The Insane Biology of: The Cicada
Real Science・18 minutes read
Periodical cicadas will emerge in large numbers in the Eastern United States this spring, belonging to the genus Magicicada and spending either 13 or 17 years underground before emerging, with trillions of cicadas creating an impressive sight across the US. Despite their strange behaviors like fungus infection altering behavior, periodical cicadas play a crucial role in their ecosystem by providing nutrients, serving as food for other creatures, and enhancing plant growth by up to 10%.
Insights
- Periodical cicadas, belonging to the genus Magicicada, emerge in trillions every 13 or 17 years in the Eastern US, with the males producing exceptionally loud calls to attract females and forming distinct species groups based on geographical distribution.
- Despite their odd behaviors like fungal infections causing erratic flight patterns, periodical cicadas are essential for the environment, providing nutrients, increasing nitrogen levels in the soil, and promoting tree growth by up to 10%, showcasing their ecological significance beyond their peculiarities.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
Why are periodical cicadas emerging in large numbers this spring?
Due to their 13 or 17-year underground cycle, periodical cicadas will emerge in large numbers this spring in the Eastern United States. Trillions of cicadas will simultaneously emerge, creating a remarkable sight across the country.
How do male cicadas attract females?
Male cicadas produce one of the loudest known insect calls to attract females. This loud call helps them find mates during their emergence after spending either 13 or 17 years underground.
What are the three groups of periodical cicadas in the US?
The seven species of periodical cicadas in the US are split into three groups: Desim, Cassini, and Decula. These groups have distinct characteristics and geographical distributions.
How do female cicadas lay their eggs?
Female cicadas lay their eggs in tree branches after mating by using a metal-reinforced organ called an ovipositor to cut into the wood. This process ensures the survival of the next generation of cicadas.
What benefits do periodical cicadas provide to the environment?
Despite their unusual behaviors, periodical cicadas are beneficial to the environment. They provide nutrients through their bodies to various animals and plants, increase nitrogen levels in the soil, and promote tree growth by up to 10% after their emergence.
Related videos
Summary
00:00
"Rare Cicada Emergence: Trillions Emerge Simultaneously"
- Periodical cicadas will emerge in large numbers in the Eastern United States this spring, a phenomenon not seen for centuries.
- These cicadas, belonging to the genus Magicicada, spend either 13 or 17 years underground before emerging.
- Trillions of cicadas will emerge simultaneously, creating an impressive sight across the US.
- The male cicadas produce one of the loudest known insect calls to attract females.
- There are seven species of periodical cicadas in the US, split into three groups: Desim, Cassini, and Decula.
- The split of these species occurred due to geological events, with the 17-year species being more Northerly than the 13-year species.
- Broods are groupings of periodical cicadas that emerge simultaneously, with Brood 19 being the largest, extending from Maryland to Georgia and Iowa to Oklahoma.
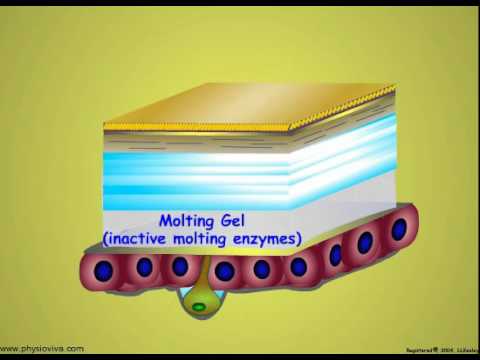
- Cicadas go through five instars underground, with their development stages being hard to monitor.
- Researchers have hypothesized that cicadas may count time based on the cycles of the trees they feed on.
- Female cicadas lay their eggs in tree branches after mating, using a metal-reinforced organ called an ovipositor to cut into the wood.
16:00
Cicadas: Strange but Essential Ecosystem Contributors
- Periodical cicadas emerge every 13 or 17 years, but a fungus can infect them, rendering them sterile and altering their behavior to spread spores, including using psilocybin to make them fly around erratically and attempt to mate without reproductive organs.
- Despite their strange behaviors, periodical cicadas are beneficial to the environment, providing nutrients through their bodies to various animals and plants, increasing nitrogen levels in the soil, and promoting tree growth by up to 10% after their emergence.
- While periodical cicadas may be loud and peculiar, they play a crucial role in their ecosystem by unlocking nutrients, serving as food for other creatures, and enhancing plant growth, making them valuable despite their unusual behaviors.