The Nervous System In 9 Minutes
CTE Skills.com・6 minutes read
The nervous system, divided into the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS), coordinates body activities and responses to changes both internally and externally. The CNS, comprising the brain and spinal cord, has specific regions responsible for various functions, while the PNS regulates voluntary movements and involuntary body functions through its somatic and autonomic systems.
Insights
- The nervous system is essential for coordinating body activities and responding to changes, consisting of two main parts: the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which connects the CNS to the rest of the body.
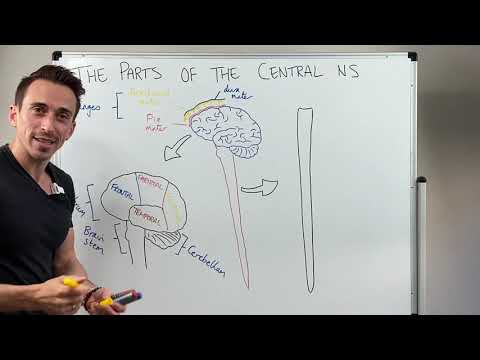
- The brain, the largest component of the CNS, is organized into six sections, with the cerebrum playing a key role in reasoning, sensory integration, auditory processing, and visual processing through its distinct lobes, while the spinal cord facilitates communication between the brain and body via afferent and efferent nerves, ensuring proper function of both voluntary and involuntary actions.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is the nervous system's function?
The nervous system plays a crucial role in coordinating and regulating various body activities, allowing organisms to respond effectively to both internal and external stimuli. It is essential for maintaining homeostasis and facilitating communication between different body parts. The system is divided into two main components: the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS), which connects the CNS to the rest of the body. This intricate network ensures that signals are transmitted efficiently, enabling quick reactions to changes in the environment.
What are the parts of the brain?
The brain is a complex organ composed of several distinct sections, each responsible for specific functions. It is primarily divided into six main parts: the cerebrum, cerebellum, diencephalon, midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata. The cerebrum, being the largest part, is further divided into two hemispheres and four lobes: the frontal lobe, which is involved in reasoning and decision-making; the parietal lobe, which integrates sensory information; the temporal lobe, responsible for auditory processing; and the occipital lobe, which handles visual information. Each of these sections works together to facilitate complex behaviors and cognitive functions.
How does the spinal cord work?
The spinal cord serves as a vital communication pathway between the brain and the rest of the body. It is structured into several regions: cervical, thoracic, and lumbar, each containing a series of spinal nerves. These nerves are categorized into afferent nerves, which carry sensory information from the body to the brain, and efferent nerves, which transmit motor commands from the brain to the body. This organization allows for the rapid transmission of signals, enabling reflex actions and voluntary movements. The spinal cord's role is essential for coordinating bodily functions and responding to stimuli.
What is the peripheral nervous system?
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is a critical component of the overall nervous system, functioning to connect the central nervous system (CNS) to the limbs and organs. It is divided into two main systems: the somatic nervous system, which governs voluntary movements and sensory information, and the autonomic nervous system, which regulates involuntary body functions. The autonomic system is further split into the sympathetic division, responsible for the body's fight-or-flight response, and the parasympathetic division, which promotes a calming effect. Together, these systems ensure that the body can respond appropriately to various situations and maintain internal balance.
What are the functions of the brain lobes?
The brain lobes each have distinct functions that contribute to overall cognitive and sensory processing. The frontal lobe is primarily involved in higher-level functions such as reasoning, planning, and problem-solving, making it essential for decision-making. The parietal lobe integrates sensory information from various modalities, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of the environment. The temporal lobe plays a key role in auditory processing and memory, while the occipital lobe is dedicated to visual processing, interpreting visual stimuli. Together, these lobes work in concert to facilitate complex behaviors, perceptions, and interactions with the world.
Related videos

JamJarMMX
GCSE Science Revision - The Nervous System

bibliomedtv I Cours de Médecine
l'explication la plus facile - le Système Nerveux

EMT & PARAMEDIC Preparation
Chapter 8, Part 2, Anatomy and Physiology
Dr Matt & Dr Mike
Overview of the Central Nervous System (CNS)

RajNEET Medical Education
Parts of brain in Hindi | Fore Brain | Mid Brain | Hind Brain | Cerebellum | Functions | Location
Summary
00:00
Understanding the Nervous System Structure and Function
- The nervous system coordinates body activities, enabling responses to internal and external changes, and is divided into the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS).
- The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord; the brain has six sections: cerebrum, cerebellum, diencephalon, midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata, each with specific functions.
- The cerebrum, the largest brain section, has two hemispheres and four lobes: frontal (reasoning), parietal (sensory integration), temporal (auditory processing), and occipital (visual processing).
- The spinal cord connects the brain to the body, divided into cervical, thoracic, lumbar regions, and includes afferent (to brain) and efferent (from brain) spinal nerves forming peripheral nerves.
- The PNS includes the somatic system (voluntary movements and sensory information) and autonomic system (sympathetic for fight or flight, parasympathetic for calming), regulating body functions.




