Die AKKOMMODATION des Auges (Nahsicht und Fernsicht)
BioLogisch・2 minutes read
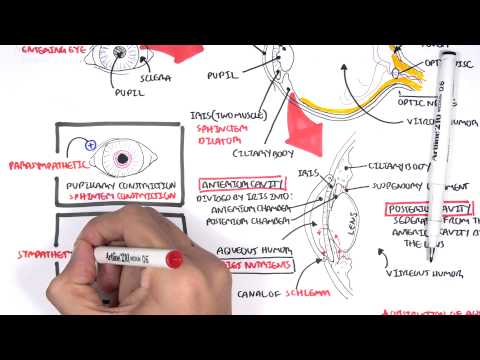
Accommodation refers to the eye's ability to focus on objects at different distances, involving the lens's shape changes controlled by the ciliary muscle. As people age, the lens becomes less elastic, resulting in presbyopia, which can be corrected with glasses or contact lenses.
Insights
- Accommodation is the process by which the eye adjusts its focus on objects at different distances, involving the ciliary muscle's actions that either relax or tense to change the shape of the lens; this allows for clear vision both far and near, but as people age, the lens becomes less flexible, resulting in presbyopia, a condition that can be managed with corrective eyewear.
- Understanding the mechanics of accommodation reveals the importance of the lens's adaptability in maintaining clear vision, highlighting how age-related changes can impact this ability and necessitate interventions like glasses or contacts, emphasizing the need for regular eye care to address these changes.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is accommodation in the eye?
Accommodation refers to the eye's ability to adjust its focus on objects at different distances. This process is primarily managed by the lens of the eye, which can change shape to either flatten for distant vision or become rounder for near vision. When focusing on faraway objects, the ciliary muscle relaxes, allowing the zonular fibers to pull tight and flatten the lens, reducing its refractive power. Conversely, when looking at nearby objects, the ciliary muscle contracts, enabling the lens to bulge and increase its refractive power, thus providing a clear image. This dynamic adjustment is crucial for maintaining clear vision across various distances.
How does aging affect vision?
As people age, the lens of the eye undergoes changes that can significantly impact vision. One of the most common issues is the loss of elasticity in the lens, which makes it harder for the eye to focus on close objects. This condition is known as presbyopia, and it typically begins to affect individuals in their 40s or 50s. The inability to accommodate effectively for near vision can lead to difficulties in reading or performing tasks that require close focus. Fortunately, presbyopia can often be corrected with the use of reading glasses or contact lenses, allowing individuals to regain clear vision for near tasks.
What causes presbyopia?
Presbyopia is primarily caused by the natural aging process of the eye, specifically the gradual loss of elasticity in the lens. As the lens becomes stiffer over time, it loses its ability to change shape effectively, which is essential for focusing on close objects. This reduced flexibility means that the ciliary muscle, which controls the lens's shape, cannot contract as efficiently, leading to difficulties in near vision. The onset of presbyopia is a common experience for many individuals as they reach middle age, and it is a normal part of the aging process rather than a disease or disorder.
What are the symptoms of presbyopia?
The symptoms of presbyopia typically include difficulty reading small print, the need to hold reading materials at arm's length to see them clearly, and experiencing eye strain or fatigue after prolonged close-up work. Individuals may also notice that they require brighter lighting for reading or other detailed tasks. These symptoms can become more pronounced over time, making it increasingly challenging to perform activities that require near vision. As presbyopia progresses, many people find that they need to use reading glasses or other corrective lenses to alleviate these issues and restore clear vision for close tasks.
How can presbyopia be corrected?
Presbyopia can be effectively corrected through various means, with the most common solutions being reading glasses and contact lenses. Reading glasses are typically prescribed to help individuals see close objects more clearly, and they come in different strengths based on the severity of the condition. Multifocal lenses, such as bifocals or progressive lenses, can also be used to provide clear vision at multiple distances, accommodating both near and far sight. Additionally, some individuals may opt for surgical options, such as LASIK or lens implants, to address presbyopia. These corrective measures allow individuals to regain their ability to focus on close objects and improve their overall quality of life.
Related videos
Armando Hasudungan
Anatomy - Eye Overview

Amber Stokes
3020 Lecture 12

Magnet Brains
Light Full Chapter Class 8 Science | NCERT Science Class 8 Chapter 16

Class 10 Learn With Mansi
Light Reflection and Refraction | Chapter 9 | Complete Chapter - Part 2 | "लक्ष्य" 2025

Exphub 9th &10th
Human Eye and the Colourful World in 20 Minutes🔥| Class 10th | Rapid Revision | Prashant Kirad
Summary
00:00
Understanding Eye Accommodation and Presbyopia
- Accommodation is the eye's ability to focus on objects at varying distances, achieved through the lens's deformability; for distant vision (long-distance accommodation), the ciliary muscle relaxes, causing the zonular fibers to tense and flatten the lens, reducing its refractive power, while for near vision (near-accommodation), the ciliary muscle tenses, allowing the lens to become rounder and increase its refractive power, enabling clear focus on close objects; however, with age, the lens loses elasticity, leading to presbyopia, which can be corrected with glasses or contact lenses.




