Unit 1 physical quantities | introduction & branches of physics class 9 New physics book Sindh board
ME English Center・24 minutes read
Physics is the oldest branch of science that studies energy conversion and matter at micro and macro levels, representing natural phenomena mathematically with a focus on matter's structure, motion, and energy conversion. It branches into mechanics, thermodynamics, electricity, magnetism, atomic physics, optics, sound, particle physics, astrophysics, and plasma physics, showcasing its importance in driving industrial advancements and technological innovations for everyday life.
Insights
- Physics, the oldest branch of science, studies energy, matter, and natural phenomena mathematically, categorizing scientists as theoretical or experimental physicists and branching into mechanics, thermodynamics, electricity, magnetism, atomic physics, optics, sound, particle physics, astrophysics, and plasma physics.
- Physics is indispensable in society and technology, contributing to industrial advancements and technological innovations while playing a vital role in everyday life, from powering devices through electricity to explaining concepts like friction and testing methods for practical applications.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is the oldest branch of science?
Physics
Related videos

Physics ka Safar
Introduction to physics | class 11 physics | physics ka safar

History of the Universe
What Is (Almost) Everything Made Of?

Big Think
Michio Kaku: The Universe in a Nutshell (Full Presentation) | Big Think
Math and Science
01 - Introduction to Physics, Part 1 (Force, Motion & Energy) - Online Physics Course
Lukey B. The Physics G
What is Physics?
Summary
00:00
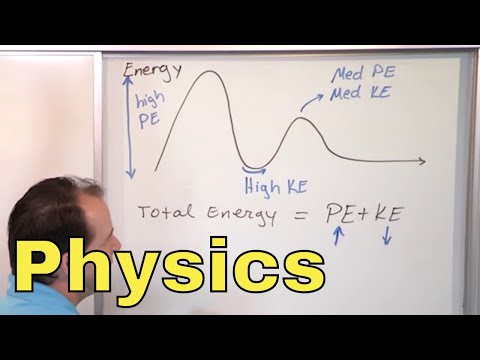
Physics: Energy, Matter, and Natural Phenomena
- The unit being covered is Physical Qualities and Measurement in Class Nine U Pratibha.
- Physics is the oldest branch of science, studying energy conversion and matter at micro and macro levels.
- Micro level refers to things seen through a microscope, while macro level is visible to the naked eye.
- Physics represents natural phenomena mathematically, like Einstein's formula E=MC squared.
- Physics studies matter's structure, motion, and energy conversion.
- Scientists in physics are categorized as theoretical or experimental physicists.
- Physics branches into mechanics, studying motion and gravity, and thermodynamics, focusing on heat and energy conversion.
- Electricity is a crucial branch of physics, essential for modern living.
- Electricity involves the study of charge, current, and its practical applications.
- Magnetism in physics explores magnetic properties and the generation of electricity through magnets.
14:11
Physics: Understanding Magnetism, Light, Sound, and More
- Magnetism is explained through the example of a pen being attracted to a magnet due to the magnetic field.
- Atomic Physics focuses on studying the motion of electrons within items, particularly iron and gold, and the presence of neutrons and protons in the nucleus.
- Optics involves studying light, which exhibits both wave and particle nature, leading to phenomena like reflection and interference.
- Sound, a branch of physics, explores properties like sound waves and their production, often related to nuclear physics and nuclear bombs.
- Particle Physics delves into the study of particles, emphasizing that items are composed of numerous particles interacting with each other.
- Astrophysics involves studying celestial bodies and phenomena, utilizing concepts like Newton's law of gravitation to understand space.
- Plasma Physics examines the behavior of matter when electrons are removed, creating holes and generating attraction forces.
- The importance of Physics in society and technology is highlighted, showcasing how discoveries in Physics drive industrial advancements and technological innovations.
- Physics plays a crucial role in everyday life, from enabling the functioning of devices like mobile phones through electricity to understanding concepts like friction and testing methods for practical applications.




