Philosophy of science Part I
Universitetet i Agder・21 minutes read
Science has played a vital role in society across history, contributing to pluralism and valid knowledge, even amidst disagreements. From the Academy in Athens to the Enlightenment period, scientific discoveries have influenced the evolution of society, leading to progress in technology, economics, and social institutions.
Insights
- Science has a rich history dating back to antiquity, with figures like Plato and Aristotle making significant contributions, highlighting the evolution of scientific thought over time.
- The Enlightenment period marked a crucial era where scientific discoveries flourished, leading to advancements in various fields like technology and social institutions, setting the stage for the Industrial Revolution.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What role does science play in society?
Science plays a crucial role in society, contributing to scientific pluralism and disagreements. It expands into various fields with more researchers and methodologies, shaping a knowledge society with conflicting interests but a reliance on common reasoning. Science's diversity contributes to pluralism while providing valid knowledge, tracing its emergence in antiquity, rediscovery in medieval times, and evolution into an independent institution.
Who founded the Academy in Athens?
The Academy in Athens was founded by Plato, with Aristotle making significant contributions to science. Despite their disagreements on general concepts impacting scientific reasoning, Aristotle's move to the Greek island of Colophon led to the discovery of biology. After a 1,500-year decline in science during the migration period, Aristotle was rediscovered in Europe, influencing the Enlightenment period's focus on scientific discoveries and new branches of science.
What did David Hume question?
David Hume, a Scottish philosopher, questioned the inductive method and argued that knowledge is based on customs and habits as much as on observation. This questioning led to the concept of Hume's fork, challenging traditional views on knowledge acquisition and emphasizing the role of human behavior and experience in shaping understanding.
Who sought to reconcile disagreements between Bacon and Hume?
Immanuel Kant, a central thinker of his time, sought to reconcile the disagreements between Francis Bacon and David Hume. He proposed the idea of epistemology and the Copernican revolution in understanding reality, aiming to bridge the gap between empirical observation and rational thought, shaping modern philosophical discourse.
What advancements did the Enlightenment period anticipate?
The Enlightenment period saw progress in technology, economics, and social institutions across Europe, with scientific discoveries leading to technical and social advancements, anticipating the Industrial Revolution. The focus on knowledge and science during this period, exemplified by institutions like the Wren Library in Cambridge, emphasized openness, accessibility, and the celebration of human intellect and progress.
Related videos

TVUP
UP TALKS | Interaction of Science, Technology and Society Through Time

Roel Ang
How History Shapes Our Future Science
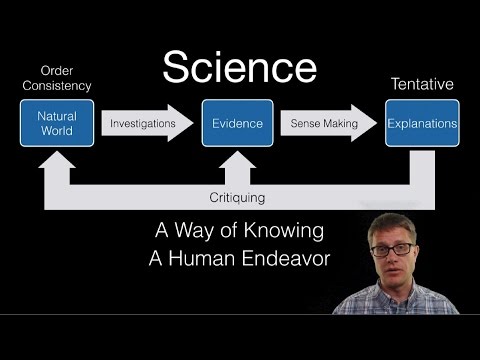
Bozeman Science
The Nature of Science
Domain of Science
Map of Science (and everything else)

TEDx Talks
Building bridges between science and society for a better future. | Nadine Bongaerts | TEDxSaclay
Summary
00:00
Evolution of Science in Society
- Science plays a crucial role in society, amidst scientific pluralism and disagreements.
- Science is expanding into various fields with more researchers and methodologies.
- Living in a knowledge society with conflicting interests but a reliance on common reasoning.
- Exploring how science can be diverse yet contribute to pluralism while providing valid knowledge.
- Science's emergence in antiquity, rediscovery in medieval times, and evolution into an independent institution.
- The Academy in Athens, founded by Plato, and Aristotle's significant contributions to science.
- Disagreement between Plato and Aristotle on general concepts and its impact on scientific reasoning.
- Aristotle's move to the Greek island of Colophon, leading to the discovery of biology.
- Rediscovery of Aristotle in Europe after a 1,500-year decline in science during the migration period.
- The Enlightenment period's focus on scientific discoveries, new branches of science, and the struggle for independence.
24:40
Enlightenment Era: Knowledge, Science, and Progress
- The Wren Library in Cambridge was built during the Enlightenment period to celebrate knowledge and science, emphasizing openness and accessibility to all.
- The painted glass window in the library, known as the Chip Leon II window, depicts an allegory of Trinity's greatness in the 1770s, featuring figures like Isaac Newton and Francis Bacon.
- David Hume, a Scottish philosopher, questioned the inductive method and argued that knowledge is based on customs and habits as much as on observation, leading to the concept of Hume's fork.
- Immanuel Kant, a central thinker of his time, sought to reconcile the disagreements between Bacon and Hume, proposing the idea of epistemology and the Copernican revolution in understanding reality.
- The Enlightenment period saw progress in technology, economics, and social institutions across Europe, with scientific discoveries leading to technical and social advancements, anticipating the Industrial Revolution.




