Science Isn't Dogma, You're Just Stupid (Response to Formscapes)
Professor Dave Explains・2 minutes read
The video "How Science Became Unscientific" critiques scientific practices, highlighting issues like fees for publishing, challenges in accessing research, and the replication crisis. It emphasizes the importance of reproducibility, distinguishing between real science and pseudoscience, and the need for genuine scientific engagement based on evidence.
Insights
- Scientific publishing involves fees for researchers, funded by taxpayers, leading to challenges in accessing scientific literature due to subscription costs. Free-access journals have emerged to address this issue, emphasizing the importance of ensuring open access to scientific research for all.
- The video highlights the replication crisis in academic research, beginning with Daryl Bem's controversial study on extrasensory perception. It underscores the significance of reproducibility in science to validate extraordinary claims, critiquing the portrayal of all scientific research as fraudulent and emphasizing the necessity of unbiased inquiry and direct engagement with nature in scientific endeavors.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is the video "How Science Became Unscientific" about?
The video critiques scientific practices and history.
How does scientific publishing involve fees?
Scientific publishing fees are funded by taxpayers.
What is the replication crisis in academic research?
The replication crisis challenges reproducing scientific experiments.
How does science education differ from indoctrination?
Science education involves practical engagement with concepts.
Why is reproducibility crucial in science?
Reproducibility validates extraordinary claims and scientific progress.
Related videos
Bozeman Science
The Nature of Science

Professor Dave Explains
Reacting to iamLucid's Garbage Anti-Evolution Video

Amoeba Sisters
Nature of Science

Starmus
Brian Cox Neil deGrasse Tyson Communicating Science in the 21st century

TEDx Talks
Building bridges between science and society for a better future. | Nadine Bongaerts | TEDxSaclay
Summary
00:00
"Uncovering Issues in Scientific Publishing Practices"
- The video "How Science Became Unscientific" on the "Formscapes" channel critiques the scientific community's practices.
- The video suggests that real science is dogmatic and suppresses innovative theories.
- The video delves into the history of Robert Maxwell, linking him to academic publishing practices.
- Maxwell's involvement in academic publishing led to financial success but also controversy.
- The video claims that scientific publishing involves fees for researchers, funded by taxpayers.
- It discusses the challenges of accessing scientific literature due to subscription costs.
- Free-access journals have emerged to address the issue of limited access to scientific research.
- The video argues against the claim that authors must pay fees for their work to be published.
- It mentions the replication crisis in academic research, highlighting challenges in reproducing scientific experiments.
- The video criticizes the portrayal of all scientific research as fraudulent or agenda-driven, emphasizing the importance and validity of scientific work.
12:46
Replication crisis challenges scientific progress and credibility.
- Molecular biologists use various plasmids with different characteristics to control variables in experiments.
- Thorough research can still result in false positives, leading to findings that fail to replicate.
- Public and professional confidence in scientific research relies on successful replication of reported findings.
- The replication crisis began with research by Daryl Bem in 2011, where he claimed evidence of extrasensory perception.
- Bem's research was criticized for methodological flaws, common in psychological, medical, and sociological research.
- Extraordinary claims in science, like ESP, are scrutinized and invalidated if results cannot be reproduced.
- Reproducibility is crucial in science to validate extraordinary claims and lead to scientific progress.
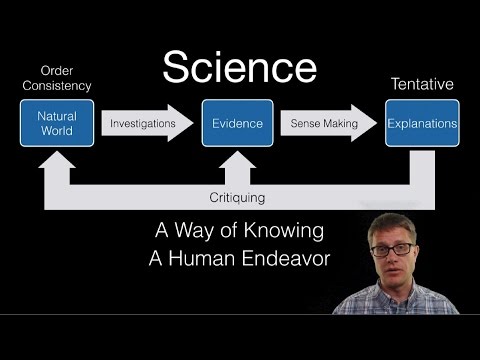
- Science is based on unbiased inquiry and direct engagement with nature, not adherence to established beliefs.
- Science education involves practical engagement with scientific concepts, not indoctrination.
- "The science" represents a doctrinal form of spirituality, conditioning beliefs and social capital in the scientific community.
26:01
Evolution of Science: Refuting Denial and Pseudoscience
- Denial of evolution is a denial of biology, leading biologists to refute this notion.
- Science is not dogma, and those who dismiss it as such are criticized for their lack of scientific understanding.
- A distinction is often made between real science and pseudoscience, with the latter being deemed worse than simply false.
- Pseudoscience is characterized as masquerading as science, exemplified by figures like Deepak Chopra.
- The scientific process involves continually reevaluating ideas when they no longer adequately explain phenomena.
- Modern physics does not negate Newtonian mechanics but extends it to explain new realms like the subatomic.
- In scientific progress, new theories must explain observable phenomena as well or better than existing ones.
- Falsifiability is crucial in science, with theories being discarded when proven false, contrary to what some claim.
- Taxonomy and the tree of life are constantly revised based on new data, strengthening the scientific understanding of the natural world.
- The evolution of atomic theory exemplifies how science progresses by refining models to fit new data, not rendering previous models obsolete.
39:23
Evolution of Scientific Theories in Physics
- The laws of thermodynamics were developed through studying steam engines, leading to a metaphorical extension to nature.
- The mechanistic understanding of nature became inadequate in the quantum realm, challenging the machine metaphor.
- The scientific community is criticized for supposedly defending technology without understanding the quantum realm.
- Astrophysicists base many conclusions on gravity-driven theories, including the age and structure of the universe.
- The scientific community is accused of clinging to incomplete theories due to professional incentives and fear of ostracism.
- General relativity faced challenges in explaining the mass of galaxies, leading to the proposal of dark matter.
- Electric universe theory, proposing electromagnetism as the primary cosmic force, is dismissed as pseudoscience.
- Newton's law of universal gravitation is highlighted for its accuracy in predicting trajectories of objects in space.
- The success of Newtonian mechanics is exemplified through precise calculations enabling the landing of probes on comets.
- Criticism is directed at those who deny the validity of established scientific theories, emphasizing the practical achievements of physics.
51:52
"Exploring Science: Understanding Physics and Electromagnetism"
- Science tutorials available to help understand classical physics
- Understanding of electromagnetism and gravity in science
- Critique of electric universe theory as paranoia and mysticism
- Misrepresentation of electric universe theory by critics
- Criticism of lack of engagement with scientific arguments in videos
- Examples of scientific phenomena like acceleration due to gravity and star life cycles
- Critique of pseudoscience and lack of engagement with concrete scientific points
- Criticism of attacking individuals without engaging with their arguments
- Importance of trusting science based on evidence and practice
- Critique of anti-science attitudes and the need for genuine scientific engagement




