Osteoarthritis vs rheumatoid arthritis pathophysiology | NCLEX-RN | Khan Academy
khanacademymedicine・8 minutes read
Osteoarthritis is linked to overuse and weight, resulting in cartilage damage; Rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune condition, leads to joint fusion and inflammation, with specific markers indicating disease severity.
Insights
- Osteoarthritis is primarily caused by overuse and affects the elderly or those with excess weight, resulting in cartilage destruction from mechanical wear and tear.
- Rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disorder, involves HLA-DR4 activation leading to synovitis and pannus formation, causing joint deformities and bone fusion, distinct from the cartilage destruction seen in osteoarthritis.
Get key ideas from YouTube videos. It’s free
Recent questions
What causes osteoarthritis?
Overuse and mechanical wear and tear.
What are osteophytes?
Bone spurs due to cartilage destruction.
What is rheumatoid arthritis?
Autoimmune disorder causing joint inflammation.
What is the role of rheumatoid factor in RA?
Indicates severity and causes inflammation.
How do RA and OA affect joints differently?
RA causes fusion and deformities, while OA leads to cartilage destruction.
Related videos
Zero To Finals
Understanding Osteoarthritis

Level Up RN
Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis - Medical-Surgical - Musculoskeletal System | @LevelUpRN

The Yoga Institute
How to cure Rheumatoid Arthritis | Symptoms, Causes & Treatment | Rheumatoid Arthritis Diet

khanacademymedicine
Osteoarthritis vs rheumatoid arthritis symptoms | NCLEX-RN | Khan Academy

The Yoga Institute
How to cure Rheumatoid Arthritis | Symptoms, Causes & Treatment | Rheumatoid Arthritis Diet
Summary
00:00
Joint Diseases: Osteoarthritis vs Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Osteoarthritis is caused by overuse, affecting elderly individuals or those with excess weight, leading to cartilage destruction due to mechanical wear and tear.
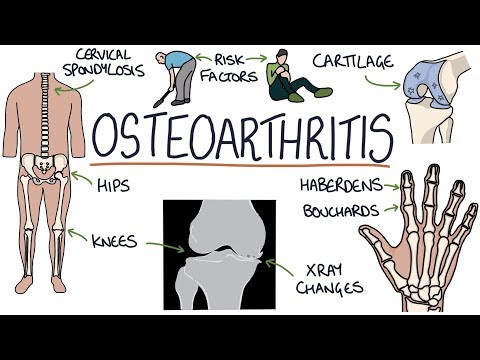
- The synovial joint consists of cartilage, synovium producing synovial fluid for lubrication, allowing bone movement; cartilage destruction leads to bone rubbing, creating osteophytes or bone spurs.
- Osteophytes can cause joint enlargement or shape changes, with specific names like Bouchard's nodes in the PIP joint and Heberden's nodes in the DIP joints.
- Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder marked by HLA-DR4 activation, causing synovitis or inflammation of the synovium, leading to the formation of granulation tissue called pannus.
- Granulation tissue contracts, causing fusion of bones and joint deformities, particularly in the PIP joints, with RA sparing the DIP joints.
- Rheumatoid factor, an IgM antibody, indicates the severity of RA, recruiting neutrophils to the area, causing inflammation in the synovial fluid.
- RA and OA affect joints differently, with RA causing joint fusion, deformities, and inflammation, while OA leads to cartilage destruction and bone rubbing.




