Anatomy - Eye Overview
Armando Hasudungan・8 minutes read
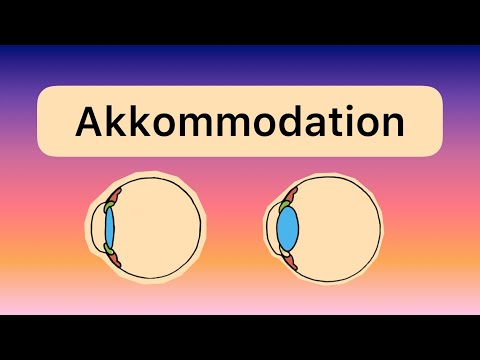
The eye's anatomy is complex, involving various structures like the cornea, lens, and retina, which work together to capture and process images sent to the brain. Accommodation, controlled by ciliary muscles and the lens, allows for adjustments in focusing light on the retina, with aging potentially leading to vision issues like presbyopia and blurry vision.
Insights
- The anatomy of the eye includes various components such as the cornea, lens, and retina, each playing a crucial role in vision.
- The process of accommodation, where the lens and ciliary bodies adjust for focusing light on the retina, can be impacted by age-related changes, leading to conditions like presbyopia and blurry vision.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What are the main parts of the eye?
The main parts of the eye include the conjunctiva, cornea, sclera, iris, pupil, lens, and retina.
How does the eye process light?
The eye processes light by capturing images through the cornea and lens, focusing them on the retina where photoreceptors, such as cones, convert them into nerve signals sent through the optic nerve.
What is the function of the iris?
The iris controls the size of the pupil, regulating the amount of light entering the eye. Sphincter muscles cause constriction in bright light, while dilator muscles cause dilation in dim light.
How does the eye adjust focus?
The eye adjusts focus through accommodation, where the lens and ciliary bodies change shape to focus light on the retina. Ciliary muscles relax for distance vision and contract for near vision.
What age-related vision changes can occur?
With age, changes in lens shape can lead to presbyopia, reducing the eye's ability to focus light on the retina. This can result in blurry vision and difficulty seeing objects up close.
Related videos
Summary
00:00
Anatomy and Function of the Eye
- The eye's anatomy includes the conjunctiva, cornea, Scara, iris, pupil, lens, and retina.
- The retina contains photo receptors, including cones in the fobia, capturing images sent through nerve fibers via the optic disc forming the optic nerve.
- The vitous humor fills the eyeball's posterior cavity, while the anterior cavity, separated by the lens, contains the aquous humor produced by the cery bodies.
- The iris controls pupil size, adjusting light entry, with sphincter muscles causing constriction and dilator muscles dilation.
- Accommodation involves the lens and cery bodies adjusting to focus light on the retina, with ciliary muscles relaxing for distance vision and contracting for near vision.
- Changes in lens shape for accommodation can be affected by age, leading to presbyopia and reduced ability to focus light on the retina, causing blurry vision.