Leaf Pigments and Light
Teacher's Pet・3 minutes read
Chlorophyll in thylakoid discs absorbs light for photosynthesis, with carotenoids helping capture additional energy. The electromagnetic spectrum explains how light energy drives the process by exciting electrons and emitting photons.
Insights
- Chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b in thylakoid discs absorb specific light wavelengths, while carotenoids complement by absorbing other colors, collectively maximizing energy capture in photosynthesis.
- The relationship between light colors, electron excitation, and photon emission elucidates how chlorophyll utilizes energy during photosynthesis, emphasizing the significance of understanding the electromagnetic spectrum for comprehending this process.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What happens during photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is a process where plants use chlorophyll to absorb light energy, converting carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
Where do light reactions occur in plants?
Light reactions occur in the thylakoid discs within the chloroplast of plant cells.
How do chlorophyll molecules capture energy?
Chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b absorb different wavelengths of light, reflecting green light and capturing energy for photosynthesis.
What is the role of carotenoids in photosynthesis?
Carotenoids help in absorbing light colors that chlorophyll cannot, enhancing energy capture for plants during photosynthesis.
Why is understanding the electromagnetic spectrum important in photosynthesis?
Understanding the electromagnetic spectrum helps in comprehending how chlorophyll harnesses energy during photosynthesis by absorbing different colors of light, which correspond to varying energy levels essential for the process.
Related videos

SLCC BIOL Videos
Light Dependent Reactions

Freesciencelessons
A Level Biology Revision (Year 13) "The Light-Dependent Reactions"

Mr Exham Biology
Photosynthesis - Light-dependent Stage - Post 16 Biology (A Level, Pre-U, IB, AP Bio)
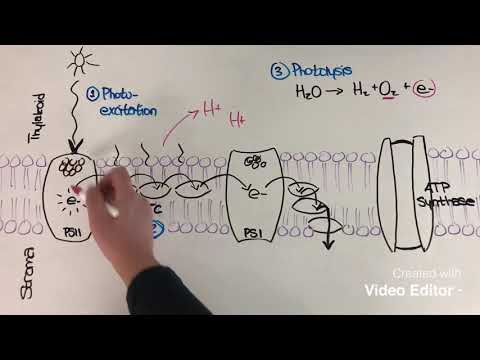
Jackie Shukin
Light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis
Beverly Biology
Photosynthesis (in detail)
Summary
00:00
Light Reactions and Energy Capture in Photosynthesis
- In photosynthesis, the light reactions take place in the thylakoid discs within the chloroplast, where chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b absorb different wavelengths of light, reflecting green light and capturing energy. Carotenoids also play a role in absorbing light colors that chlorophyll cannot, enhancing energy capture for plants.
- Understanding the electromagnetic spectrum and the behavior of light waves is crucial in comprehending how chlorophyll harnesses energy during photosynthesis. Different colors of light correspond to varying energy levels, with electrons becoming excited and emitting photons when falling to lower energy levels, a process essential for the light reactions in photosynthesis.




