What is a head injury?
Brain & Spine Foundation・2 minutes read
Head injuries can have various causes and types, ranging from minor to severe based on symptoms and the Glasgow Coma Scale. Treatment and rehabilitation are essential for moderate to severe cases, with long-term effects potentially including physical weakness, cognitive problems, and psychological issues.
Insights
- Different types of head injuries, such as closed, penetrating, and crushing, can result from accidents, falls, or attacks, with symptoms ranging from minor alertness issues to severe loss of consciousness. Long-term effects may include physical weaknesses, cognitive problems, and psychological changes like anxiety and depression.
- Head injuries are categorized by doctors as minor, moderate, or severe based on the Glasgow Coma Scale, requiring varying levels of medical attention from observation at the A&E to hospital admission, treatment, and personalized rehabilitation. Specialized assistance can be obtained from the Brain and Spine Foundation's website or helpline staffed by expert nurses for further guidance on head injuries and related neurological concerns.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What are the different types of head injuries?
Head injuries can be classified into three main types: closed, penetrating, and crushing head injuries. Closed head injuries occur when the head sustains a blow without the skull being broken, while penetrating head injuries involve an object piercing the skull and entering the brain. Crushing head injuries result from a heavy blow or compression to the head, causing damage to the brain tissue.
What are the symptoms of severe head injuries?
Severe head injuries can manifest with symptoms such as loss of consciousness, confusion, slurred speech, weakness or numbness in limbs, seizures, and dilation of one or both pupils. These symptoms indicate a significant impact on the brain and require immediate medical attention to prevent further complications and ensure proper treatment.
What are the long-term effects of head injuries?
Long-term effects of head injuries can include muscle weakness, chronic headaches, fatigue, cognitive impairments, personality changes, anxiety, and depression. These effects may persist for an extended period after the initial injury, impacting the individual's daily life, relationships, and overall well-being. Proper medical care, rehabilitation, and support are essential in managing and coping with these long-term effects.
How are moderate to severe head injuries treated?
Moderate to severe head injuries typically require immediate medical attention, starting with observation at the Accident & Emergency (A&E) department. Following assessment and diagnosis, treatment may involve surgery to relieve pressure on the brain, medication to control symptoms, and rehabilitation to aid recovery and restore function. The specific treatment plan will depend on the severity and nature of the head injury.
Where can I find more information on head injuries?
For more information on head injuries and neurological issues, you can visit the Brain and Spine Foundation's website. They provide valuable resources, articles, and support for individuals dealing with head injuries, as well as contact information for specialist nurses who can offer assistance and guidance. Whether you are seeking information for yourself or a loved one, the Brain and Spine Foundation can be a helpful resource in understanding and managing head injuries.
Related videos

Alila Medical Media
Concussion: Pathophysiology, Causes, Symptoms and Treatment, Animation

Simple Nursing
Traumatic Brain Injuries *Part 5* (Closed head injury MOST DANGEROUS)
WIRED
ER Doctor Answers Injury Questions From Twitter | Tech Support | WIRED
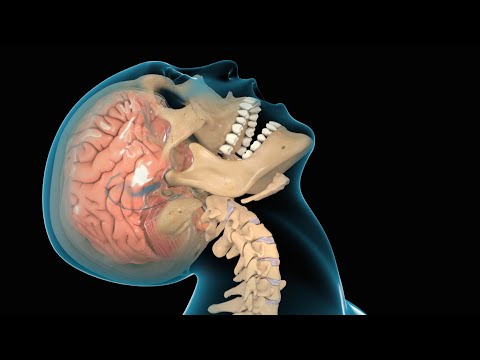
Nucleus Medical Media
Concussion / Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)

Doc Snipes
Powerful Strategies to Undo PTSD: Rewiring the Traumatized Brain
Summary
00:00
Understanding and Managing Head Injuries
- A head injury can result from external forces like accidents, falls, or attacks, with different types such as closed, penetrating, and crushing head injuries. Doctors categorize head injuries as minor, moderate, or severe based on the Glasgow Coma Scale, with symptoms ranging from alertness and ability to answer questions in minor cases to loss of consciousness and little response in severe cases. Long-term physical and psychological effects may include muscle weakness, headaches, fatigue, cognitive issues, personality changes, anxiety, and depression. Moderate to severe head injuries require observation at the A&E, followed by hospital admission, treatment, and tailored rehabilitation. For more information on head injuries and neurological issues, visit the Brain and Spine Foundation's website or contact their helpline for assistance from specialist nurses.




