Introduction to Statistics
The Organic Chemistry Tutor・35 minutes read
The text provides a comprehensive overview of statistical calculations for two data sets, detailing how to determine the mean, median, mode, range, quartiles, and interquartile range, as well as methods to identify outliers and create various types of visual data representations. Additionally, it explains constructing frequency tables, histograms, and calculating relative and cumulative relative frequencies, culminating in the identification of percentiles within data distributions.
Insights
- The calculations for the mean, median, mode, and range of two distinct data sets illustrate fundamental statistical concepts: the mean provides the average value, the median represents the middle value when data is ordered, the mode indicates the most frequently occurring number, and the range shows the spread between the highest and lowest values. For example, in the first data set, the mean is approximately 15.43, the median is 14, the mode is 7, and the range is 25.
- The identification of quartiles and the interquartile range (IQR) is essential for understanding data distribution, as it helps to detect outliers and assess the spread of the middle 50% of the data. In the example provided, the IQR is calculated as 12, and the maximum value exceeding the calculated upper limit indicates that it is an outlier, demonstrating the importance of these measures in data analysis.
- Visual representations like box and whisker plots and histograms are valuable tools for summarizing data distributions. The box plot visually encapsulates the quartiles and highlights outliers, while the histogram allows for quick assessment of frequency distribution across categories, such as grades, making data interpretation more intuitive and accessible for analysis.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is the definition of mean?
The mean is a statistical measure that represents the average of a set of numbers. It is calculated by summing all the values in the dataset and then dividing that total by the number of values. For example, if you have a dataset of five numbers, you would add them together to get a total and then divide by five to find the mean. This measure is useful in understanding the central tendency of the data, providing a single value that summarizes the overall level of the dataset.
How do I find the median?
To find the median, you first need to arrange the numbers in your dataset in ascending order. The median is the middle value of this ordered list. If there is an odd number of values, the median is the number that is exactly in the center. If there is an even number of values, the median is calculated by taking the average of the two middle numbers. This measure is particularly useful because it is not affected by extreme values, making it a robust indicator of central tendency.
What is a mode in statistics?
The mode is a statistical term that refers to the value that appears most frequently in a dataset. A dataset can have one mode, more than one mode (bimodal or multimodal), or no mode at all if all values occur with the same frequency. Identifying the mode is important in understanding the most common value in a dataset, which can provide insights into trends and patterns within the data. For example, in a set of test scores, the mode would indicate the score that most students achieved.
What does range mean in data analysis?
The range is a simple statistical measure that indicates the difference between the highest and lowest values in a dataset. It is calculated by subtracting the minimum value from the maximum value. The range provides a quick sense of the spread or dispersion of the data, helping to understand how varied the values are. A larger range suggests greater variability, while a smaller range indicates that the values are closer together. This measure is particularly useful in identifying the extent of variation in a dataset.
How is an outlier defined?
An outlier is a data point that significantly differs from the other observations in a dataset. It is typically identified as a value that lies outside the range defined by the interquartile range (IQR), which is calculated as Q1 - 1.5 * IQR and Q3 + 1.5 * IQR. Outliers can occur due to variability in the data or may indicate measurement errors. Identifying outliers is crucial because they can skew the results of statistical analyses and affect the overall interpretation of the data.
Related videos

Vedantu Telugu
Statistics | One Shot Revision | Class 10 | Haripriya Mam | Vedantu Telugu

Rajat Arora
Arithmetic Mean | Easiest way and All Numericals | Class 11 | Statistics | Part 1

Shobhit Bhaiya Maths
Statistics Class 9 One Shot By Shobhit Nirwan 🔥 |Statistics Class 9 #statisticsclass9 #shobhitnirwan

Tech Classes
Complete STATISTICS for Data Science | Data Analysis | Full Crash Course
The Organic Chemistry Tutor
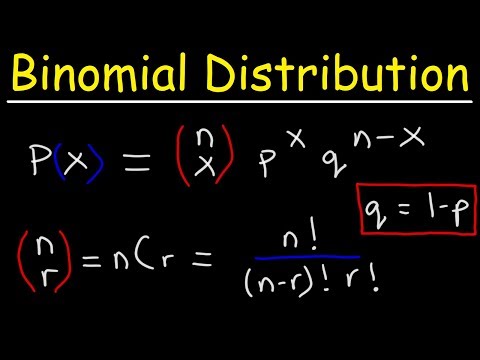
Finding The Probability of a Binomial Distribution Plus Mean & Standard Deviation
Summary
00:00
Statistical Analysis of Two Data Sets
- The data set provided consists of the numbers: 7, 7, 10, 14, 15, 23, and 32. To find the mean, sum these numbers (7 + 7 + 10 + 14 + 15 + 23 + 32) to get a total of 108, then divide by the number of values (7), resulting in a mean of approximately 15.43.
- The median is determined by arranging the numbers in order and finding the middle value. After eliminating the lowest and highest numbers, the middle number is 14, making it the median of the first data set.
- The mode is the number that appears most frequently in the data set. In this case, 7 appears twice, so the mode is 7.
- The range is calculated by subtracting the lowest number (7) from the highest number (32), resulting in a range of 25.
- The second data set consists of the numbers: 11, 15, 15, 21, 37, 41, 59. The sum of these numbers is 258, and dividing by the total count (8) gives a mean of 32.25.
- For the median of the second data set, after arranging the numbers, the two middle numbers are 21 and 37. The median is calculated by averaging these two values, resulting in a median of 29.
- The mode for the second data set is bimodal, as both 15 and 59 appear twice, making them the modes.
- The range for the second data set is calculated as 59 (highest) minus 11 (lowest), resulting in a range of 48.
- To find quartiles and the interquartile range (IQR), the data is divided into four equal parts. Q1 is the median of the lower half, Q2 is the overall median, and Q3 is the median of the upper half. The IQR is calculated as Q3 minus Q1.
- An outlier is identified if it falls outside the range defined by Q1 - 1.5 * IQR and Q3 + 1.5 * IQR. For example, in a data set of 7, 11, 14, 5, 8, 27, 16, 10, 13, 17, and 16, the calculations show that 27 is not an outlier, while a number like 29 would be considered an outlier.
21:30
Understanding Data Distribution and Outliers
- The interquartile range (IQR) is calculated as Q3 (30) minus Q1 (18), resulting in an IQR of 12. The highest point of the range is determined by adding 1.5 times the IQR to Q3, which is 30 + (1.5 * 12) = 48.
- The minimum value in the dataset is 13, and the maximum value is 50. Since the maximum (50) exceeds the calculated upper limit (48), it is identified as an outlier.
- To create a box and whisker plot, draw a number line from 0 to 50, marking intervals of 10, and include a midpoint for 5s. The box will range from Q1 (18) to Q3 (30), with the minimum (13) and maximum (50) noted, placing a point at 50 to indicate the outlier.
- The median (Q2) is 24, positioned within the box plot, which visually represents the interquartile range of 12 (30 - 18). The box plot illustrates the distribution of the data, highlighting the outlier.
- Skewness is discussed, noting that a symmetrical distribution has equal lengths on both sides of the median, where the mean equals the median. In contrast, a right-skewed distribution has a longer tail on the right, indicating that the mean is greater than the median.
- For a right-skewed distribution, the box plot shows that Q3 - Q2 is greater than Q2 - Q1, indicating the right side of the box is longer. Conversely, a left-skewed distribution has a longer tail on the left, with the mean being less than the median.
- To create a dot plot from the dataset (5, 8, 3, 7, 1, 5, 3, 2, 3, 3, 8, 5), draw a number line and place dots above each corresponding number, with the mode being the number that appears most frequently, which is 3.
- A stem-and-leaf plot is constructed using the numbers (4, 9, 13, 13, 17, 21, 36, 38, 38, 56) by creating two columns: the stem (left) and the leaf (right). For example, 4 is represented as 0 | 4, and 13 as 1 | 3.
- A frequency table can be created from a dataset (5, 9, 8, 7, 8, 12, 9, 8, 10, 8, 9, 7) by listing each unique number in one column and counting its occurrences in another. For instance, the number 8 appears four times.
- To calculate the sample mean using the frequency table, multiply each number by its frequency to get a sum, then divide the total sum by the total frequency. For example, if the total sum is 100 and the total frequency is 12, the mean is 100 / 12 = 8.33 (repeating).
43:34
Analyzing Student Grades with Frequency Distribution
- To create a frequency distribution table, categorize grades into four classes: D (60-69), C (70-79), B (80-89), and A (90-100). Count the number of students in each category: 2 students received a D, 4 received a C, 6 received a B, and 3 received an A.
- Construct a histogram using the frequency distribution table, plotting frequency on the y-axis and grade categories on the x-axis. The grade intervals are 60, 70, 80, 90, and 100, with the highest frequency being 6 for the B category.
- Create a table with four columns: value, frequency, relative frequency, and cumulative relative frequency. For example, the frequency of the number 2 is 2, the frequency of 3 is 7, the frequency of 5 is 3, the frequency of 6 is 1, the frequency of 7 is 3, and the frequency of 8 is 4, totaling 20 numbers.
- Calculate relative frequency by dividing each frequency by the total count (20). For instance, the relative frequency for 2 is 2/20 = 0.10, for 3 is 7/20 = 0.35, for 5 is 3/20 = 0.15, for 6 is 1/20 = 0.05, for 7 is 3/20 = 0.15, and for 8 is 4/20 = 0.20.
- Determine cumulative relative frequency by adding the relative frequencies sequentially. Starting with 0.10, add 0.35 to get 0.45, then add 0.15 for 0.60, add 0.05 for 0.65, add 0.15 for 0.80, and finally add 0.20 to reach 1.00.
- To find percentiles, use the cumulative relative frequency table. For the 60th percentile, average the values corresponding to 0.60, which are 5 and 6, resulting in 5.5. For the 80th percentile, average 7 and 8 to get 7.5.
- For percentiles not directly listed, identify the range they fall into. For example, the 20th percentile is between 0.10 and 0.45, corresponding to the value 3, while the 75th percentile is between 0.65 and 0.80, corresponding to the value 7.




