Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration
Free Animated Education・3 minutes read
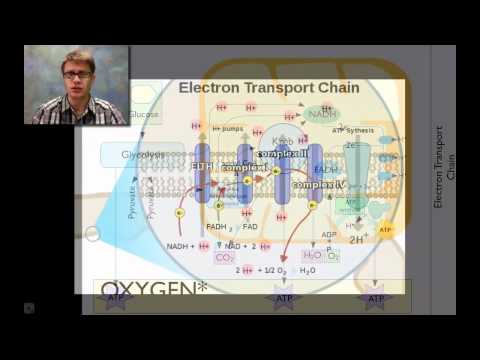
Respiration includes breathing, internal respiration, and cellular respiration, with aerobic respiration requiring oxygen and producing 36 ATP molecules, while anaerobic respiration occurs without oxygen, producing energy through fermentation processes, essential for bodily functions like muscle contraction and nerve impulse transmission.
Insights
- Cellular respiration consists of aerobic and anaerobic processes, where aerobic respiration is highly efficient, producing 36 ATP molecules from one glucose molecule with the aid of oxygen, while anaerobic respiration occurs without oxygen, leading to the production of energy through fermentation processes.
- Aerobic respiration plays a vital role in various bodily functions such as muscle contraction, protein synthesis, nerve impulse transmission, and temperature regulation, highlighting the importance of oxygen intake for sustaining these essential processes and preventing muscle fatigue and cramps associated with anaerobic respiration.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is respiration?
Respiration is the process of obtaining oxygen to produce energy through breathing, internal respiration, and cellular respiration.
Related videos
Summary
00:00
"Cellular Respiration: Oxygen's Role in Energy"
- Respiration is the process by which the body obtains and utilizes oxygen to produce energy, with three steps: breathing, internal respiration, and cellular respiration. Cellular respiration involves two types: aerobic, which is highly efficient and requires oxygen, producing 36 ATP molecules from one glucose molecule, and anaerobic, which occurs in the absence of oxygen, producing energy through processes like alcoholic fermentation and lactic acid fermentation.
- Aerobic respiration is crucial for various bodily functions like muscle contraction, protein synthesis, cell division, nerve impulse transmission, and temperature regulation. Anaerobic respiration occurs during strenuous activities when oxygen is insufficient, leading to the production of lactic acid, causing muscle cramps and fatigue, which can be alleviated by increasing oxygen levels through rapid breathing.