Electrolysis
Tyler DeWitt・26 minutes read
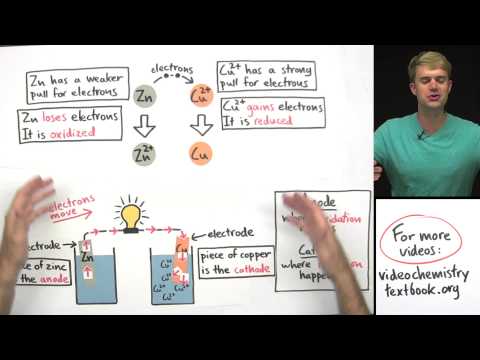
Electrolysis uses electricity to separate compounds, like sodium chloride into sodium and chlorine. An electrolytic cell with electrodes and a battery is crucial for the process, with oxidation and reduction reactions involving electron transfers.
Insights
- Electrolysis is a controlled chemical reaction powered by electricity that breaks compounds into their basic elements, such as sodium chloride into sodium metal and chlorine gas.
- The process of oxidation and reduction in electrolysis involves electron transfer between atoms, where the oxidation number of elements changes – for example, sodium's oxidation number decreases during reduction, while chlorine's increases during oxidation.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is electrolysis?
Electrolysis is a process that uses electricity to induce a chemical change that wouldn't naturally occur. It is commonly used to break compounds into their constituent elements by passing an electric current through an electrolyte solution.
How does oxidation-reduction occur in electrolysis?
Oxidation-reduction reactions in electrolysis involve electron transfer between atoms. For example, in the electrolysis of water, oxygen's oxidation number goes from -2 to 0, indicating oxidation, while gaining electrons signifies reduction.
What is the role of an electrolytic cell in electrolysis?
An electrolytic cell, consisting of electrodes and a battery, is used for electrolysis. The battery's positive side attracts electrons, while the negative side pushes them, facilitating the chemical reactions that occur during the process.
Why is external energy required for electrolysis?
Electrolysis requires external energy because it is a non-spontaneous process. The external electrical energy provided by the battery is necessary to drive the chemical reactions that break down compounds into their constituent elements.
How is water electrolyzed in the process?
In the electrolysis of water, an electrolytic cell with water, electrodes, and a battery is used. Sulfuric acid is added to act as an electrolyte, allowing electricity to flow through. Reduction occurs at the cathode, producing hydrogen gas, while oxidation happens at the anode, generating oxygen gas.
Related videos

KayScience
What is Electrolysis - GCSE Chemistry | kayscience.com

RTSH
Elektroliza| Kimi 11
Tyler DeWitt
Introduction to Electrochemistry

Xylem Class 12 CBSE
CLASS 12 CBSE - Chemistry - Electrochemistry | Xylem CBSE 11 & 12

SD Chemistry
Group 17/Manufacture of Chlorine/Deacon Process/Brine electrolysis/P block Elements/Vol1/Unit3/TN 12
Summary
00:00
"Electrolysis: Inducing Chemical Change with Electricity"
- Electrolysis is a process using electricity to induce a chemical change that wouldn't occur naturally.
- It is commonly employed to break compounds into their constituent elements.
- Sodium chloride can be electrolyzed into sodium metal and chlorine gas.
- Water can be electrolyzed into hydrogen gas and oxygen gas.
- Diatomic elements like chlorine always pair up, hence written as Cl2.
- Oxidation-reduction reactions involve electron transfer between atoms.
- Sodium's oxidation number decreases during reduction, while chlorine's increases during oxidation.
- Electrolysis requires external energy, as the process is non-spontaneous.
- An electrolytic cell, with electrodes and a battery, is used for electrolysis.
- The battery's positive side attracts electrons, while the negative side pushes them, facilitating the chemical reactions.
17:33
Electrolysis: Oxygen Reduction, Hydrogen Production Reactions
- Oxygen's oxidation number goes from -2 to 0, indicating oxidation, while gaining electrons signifies reduction.
- The process of oxidation and reduction is crucial as it requires external electrical energy to occur, similar to the example of sodium chloride.
- Electrolysis of water involves an electrolytic cell with water, test tubes filled with water, and electrodes connected to a battery.
- Sulfuric acid is added to the water to act as an electrolyte, allowing electricity to flow through.
- The cathode, connected to the negative side of the battery, is where reduction occurs, producing hydrogen gas.
- The anode, linked to the positive side of the battery, is where oxidation happens, generating oxygen gas.
- The balanced equation shows a 2:1 ratio of hydrogen gas to oxygen gas, resulting in twice as much hydrogen being produced.
- The process involves bubbles forming on the electrodes, moving up to the test tubes, causing the water level to decrease as gas collects at the top.
- Half reactions for the reduction of hydrogen and the oxidation of oxygen are detailed, showing the movement of electrons and atoms in the process.




