What is Electrolysis - GCSE Chemistry | kayscience.com
KayScience・5 minutes read
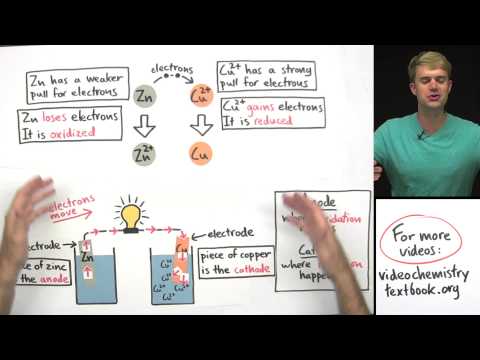
Electrolysis breaks down ionic compounds with electricity to extract metals and nonmetals for various applications, achieved by melting the compound or dissolving it in water. Direct current power pack with positive and negative terminals connected to electrodes like graphite or platinum facilitate the movement of ions to form elemental substances like magnesium and oxygen.
Insights
- Electrolysis uses electricity to break down compounds into individual components, crucial for extracting metals and nonmetals for various applications.
- The process of electrolysis involves breaking strong ionic bonds by melting the compound or dissolving it in water, using a direct current power pack to facilitate the movement of ions towards specific electrodes, resulting in the formation of elemental substances.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is electrolysis?
The process of using electricity to break down ionic compounds.
How does electrolysis work?
By separating ions at electrodes to form elemental substances.
Why is electrolysis important?
It is crucial for extracting metals and nonmetals.
What are the electrodes in electrolysis made of?
Graphite or platinum.
What happens to ions during electrolysis?
They move towards the respective electrodes.
Related videos
Summary
00:00
"Electrolysis: Extracting Elements with Electricity"
- Electrolysis is a process utilizing electricity to break down ionic compounds into individual components; it is crucial for extracting metals and nonmetals from their compounds for various applications.
- To enable electrolysis, the strong ionic bonds holding ions in place must be broken, achieved by either melting the compound to form a hot liquid or dissolving it in water to create an aqueous solution, allowing ions to move freely.
- During electrolysis, a direct current power pack is used with positive and negative terminals connected to electrodes (cathode and anode) made of graphite or platinum, facilitating the movement of ions towards the respective electrodes to form elements like magnesium and oxygen.
- The process of electrolysis involves the separation of ions at the electrodes, with anions attracted to the anode and cations to the cathode, resulting in the formation of elemental substances through the breakdown of the ionic compound.