.
- The subnet mask is a number resembling an IP address that reveals the network portion by masking it.
- Default subnet masks for Class A, B, and C IP addresses determine the network and host portions.
- IP addresses are assigned in blocks to different organizations, with Class A, B, and C being the most common.
- Private IP addresses are not publicly registered and are used for local networks, while public IP addresses provide internet access.
- Dynamic IP addresses are assigned automatically by a DHCP server, while static IP addresses are manually assigned.
- APIPA assigns a self-assigned IP address to a computer if it cannot reach a DHCP server.
- TCP is a connection-oriented protocol that guarantees data delivery, while UDP is connectionless and faster.
- DNS translates domain names to IP addresses, allowing computers to communicate.
03:14:11
Network Security and Connectivity Essentials
- HTTP sends information in clear text, which can be risky for sensitive data like passwords or credit card information.
- HTTPS encrypts data in HTTP, adding security for sensitive information.
- Telnet is a fast terminal emulation program for remote server access but lacks security as commands are sent in clear text.
- SSH is a secure alternative to Telnet, protecting data during transfer over a network.
- SNMP is a network management protocol used for collecting data from network devices like routers and servers.
- Ports are logical connections for programs to exchange information, identified by unique numbers ranging from 0 to 65535.
- DSL is a high-speed technology for broadband data access using telephone lines, with variations like ADSL, SDSL, and VDSL.
- Cable modems provide fast internet access through coaxial cables, often offered by cable television providers.
- POTS/PSTN are traditional telephone services becoming obsolete due to slow speeds compared to broadband.
- ISDN offers faster data transmission over telephone lines than standard modems but was surpassed by DSL and cable.
- Satellite communication is costly and less common due to advancements in other internet access options like DSL and cable.
- Mobile hotspots use cellular networks to connect wireless devices to the internet within a 30-foot range.
- PAN connects personal devices like phones and laptops using Bluetooth for file transfers.
- LAN is a local network of devices like computers and printers in close proximity, often connected via Ethernet cables.
- MAN spans multiple buildings in a city or town, typically using fiber optic cables for high-speed connections.
- WAN is the largest network type, covering large geographical areas like countries or continents, exemplified by the internet.
- Wire crimpers create custom network cables by attaching RJ-45 adapters to twisted pair cables.
- Punch down tools connect wires to punch-down blocks, resembling screwdrivers.
- Media testers verify custom cables for correct wiring after crimping.
- Cable strippers remove plastic shielding from network cables for connector crimping.
- Multimeters test electrical circuits for voltage, resistance, current, and continuity.
- Tone generators locate cables by generating tones for detection from one end to the other.
- SOHO routers are common, inexpensive routers for home and small business use, requiring proper configuration for network access.
- SOHO routers are set up and configured through the router's built-in configuration web page using the router's IP address.
- SOHO routers have DHCP servers for automatic IP address assignment and wireless settings for SSID, channels, and security modes like WEP, WPA, and WPA2.
- WEP, WPA, and WPA2 are wireless security protocols, with WPA2 offering the strongest encryption using CCMP for enhanced security.
03:34:42
Wi-Fi Security and Network Troubleshooting Methods
- WPA2 has been available on all certified Wi-Fi hardware since 2006, offering enhanced data cryptographic encapsulation.
- WPS, or Wi-Fi Protected Setup, is a wireless security protocol designed for users with limited knowledge of wireless networks to easily join secure networks.
- WPS configuration offers three methods for joining a wireless network, including using a WPS button, a client's WPS pin number, or the router's pin number.
- MAC filter allows users to permit or prevent access to a wireless network based on a device's MAC address.
- The DMZ, or demilitarized zone, exposes a designated computer on a network to the internet by forwarding all ports to it, typically used for testing purposes.
- Port forwarding customizes port services for specific applications, directing requests from the internet to the appropriate computer on the network.
- The ping command tests network connectivity and name resolution, providing information on issues like network connectivity, host availability, and routing problems.
- Tracert, or traceroute, identifies the path data packets take to reach a destination, helping pinpoint network issues if packets fail to reach their destination.




