A Level Biology Revision (Year 13) "The Light-Dependent Reactions"
Freesciencelessons・4 minutes read
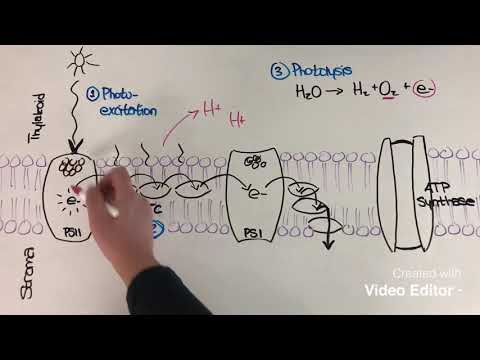
Photosynthesis involves light-dependent reactions on thylakoid membranes to produce ATP, NADPH, and oxygen, which is then used in light-independent reactions to convert CO2 to glucose. Two photo systems, PS2 and PS1, absorb light energy, generate ATP through chemiosmosis, and produce oxygen through photolysis in the crucial process of photosynthesis.
Insights
- Light-dependent reactions in photosynthesis involve two photo systems, PS2 and PS1, where light energy is absorbed, electrons are excited, and ATP is generated through chemiosmosis, with photolysis producing oxygen as a byproduct.
- The electron transport chain in photosynthesis creates a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane, which is crucial for ATP production by ATP synthase through chemiosmosis, highlighting the significance of this mechanism in the overall process.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is the process of photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is a biological process where plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy to produce glucose and oxygen. It involves two main stages: light-dependent reactions occurring on thylakoid membranes and light-independent reactions in the stroma.
How do light-dependent reactions contribute to photosynthesis?
Light-dependent reactions in photosynthesis involve two photo systems, PS2 and PS1, where light energy is absorbed, electrons are excited, and ATP is generated through chemiosmosis. These reactions produce ATP, reduced NADP, and oxygen, which are essential for the light-independent reactions to convert carbon dioxide to glucose.
What is the role of photolysis in photosynthesis?
Photolysis is the process of splitting water molecules to replace lost electrons in PS2 during photosynthesis. This process releases oxygen as a byproduct, which is crucial for sustaining life on Earth. Photolysis ensures a continuous supply of electrons for the light-dependent reactions to produce ATP and reduced NADP.
How is ATP generated in photosynthesis?
ATP is generated in photosynthesis through non-cyclic and cyclic photophosphorylation processes. The electron transport chain creates a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane, which is utilized by ATP synthase to produce ATP from ADP and Pi through chemiosmosis. This mechanism plays a vital role in converting light energy into chemical energy.
What are the key components of photosynthesis?
The key components of photosynthesis include light-dependent reactions, which occur on thylakoid membranes and produce ATP, reduced NADP, and oxygen, and light-independent reactions in the stroma, where carbon dioxide is converted to glucose. These processes work together to sustain life by providing energy for plants and oxygen for the atmosphere.
Related videos
Jackie Shukin
Light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis

Mr Exham Biology
Photosynthesis - Light-dependent Stage - Post 16 Biology (A Level, Pre-U, IB, AP Bio)

SLCC BIOL Videos
Light Dependent Reactions

BioMan Biology
Photosynthesis Intro and Light-Dependent Reactions

Freesciencelessons
A Level Biology Revision (Year 13) "Two Key Reactions in Photosynthesis"
Summary
00:00
Light-dependent reactions in photosynthesis: ATP production explained
- Photosynthesis involves light-dependent reactions occurring on thylakoid membranes, utilizing light energy to produce ATP, reduced NADP, and oxygen. These products are then utilized in the light-independent reactions in the stroma to convert carbon dioxide to glucose.
- The light-dependent reactions encompass two photo systems, PS2 and PS1, where light energy is absorbed, electrons are excited, and ATP is generated through chemiosmosis. Photolysis, splitting water to replace lost electrons in PS2, produces oxygen, a crucial part of photosynthesis.
- Non-cyclic and cyclic photophosphorylation processes are involved in generating ATP, with the electron transport chain creating a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane. This gradient is utilized by ATP synthase to produce ATP from ADP and Pi through chemiosmosis, a key mechanism in photosynthesis.




