Learn The Steps Of Glycolysis Like Never Before 🎵🔥
PW English Medium・2 minutes read
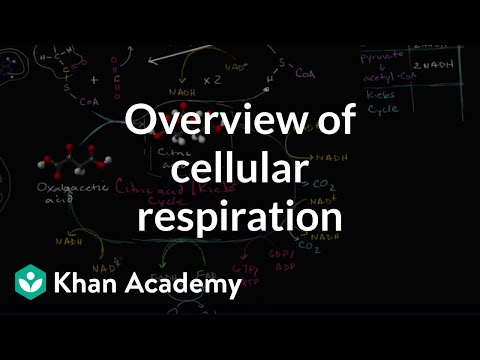
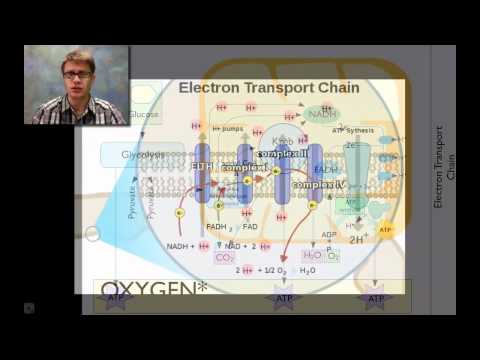
Cellular respiration involves aerobic and anaerobic processes, with glycolysis being the common starting point that produces ATP. Aerobic respiration requires oxygen, while anaerobic respiration does not, and both processes result in a net gain of two ATP molecules.
Insights
- **Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Respiration:** Cellular respiration consists of aerobic, which needs oxygen, and anaerobic, which doesn't. Both begin with glycolysis, converting glucose into pyruvic acid and producing ATP.
- **Glycolysis and ATP Production:** Glycolysis, a 10-step process in cellular respiration, occurs in the cytoplasm, yielding two ATP molecules. This initial step is crucial in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration, highlighting its significance in energy production.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What are the two main processes of cellular respiration?
Aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
What is the initial step of cellular respiration?
Glycolysis.
What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
Oxygen requirement.
Where does glycolysis occur in cellular respiration?
Cytoplasm.
What is the end result of glycolysis in cellular respiration?
Gain of two ATP molecules.
Related videos
Summary
00:00
Cellular Respiration: Aerobic vs Anaerobic Processes
- Cellular respiration involves two main processes: aerobic and anaerobic. Aerobic respiration requires oxygen, while anaerobic does not. Both processes start with glycolysis, a 10-step reaction that converts glucose into pyruvic acid. This reaction occurs in the cytoplasm and produces ATP, with the end result being a gain of two ATP molecules.