Intermolecular Forces - Hydrogen Bonding, Dipole Dipole Interactions - Boiling Point & Solubility
The Organic Chemistry Tutor・7 minutes read
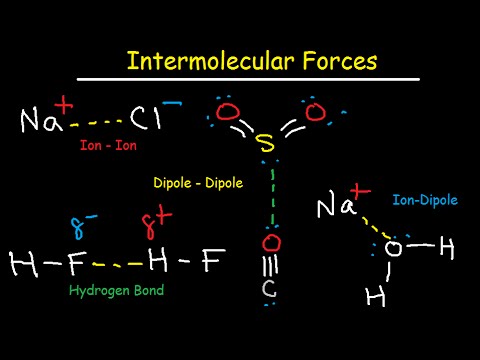
Dipole-dipole interactions happen in polar molecules with partial charges attracting each other. Hydrogen bonding, a special case of dipole-dipole interactions, results in stronger intermolecular forces in molecules like ammonia and methanol, leading to higher boiling points and water solubility.
Insights
- Dipole-dipole interactions between polar molecules like acetone and carbon monoxide create attractions between partial charges, influencing intermolecular forces.
- Hydrogen bonding, a special dipole-dipole interaction, occurs in molecules like water, ammonia, and methanol, leading to stronger forces, higher boiling points, and increased solubility in water.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What are dipole-dipole interactions?
Dipole-dipole interactions occur between polar molecules, where partial charges attract each other, creating a dipole-dipole interaction.
How do hydrogen bonds form?
Hydrogen bonding occurs when hydrogen is attached to nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine.
What is the impact of hydrogen bonding on boiling points?
Molecules with hydrogen bonding have higher boiling points due to stronger intermolecular forces.
How does hydrogen bonding affect water solubility?
Hydrogen bonding increases water solubility in molecules.
Why do molecules with hydrogen bonding have higher boiling points?
Hydrogen bonds in molecules lead to stronger intermolecular forces, resulting in higher boiling points.
Related videos

FuseSchool - Global Education
What Are Intermolecular Forces | Properties of Matter | Chemistry | FuseSchool
The Organic Chemistry Tutor
Intermolecular Forces - Hydrogen Bonding, Dipole-Dipole, Ion-Dipole, London Dispersion Interactions

Miss Natalie Chemistry
7A Intermolecular Forces - Edexcel IAS Chemistry (Unit 2)

Allery Chemistry
EDEXCEL Topic 2 Bonding and Structure REVISION

The Organic Chemistry Tutor
Polar and NonPolar Molecules: How To Tell If a Molecule is Polar or Nonpolar
Summary
00:00
Intermolecular Forces: Dipole-Dipole and Hydrogen Bonding
- Dipole-dipole interactions occur between polar molecules, such as acetone, where the partial positive and negative charges attract each other, creating a dipole-dipole interaction.
- Carbon monoxide molecules exhibit dipole moments, leading to dipole-dipole interactions between separate molecules due to the attraction of oppositely charged ends.
- Hydrogen bonding, a special type of dipole-dipole interaction, occurs when hydrogen is attached to nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine, as seen in water molecules where hydrogen bonds keep them together.
- Molecules with hydrogen bonding, like ammonia and methanol, have higher boiling points and increased water solubility due to the stronger intermolecular forces.
- Comparing molecules like ethanol and dimethyl ether, the presence of hydrogen bonds leads to higher boiling points and solubility in water, with ethanol having a significantly higher boiling point and solubility due to its hydrogen bonds.




