Photosynthesis - Light Dependent Reactions and the Calvin Cycle
The Organic Chemistry Tutor・11 minutes read
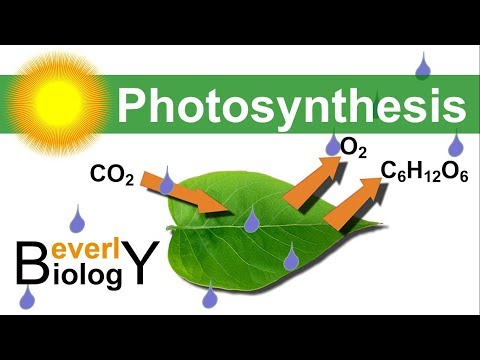
Photosynthesis is a complex process where plants use light energy to create glucose from water and carbon dioxide, producing oxygen as a byproduct. Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, converting carbon dioxide into glucose through light-dependent reactions in thylakoids and light-independent reactions in the stroma.
Insights
- Chloroplasts are crucial in photosynthesis, absorbing blue and red light to produce glucose, while mitochondria handle cellular respiration, creating a balance in plant metabolism.
- The intricate process of photosynthesis involves light-dependent reactions in thylakoids generating oxygen, ATP, and NADPH, while light-independent reactions in the stroma convert carbon dioxide into glucose, highlighting the detailed steps and energy requirements involved in this essential biological function.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What is photosynthesis and its main components?
Photosynthesis is the process where plants use light energy to create carbohydrates like glucose from water and carbon dioxide, releasing oxygen as a byproduct. It involves chloroplasts, which contain chlorophyll that absorbs light, and mitochondria for cellular respiration.
How do plants absorb water and carbon dioxide?
Plants absorb water and minerals through their roots, while carbon dioxide enters through small openings called stomata in the leaves. Oxygen, a byproduct of photosynthesis, is also released through these same openings.
What is the role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis?
Chlorophyll, located in thylakoids within chloroplasts, absorbs blue and red light while reflecting green light, giving plants their green color. It plays a crucial role in capturing light energy for the photosynthesis process.
What are the two main stages of photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis consists of light-dependent reactions within thylakoids, producing oxygen, ATP, and NADPH from water, and light-independent reactions in the stroma, converting carbon dioxide into glucose using ATP and NADPH.
How is glucose produced in photosynthesis?
Glucose is produced in the Calvin Cycle, involving carbon fixation, reduction, and regeneration of ribulose 1,5-biphosphate. This process converts carbon dioxide into sugars like glucose using ATP and NADPH generated from the light-dependent reactions.
Related videos
Beverly Biology
Photosynthesis (in detail)

Biology Simplified Tamil
Photosynthesis in higher plants | One shot revision | Target 360 Biology

Freesciencelessons
A Level Biology Revision (Year 13) "Two Key Reactions in Photosynthesis"

CrashCourse
Photosynthesis: Crash Course Biology #8

The Science Break
Key Stage 3 Science (Biology) - Photosynthesis
Summary
00:00
"Photosynthesis: Light to Glucose, Oxygen Production"
- Photosynthesis is the process of using light energy to build carbohydrates like glucose from water and carbon dioxide, producing oxygen as a byproduct.
- Water and minerals are absorbed by plants through the roots, while carbon dioxide enters through stomata in the leaves, with oxygen being released through the same openings.
- Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, while mitochondria handle cellular respiration, with the two processes being opposites of each other.
- Chlorophyll, found in thylakoids within chloroplasts, absorbs blue and red light, reflecting green light, giving plants their green color.
- Photosynthesis consists of light-dependent reactions within thylakoids and light-independent reactions in the stroma, with the former producing oxygen, ATP, and NADPH from water, and the latter converting carbon dioxide into glucose using ATP and NADPH.
- The light-dependent reactions involve an electron transport chain within thylakoids, where water is oxidized into oxygen, ATP is produced, and NADPH is generated.
- The Calvin Cycle, or light-independent reactions, involves carbon fixation, reduction, and regeneration of ribulose 1,5-biphosphate, ultimately converting carbon dioxide into sugars like glucose using ATP and NADPH.
- To produce one molecule of glucose, six molecules of carbon dioxide are needed, requiring 18 ATP and 12 NADPH molecules, showcasing the complexity of photosynthesis.




